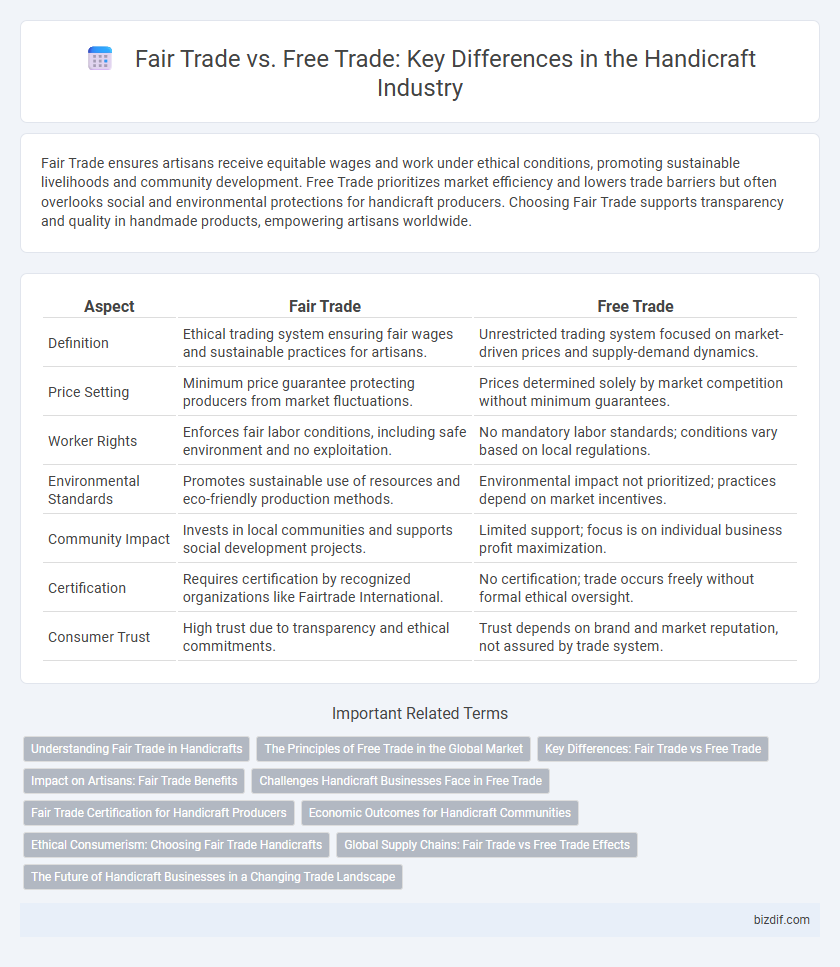
Fair Trade ensures artisans receive equitable wages and work under ethical conditions, promoting sustainable livelihoods and community development. Free Trade prioritizes market efficiency and lowers trade barriers but often overlooks social and environmental protections for handicraft producers. Choosing Fair Trade supports transparency and quality in handmade products, empowering artisans worldwide.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Fair Trade | Free Trade |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Ethical trading system ensuring fair wages and sustainable practices for artisans. | Unrestricted trading system focused on market-driven prices and supply-demand dynamics. |
| Price Setting | Minimum price guarantee protecting producers from market fluctuations. | Prices determined solely by market competition without minimum guarantees. |
| Worker Rights | Enforces fair labor conditions, including safe environment and no exploitation. | No mandatory labor standards; conditions vary based on local regulations. |
| Environmental Standards | Promotes sustainable use of resources and eco-friendly production methods. | Environmental impact not prioritized; practices depend on market incentives. |
| Community Impact | Invests in local communities and supports social development projects. | Limited support; focus is on individual business profit maximization. |
| Certification | Requires certification by recognized organizations like Fairtrade International. | No certification; trade occurs freely without formal ethical oversight. |
| Consumer Trust | High trust due to transparency and ethical commitments. | Trust depends on brand and market reputation, not assured by trade system. |
Understanding Fair Trade in Handicrafts
Fair Trade in handicrafts ensures artisans receive equitable wages and work under ethical conditions, promoting sustainable livelihoods and preserving cultural heritage. It emphasizes transparency, community empowerment, and environmental responsibility throughout the production process. Unlike Free Trade, which prioritizes market competition and cost reduction, Fair Trade centers on social justice and quality craftsmanship.
