Organic dyes, derived from natural sources such as plants and minerals, offer eco-friendly and biodegradable alternatives that preserve traditional artistry in handicrafts. Synthetic dyes, while providing a wider range of vibrant colors and greater consistency, often involve chemical processes that can harm the environment and human health. Choosing organic dyes supports sustainable practices and enhances the cultural value of handcrafted goods.
Table of Comparison
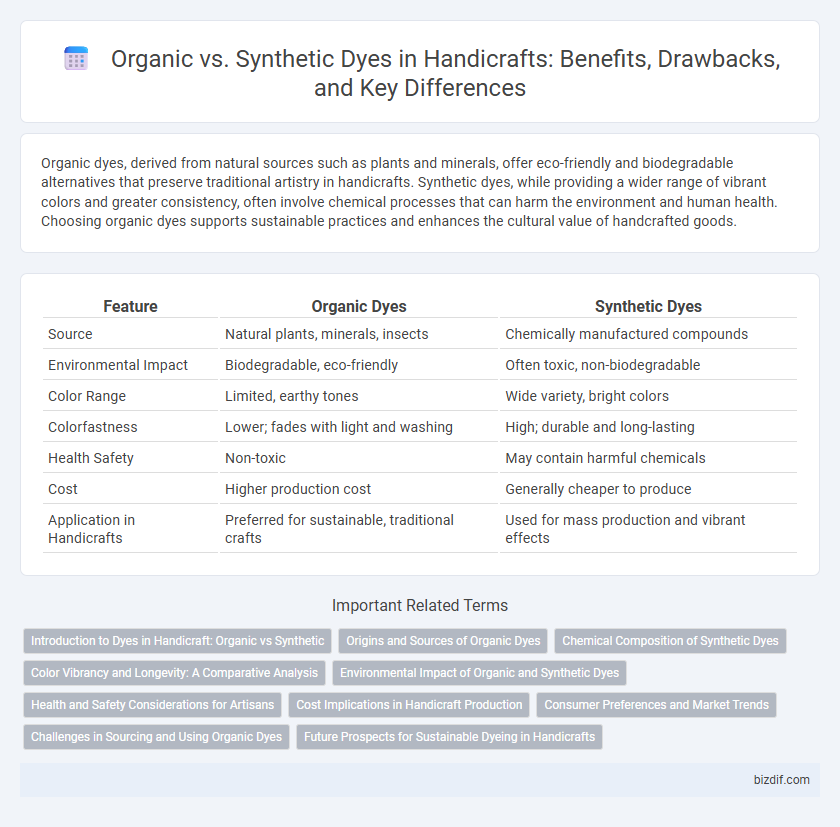
| Feature | Organic Dyes | Synthetic Dyes |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Natural plants, minerals, insects | Chemically manufactured compounds |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, eco-friendly | Often toxic, non-biodegradable |
| Color Range | Limited, earthy tones | Wide variety, bright colors |
| Colorfastness | Lower; fades with light and washing | High; durable and long-lasting |
| Health Safety | Non-toxic | May contain harmful chemicals |
| Cost | Higher production cost | Generally cheaper to produce |
| Application in Handicrafts | Preferred for sustainable, traditional crafts | Used for mass production and vibrant effects |
Introduction to Dyes in Handicraft: Organic vs Synthetic
Organic dyes, derived from natural sources such as plants, insects, and minerals, offer eco-friendly and biodegradable options for handicraft coloring, emphasizing sustainability in artistic practices. Synthetic dyes, created through chemical processes, provide a broader color spectrum and greater consistency, catering to mass production demands with cost-effective solutions. Understanding the strengths and limitations of both dye types enables artisans to select materials that align with their creative goals and environmental values.
Origins and Sources of Organic Dyes
Organic dyes originate from natural sources such as plants, minerals, and insects, with indigo from indigofera plants and cochineal from scale insects being classic examples. These dyes have been used for centuries in traditional handicraft practices due to their biodegradable and eco-friendly properties. Compared to synthetic dyes derived from petrochemicals, organic dyes offer unique hues and sustainable sourcing that appeal to artisans focused on environmentally conscious production.
