Sustainable materials in handicraft, such as bamboo, organic cotton, and recycled fibers, offer eco-friendly alternatives that reduce environmental impact and promote ethical sourcing. In contrast, synthetic materials like polyester and acrylic are derived from non-renewable petroleum resources, contributing to pollution and waste. Choosing sustainable materials supports long-term ecological balance while maintaining the quality and durability essential for handcrafted products.
Table of Comparison
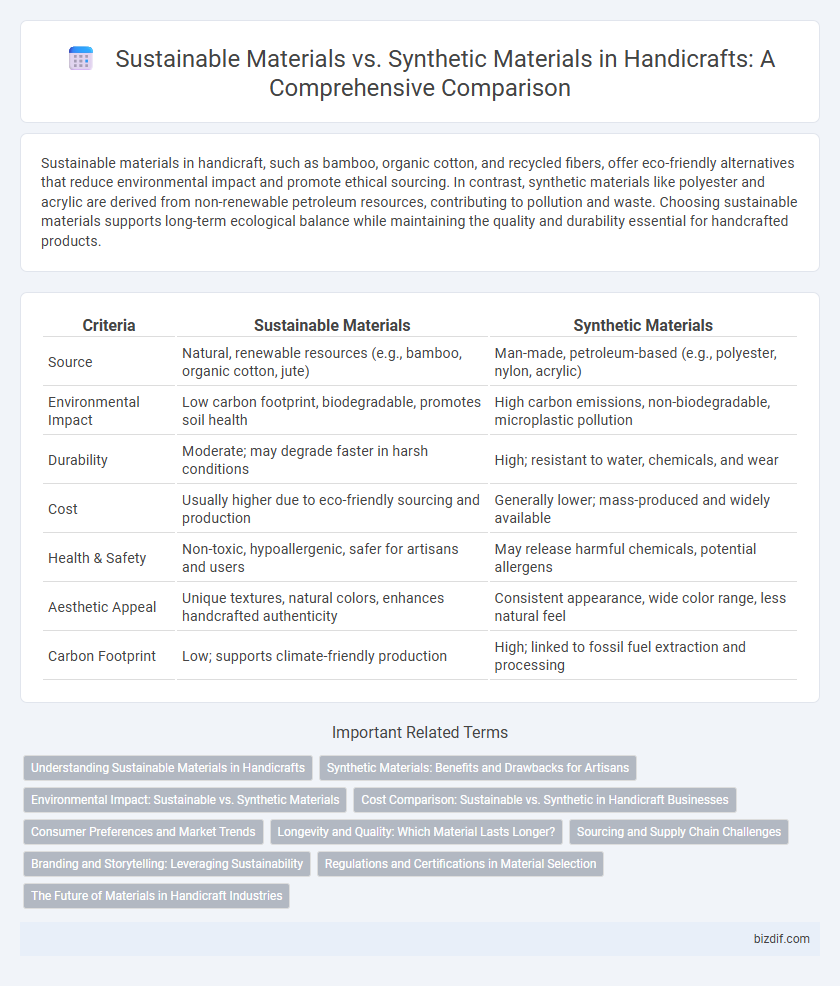
| Criteria | Sustainable Materials | Synthetic Materials |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Natural, renewable resources (e.g., bamboo, organic cotton, jute) | Man-made, petroleum-based (e.g., polyester, nylon, acrylic) |
| Environmental Impact | Low carbon footprint, biodegradable, promotes soil health | High carbon emissions, non-biodegradable, microplastic pollution |
| Durability | Moderate; may degrade faster in harsh conditions | High; resistant to water, chemicals, and wear |
| Cost | Usually higher due to eco-friendly sourcing and production | Generally lower; mass-produced and widely available |
| Health & Safety | Non-toxic, hypoallergenic, safer for artisans and users | May release harmful chemicals, potential allergens |
| Aesthetic Appeal | Unique textures, natural colors, enhances handcrafted authenticity | Consistent appearance, wide color range, less natural feel |
| Carbon Footprint | Low; supports climate-friendly production | High; linked to fossil fuel extraction and processing |
Understanding Sustainable Materials in Handicrafts
Sustainable materials in handicrafts include natural fibers like organic cotton, bamboo, and jute, which minimize environmental impact through biodegradability and renewable sourcing. These materials support eco-friendly practices by reducing reliance on petroleum-based synthetics and lowering carbon footprints. Artisans using sustainable resources contribute to preserving biodiversity and promoting ethical labor standards within the craft industry.
