Handicraft serves as a vital means of cultural preservation, carrying traditional techniques and stories passed down through generations. While commercialization can introduce these crafts to a broader audience, it often risks diluting their authenticity and cultural significance. Balancing respectful promotion with protecting artisans' heritage is essential to sustain the true value of handicraft.
Table of Comparison
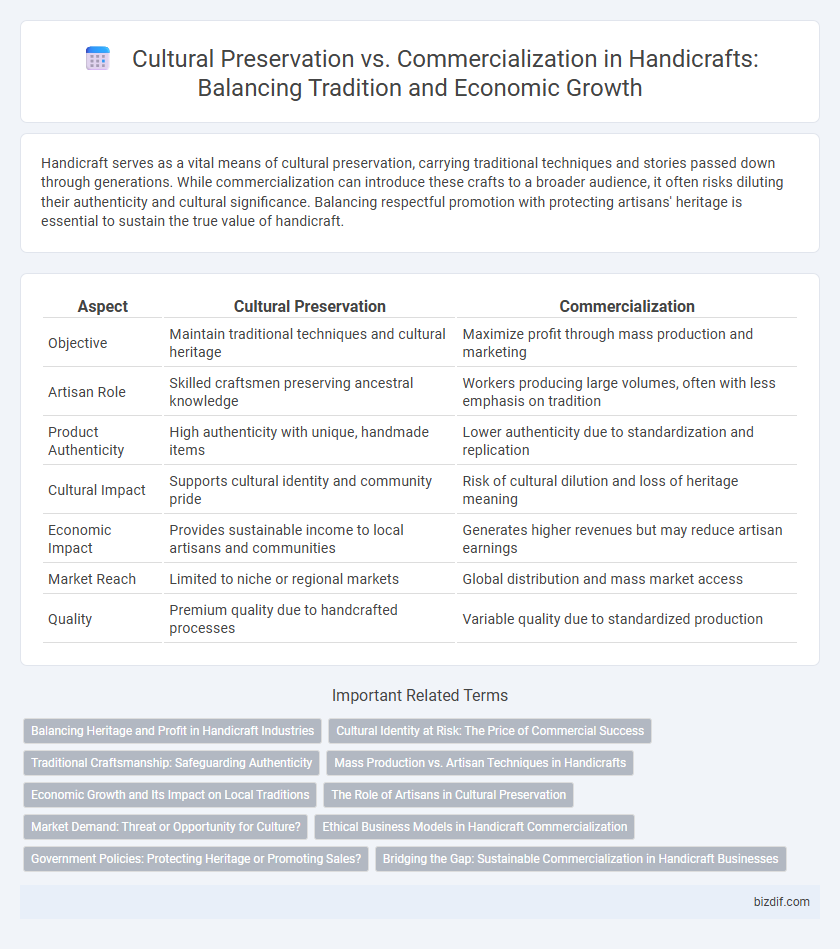
| Aspect | Cultural Preservation | Commercialization |
|---|---|---|
| Objective | Maintain traditional techniques and cultural heritage | Maximize profit through mass production and marketing |
| Artisan Role | Skilled craftsmen preserving ancestral knowledge | Workers producing large volumes, often with less emphasis on tradition |
| Product Authenticity | High authenticity with unique, handmade items | Lower authenticity due to standardization and replication |
| Cultural Impact | Supports cultural identity and community pride | Risk of cultural dilution and loss of heritage meaning |
| Economic Impact | Provides sustainable income to local artisans and communities | Generates higher revenues but may reduce artisan earnings |
| Market Reach | Limited to niche or regional markets | Global distribution and mass market access |
| Quality | Premium quality due to handcrafted processes | Variable quality due to standardized production |
Balancing Heritage and Profit in Handicraft Industries
Balancing cultural preservation and commercialization in handicraft industries requires safeguarding traditional techniques and authentic designs while adapting to modern market demands. Effective strategies include community involvement in decision-making, fair trade practices, and educating consumers on the cultural significance of products. This approach ensures sustainable income for artisans without compromising the heritage and identity embedded in their crafts.
