Value addition in handicrafts transforms raw materials into unique, high-quality products that command higher market prices and foster cultural heritage. Selling raw materials often yields lower profit margins and misses opportunities for brand differentiation and customer engagement. Emphasizing value-added products enhances sustainability and supports artisan livelihoods by creating demand for skilled craftsmanship.
Table of Comparison
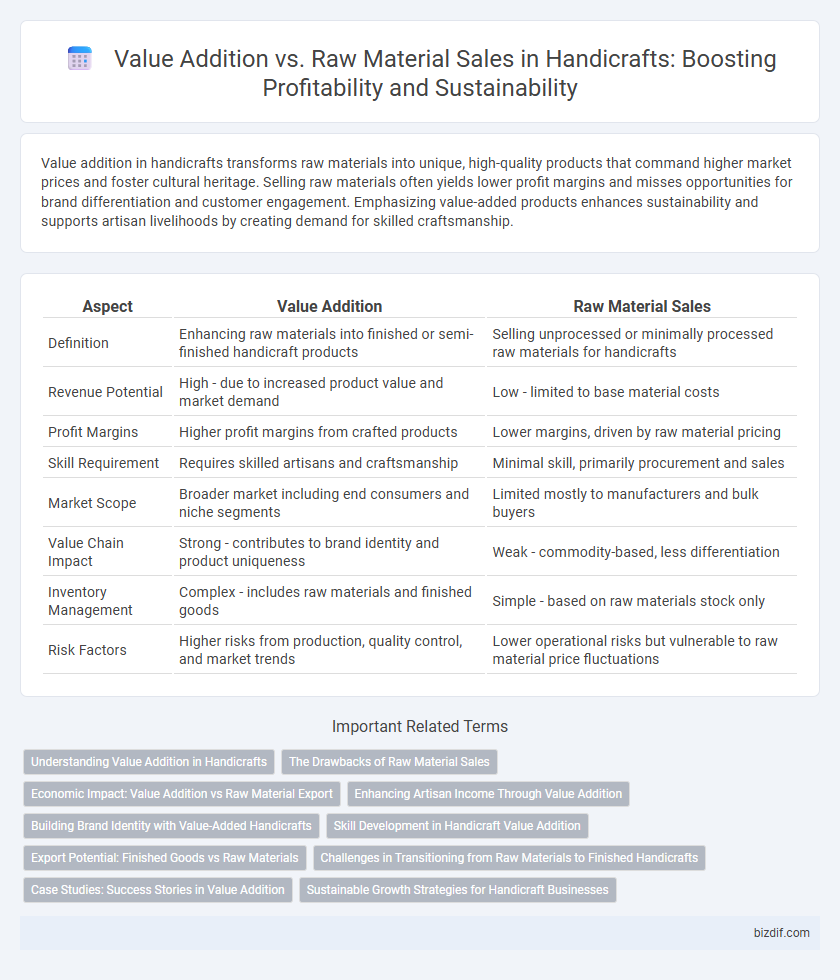
| Aspect | Value Addition | Raw Material Sales |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Enhancing raw materials into finished or semi-finished handicraft products | Selling unprocessed or minimally processed raw materials for handicrafts |
| Revenue Potential | High - due to increased product value and market demand | Low - limited to base material costs |
| Profit Margins | Higher profit margins from crafted products | Lower margins, driven by raw material pricing |
| Skill Requirement | Requires skilled artisans and craftsmanship | Minimal skill, primarily procurement and sales |
| Market Scope | Broader market including end consumers and niche segments | Limited mostly to manufacturers and bulk buyers |
| Value Chain Impact | Strong - contributes to brand identity and product uniqueness | Weak - commodity-based, less differentiation |
| Inventory Management | Complex - includes raw materials and finished goods | Simple - based on raw materials stock only |
| Risk Factors | Higher risks from production, quality control, and market trends | Lower operational risks but vulnerable to raw material price fluctuations |
Understanding Value Addition in Handicrafts
Value addition in handicrafts involves enhancing raw materials through skilled craftsmanship, design innovation, and finishing techniques to increase product worth and market appeal. This process transforms basic resources into unique, culturally rich items that command higher prices compared to raw material sales. Understanding value addition is crucial for artisans aiming to maximize revenue, preserve traditional skills, and gain competitive advantage in the global handicraft market.