Synthetic Materials: Benefits and Drawbacks for Artisans
Synthetic materials offer artisans consistent quality, durability, and a wide range of vibrant colors, enabling intricate and long-lasting handicraft designs. These materials often provide cost-effective alternatives to natural fibers, facilitating mass production and accessibility for emerging artisans. However, synthetic materials can lack the environmental benefits of sustainable fibers and may introduce health risks due to chemical exposure during handling and production.
Environmental Impact: Sustainable vs. Synthetic Materials
Sustainable materials in handicraft, such as bamboo, organic cotton, and recycled wood, significantly reduce environmental impact by lowering carbon footprints and minimizing waste through biodegradability and renewability. Synthetic materials like plastic and polyester contribute to pollution and resource depletion due to their non-biodegradable nature and reliance on fossil fuels for production. Choosing sustainable materials promotes ecological balance, conserves natural resources, and supports the circular economy within the crafts industry.
Cost Comparison: Sustainable vs. Synthetic in Handicraft Businesses
Sustainable materials in handicraft businesses often have a higher upfront cost compared to synthetic materials but offer long-term savings through durability and eco-friendly branding appeal. Synthetic materials typically cost less initially but may incur additional expenses due to wear, environmental impact fees, and decreasing consumer demand for non-eco-friendly products. Investing in sustainable materials enhances marketability and aligns with growing consumer preferences for ethical craftsmanship, providing a competitive advantage despite the higher initial price.
Consumer Preferences and Market Trends
Consumers increasingly favor sustainable materials in handicrafts due to growing environmental awareness and demand for eco-friendly products. Market trends indicate a rise in the use of natural fibers, recycled materials, and biodegradable components, reflecting a shift away from synthetic alternatives. This preference drives artisans and manufacturers to prioritize sustainability, enhancing product appeal and market competitiveness.
Longevity and Quality: Which Material Lasts Longer?
Sustainable materials such as bamboo, jute, and organic cotton typically offer superior longevity and quality due to their natural durability and resistance to wear over time. Synthetic materials like polyester and nylon may initially appear strong but tend to degrade faster under environmental stress, losing structural integrity and aesthetic appeal. Handcrafted products made from sustainable fibers not only maintain their form longer but also age gracefully, appealing to consumers seeking lasting quality and environmental responsibility.
Sourcing and Supply Chain Challenges
Sourcing sustainable materials for handicrafts often involves complex supply chains reliant on organic fibers, recycled textiles, or locally harvested natural resources, which can be inconsistent and limited by seasonal availability. Synthetic materials benefit from streamlined, large-scale industrial supply chains with predictable production rates but pose environmental concerns due to their non-biodegradable nature and dependence on fossil fuels. Balancing supply chain transparency, ethical sourcing, and ecological impact remains a significant challenge for artisans committed to sustainability in their craft.
Branding and Storytelling: Leveraging Sustainability
Sustainable materials in handicrafts enhance branding by conveying authentic eco-friendly values that resonate with conscious consumers. Storytelling centered on the use of renewable, biodegradable resources strengthens emotional connections and differentiates products in competitive markets. Emphasizing craftsmanship with natural fibers or recycled components elevates brand narratives and supports transparent, ethical sourcing claims.
Regulations and Certifications in Material Selection
Sustainable materials in handicraft are often prioritized due to strict regulations and certifications such as FSC (Forest Stewardship Council) and GOTS (Global Organic Textile Standard), which ensure ethical sourcing and environmental responsibility. Synthetic materials, while widely available, face increasing scrutiny under regulations targeting harmful chemicals and non-biodegradable waste, including REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals) compliance in Europe. Selecting certified sustainable materials not only enhances market credibility but also aligns handicraft production with global sustainability goals and consumer demands for eco-friendly products.
The Future of Materials in Handicraft Industries
Sustainable materials such as bamboo, organic cotton, and recycled fibers offer eco-friendly alternatives to synthetic materials like polyester and nylon, which are derived from non-renewable petrochemicals and contribute to environmental pollution. The future of materials in handicraft industries hinges on adopting biodegradable, renewable resources that reduce carbon footprints and support ethical production practices while maintaining durability and aesthetic appeal. Innovations in bio-based composites and natural dyes are driving a shift towards greener supply chains, ensuring handicrafts remain both culturally authentic and environmentally responsible.
Sustainable materials vs Synthetic materials Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com