Cultural Identity at Risk: The Price of Commercial Success
The commercialization of handicrafts often jeopardizes cultural identity by prioritizing mass production over traditional techniques, diminishing the authenticity and heritage embedded in each piece. As cultural motifs are altered or simplified to appeal to global markets, the original meanings and stories integral to the craft face erosion. This tension between economic gain and cultural preservation threatens the survival of unique artisanal traditions passed down through generations.
Traditional Craftsmanship: Safeguarding Authenticity
Traditional craftsmanship plays a critical role in safeguarding the authenticity of handicrafts by preserving age-old techniques handed down through generations. Cultural preservation emphasizes the intrinsic value of these artisanal skills, resisting the dilution caused by mass production and commercialization. Maintaining the integrity of native methods ensures that each handcrafted item embodies heritage, identity, and cultural narratives unique to its origin.
Mass Production vs. Artisan Techniques in Handicrafts
Mass production in handicrafts often compromises the intricate details and cultural significance inherent in artisan techniques, leading to a loss of heritage authenticity. Artisan craftsmanship preserves traditional methods passed down through generations, maintaining the cultural identity and unique storytelling embedded in each piece. Balancing commercial demands with cultural preservation requires prioritizing handcrafted quality over mass-produced uniformity to sustain the artistic and historical value of handicrafts.
Economic Growth and Its Impact on Local Traditions
Economic growth driven by the commercialization of handicrafts often risks diluting authentic cultural expressions as artisans alter designs to meet market demands. While increased income from mass production can improve local livelihoods, it may lead to the loss of traditional techniques and symbolic meanings embedded in crafts. Balancing economic development with cultural preservation requires strategies that support sustainable artisan practices and protect heritage skills.
The Role of Artisans in Cultural Preservation
Artisans serve as vital custodians of cultural heritage by meticulously preserving traditional techniques and symbolic designs passed down through generations. Their expertise ensures the authenticity of handicrafts, maintaining cultural identity amidst modern industrial influences. Supporting artisans strengthens cultural preservation efforts by fostering sustainable livelihoods that resist the homogenizing effects of commercialization.
Market Demand: Threat or Opportunity for Culture?
Market demand for handicrafts presents both a threat and an opportunity for cultural preservation by influencing artisans to balance traditional techniques with consumer preferences. High demand can drive the commodification of cultural symbols, risking loss of authenticity and meaning. Conversely, it can also provide financial incentives for communities to sustain and revive endangered crafts, ensuring cultural continuity.
Ethical Business Models in Handicraft Commercialization
Ethical business models in handicraft commercialization prioritize fair trade practices that ensure artisans receive equitable compensation while preserving traditional craftsmanship. These models emphasize sustainable sourcing of materials and transparent supply chains to protect cultural heritage from exploitation. Supporting community-based enterprises fosters cultural preservation by empowering artisans and promoting authentic, ethically produced handicrafts.
Government Policies: Protecting Heritage or Promoting Sales?
Government policies in the handicraft sector often balance cultural preservation with commercialization by implementing regulations that safeguard traditional techniques and motifs while encouraging market access for artisans. Heritage protection laws emphasize the documentation and transmission of indigenous knowledge, ensuring authentic cultural representation. Simultaneously, trade incentives and export facilitation aim to boost sales, raising the economic value of handicrafts but sometimes risking the commodification of cultural expressions.
Bridging the Gap: Sustainable Commercialization in Handicraft Businesses
Sustainable commercialization in handicraft businesses promotes cultural preservation by integrating traditional craftsmanship with modern market strategies that respect artisans' heritage and ethical production methods. Implementing fair trade practices and community-based tourism initiatives helps maintain authentic cultural narratives while generating economic benefits for artisans. Technology-driven platforms enhance global visibility, ensuring that commercialization supports cultural continuity rather than exploiting or diluting artisanal traditions.
Cultural preservation vs Commercialization Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com