The Drawbacks of Raw Material Sales
Selling raw materials in handicraft limits profit margins and reduces opportunities for brand differentiation. It often results in lower customer engagement since consumers miss out on the unique story and craftsmanship behind finished products. Dependence on raw material sales can also lead to market volatility, making artisans vulnerable to price fluctuations and reduced income stability.
Economic Impact: Value Addition vs Raw Material Export
Value addition in handicrafts significantly boosts economic impact by increasing product worth through skilled craftsmanship, design enhancement, and branding, resulting in higher market prices and greater profit margins compared to raw material exports. Exporting finished handicraft products generates more employment opportunities, supports local artisans, and contributes to sustainable economic development within the community. Conversely, raw material sales offer limited income and do not capitalize on the full potential of creative labor or global market demand for culturally rich, value-added goods.
Enhancing Artisan Income Through Value Addition
Enhancing artisan income through value addition involves transforming raw materials into finished handicraft products that carry higher market value due to craftsmanship, design, and uniqueness. By incorporating techniques such as intricate detailing, customization, and quality finishing, artisans can significantly increase the selling price compared to mere raw material sales. This approach fosters sustainable livelihoods, promotes cultural heritage, and creates opportunities for branding and export in the handicraft sector.
Building Brand Identity with Value-Added Handicrafts
Value addition in handicrafts transforms raw materials into unique, high-quality products that emphasize cultural heritage and craftsmanship, significantly enhancing market value and customer appeal. Building brand identity through value-added handicrafts creates differentiation, fosters customer loyalty, and enables premium pricing by showcasing intricate designs and sustainable production methods. This strategic focus on value addition supports artisans' economic upliftment and promotes the preservation of traditional skills in competitive markets.
Skill Development in Handicraft Value Addition
Skill development in handicraft value addition significantly enhances artisans' capabilities to transform raw materials into unique, high-quality products, increasing market competitiveness and profit margins. By mastering advanced techniques such as intricate carving, embroidery, and finishing, artisans add aesthetic and functional value, differentiating their creations from mass-produced items. Investment in skill training programs fosters innovation, preserves cultural heritage, and drives sustainable economic growth within handicraft communities.
Export Potential: Finished Goods vs Raw Materials
Exporting finished handicraft goods generates higher revenue and enhances market positioning compared to raw material sales, due to added artistic value and craftsmanship. Finished products attract premium prices in international markets by reflecting cultural uniqueness and quality, driving greater foreign exchange earnings. Emphasizing value addition boosts brand recognition and sustainable growth within the global handicraft export sector.
Challenges in Transitioning from Raw Materials to Finished Handicrafts
Transitioning from raw material sales to finished handicrafts presents challenges such as the need for skilled artisans capable of intricate craftsmanship, which often requires extensive training and preservation of traditional techniques. Market access limitations and the lack of efficient distribution channels hinder artisans from reaching broader consumer bases willing to pay a premium for value-added products. Moreover, financing constraints and higher production costs can restrict small-scale producers from scaling up operations and investing in quality improvements essential for competitive handicraft offerings.
Case Studies: Success Stories in Value Addition
Case studies in handicraft demonstrate significant revenue growth when artisans engage in value addition rather than solely selling raw materials. For example, communities in Rajasthan increased their earnings by 40% through designing finished products with intricate embroidery and packaging innovations. These success stories underscore the economic impact of transforming raw materials into branded, market-ready crafts that capture higher market demand.
Sustainable Growth Strategies for Handicraft Businesses
Value addition in handicraft businesses transforms raw materials into unique, high-quality products that command premium prices and enhance brand identity. Sustainable growth strategies emphasize eco-friendly sourcing, skilled craftsmanship, and cultural authenticity, which differentiate products and attract conscious consumers. Investing in value addition drives higher profitability and long-term market resilience compared to merely selling raw materials.
Value Addition vs Raw Material Sales Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com