Chemical Composition of Synthetic Dyes
Synthetic dyes are composed of complex chemical compounds derived from petrochemicals, such as azo, anthraquinone, and phthalocyanine structures, which provide vibrant and long-lasting colors. These chemically engineered molecules offer greater consistency in hue and improved resistance to light and washing compared to organic dyes. However, their composition often includes aromatic amines and heavy metals, raising environmental and health concerns during production and disposal.
Color Vibrancy and Longevity: A Comparative Analysis
Organic dyes, derived from natural sources like plants and insects, offer subtle, earthy tones with moderate color vibrancy but tend to fade more quickly under sunlight and washing conditions. Synthetic dyes, manufactured through chemical processes, provide intense, vivid colors that maintain their brightness and resist fading over extended periods, making them ideal for products requiring high durability. The choice between organic and synthetic dyes hinges on the desired balance between eco-friendliness and long-lasting color vibrancy in handicraft products.
Environmental Impact of Organic and Synthetic Dyes
Organic dyes, derived from natural sources like plants and minerals, exhibit lower toxicity and biodegradability, significantly reducing environmental pollution in handicraft production. Synthetic dyes, however, often contain harmful chemicals such as heavy metals and aromatic amines, leading to water contamination, soil degradation, and adverse health effects on local ecosystems. Choosing organic dyes supports sustainable handicraft practices by minimizing chemical runoff and promoting ecological balance.
Health and Safety Considerations for Artisans
Organic dyes derived from natural sources such as plants and minerals tend to be less toxic and pose fewer health risks to artisans, reducing exposure to harmful chemicals and allergens. Synthetic dyes, while offering vibrant and consistent colors, often contain hazardous substances like heavy metals and carcinogens that can cause respiratory problems, skin irritations, and long-term health issues. Proper ventilation, protective gear, and adherence to safety guidelines are crucial for artisans working with synthetic dyes to minimize health hazards in handicraft production.
Cost Implications in Handicraft Production
Organic dyes generally incur higher cost implications in handicraft production due to the labor-intensive extraction process and limited availability of natural raw materials. Synthetic dyes offer cost advantages with mass production, consistent quality, and higher colorfastness, reducing long-term expenses in dyeing. However, artisans prioritizing eco-friendly practices may accept elevated costs for organic dyes to meet market demand for sustainable handicrafts.
Consumer Preferences and Market Trends
Organic dyes, derived from natural sources like plants and minerals, are increasingly preferred by eco-conscious consumers seeking sustainable handicraft products with minimal environmental impact. Market trends indicate a growing demand for handcrafted items using organic dyes, driven by their biodegradability and unique color variations, contrasting with the uniformity and chemical intensity of synthetic dyes. Consumer preferences lean towards authenticity and health safety, positioning organic-dyed handicrafts as a premium niche in the competitive market.
Challenges in Sourcing and Using Organic Dyes
Sourcing organic dyes for handicrafts poses significant challenges due to their seasonal availability, limited geographic regions, and reliance on sustainable harvesting practices that impact quantity and consistency. Artisans face difficulties in achieving color uniformity and durability compared to synthetic dyes, as organic dyes are prone to fading and require specialized mordants to fix colors effectively. High production costs and the labor-intensive extraction process also restrict the widespread use of organic dyes in modern handicraft manufacturing.
Future Prospects for Sustainable Dyeing in Handicrafts
Organic dyes derived from natural sources like plants and minerals offer biodegradable and eco-friendly alternatives to synthetic dyes, reducing environmental pollution in handicraft production. Advances in biotechnology and natural pigment extraction techniques promise increased colorfastness and scalability, making organic dyes more competitive for mass application in sustainable handicraft dyeing. Integrating organic dyes with innovative mordanting methods and waste-free processes is expected to drive a green transformation in the handicraft industry's future, promoting circular economy principles and preserving traditional artisan skills.
Organic Dyes vs Synthetic Dyes Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com