The Principles of Free Trade in the Global Market
Free Trade in the global handicraft market emphasizes the unrestricted exchange of goods, aiming to reduce tariffs, quotas, and trade barriers between countries. It fosters competitive pricing and innovation but may overlook social and environmental factors, potentially disadvantaging artisanal producers in developing regions. Principles of Free Trade promote efficiency and market access yet often lack mechanisms to ensure fair wages or sustainable practices critical to the handicraft sector's ethical growth.
Key Differences: Fair Trade vs Free Trade
Fair Trade emphasizes equitable trading conditions, ensuring fair wages and sustainable livelihoods for artisans and producers, especially in developing countries. Free Trade prioritizes the reduction of tariffs and trade barriers to encourage unregulated market competition, often benefiting larger corporations over individual craftsmen. While Fair Trade fosters environmental sustainability and community development in handicraft production, Free Trade primarily focuses on maximizing efficiency and profit.
Impact on Artisans: Fair Trade Benefits
Fair Trade ensures artisans receive equitable wages, fostering sustainable livelihoods and enhancing community development in handicraft sectors. It promotes ethical sourcing by prioritizing transparency and direct trade relationships, empowering artisans with greater control over their work. Enhanced access to global markets and fair pricing enables artisans to invest in quality materials and skill development, preserving traditional craftsmanship.
Challenges Handicraft Businesses Face in Free Trade
Handicraft businesses face significant challenges in free trade environments due to intense competition from mass-produced goods that often undercut handmade products on price. Limited access to global markets and inadequate certification can hinder artisans' ability to showcase the authenticity and cultural value of their crafts. Moreover, lack of trade protections exposes small-scale producers to exploitation and market volatility, threatening the sustainability of traditional handicraft industries.
Fair Trade Certification for Handicraft Producers
Fair Trade certification for handicraft producers ensures ethical standards, fair wages, and safer working conditions, promoting sustainability and social equity in vulnerable artisan communities. This certification empowers producers by providing market access, guaranteed pricing, and support for community development, contrasting free trade's often unregulated competition. Emphasizing transparency and accountability, Fair Trade labels help consumers identify authentic, ethically sourced handicrafts, fostering responsible consumption.
Economic Outcomes for Handicraft Communities
Fair Trade practices in handicraft communities often lead to higher and more stable incomes by ensuring fair wages and long-term trade relationships, which promote economic sustainability. Free Trade can increase market access but may expose artisans to volatile pricing and competition, potentially undermining local economic stability. Empirical studies show Fair Trade initiatives contribute to poverty reduction and community development by prioritizing equitable economic outcomes over pure market efficiency.
Ethical Consumerism: Choosing Fair Trade Handicrafts
Fair Trade handicrafts guarantee artisans receive fair wages and work under safe conditions, promoting sustainable livelihoods and preserving cultural heritage. Ethical consumerism prioritizes these products to support transparency and social justice, contrasting with Free Trade goods that often overlook labor rights for lower prices. Choosing Fair Trade handicrafts empowers communities and encourages environmentally responsible production practices.
Global Supply Chains: Fair Trade vs Free Trade Effects
Fair Trade in handicraft global supply chains ensures ethical sourcing, fair wages, and sustainable production practices, promoting socioeconomic equity among artisans. Free Trade emphasizes market efficiency and lower costs but often overlooks labor rights and environmental protections, potentially exploiting vulnerable producers. Fair Trade models create more resilient and transparent supply chains by prioritizing social impact over purely economic gains.
The Future of Handicraft Businesses in a Changing Trade Landscape
Fair Trade prioritizes ethical sourcing, ensuring artisans receive fair wages and promoting sustainable practices, which can enhance brand value and consumer trust in handicraft businesses. Free Trade fosters increased market access and reduced tariffs, allowing handicraft producers to reach broader audiences but may expose them to competitive pressures without guaranteed ethical standards. Balancing these trade models is crucial for the future of handicraft businesses to thrive amid evolving global trade policies and growing consumer demand for transparency and social responsibility.
Fair Trade vs Free Trade Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com