Hand-looming produces unique, high-quality textiles with intricate designs, emphasizing artisanal craftsmanship and cultural heritage. Machine-weaving offers faster production and consistent fabric quality, suitable for large-scale manufacturing and commercial use. Choosing between hand-looming and machine-weaving depends on the balance between tradition, customization, and efficiency in textile creation.
Table of Comparison
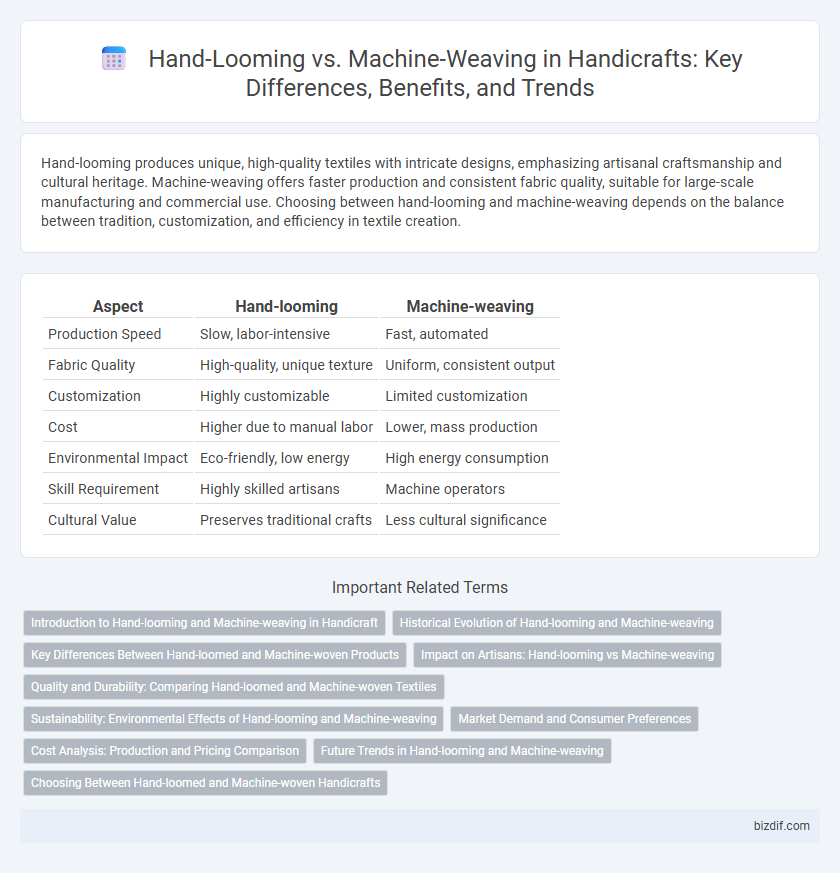
| Aspect | Hand-looming | Machine-weaving |
|---|---|---|
| Production Speed | Slow, labor-intensive | Fast, automated |
| Fabric Quality | High-quality, unique texture | Uniform, consistent output |
| Customization | Highly customizable | Limited customization |
| Cost | Higher due to manual labor | Lower, mass production |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly, low energy | High energy consumption |
| Skill Requirement | Highly skilled artisans | Machine operators |
| Cultural Value | Preserves traditional crafts | Less cultural significance |
Introduction to Hand-looming and Machine-weaving in Handicraft
Hand-looming in handicraft involves manually operating traditional looms to weave fabric, emphasizing intricate designs and cultural heritage, often resulting in unique, high-quality textiles. Machine-weaving uses automated industrial looms to produce larger quantities of fabric quickly and uniformly, catering to mass production demands. Both techniques contribute significantly to the textile industry, with hand-looming preserving artisanal skills and machine-weaving enhancing efficiency.
Historical Evolution of Hand-looming and Machine-weaving
Hand-looming dates back thousands of years as one of the earliest textile production methods, originating in ancient civilizations like Mesopotamia and India, emphasizing artisanal craftsmanship and cultural heritage. Machine-weaving emerged during the Industrial Revolution in the 18th century with the invention of devices such as the power loom by Edmund Cartwright, revolutionizing textile manufacturing through increased speed and mass production capabilities. The historical evolution reflects a shift from manual, labor-intensive processes to mechanized systems that transformed global textile economies and trade.
Key Differences Between Hand-loomed and Machine-woven Products
Hand-loomed products showcase intricate craftsmanship, with each piece reflecting unique variations and cultural heritage due to manual weaving techniques, resulting in limited production speed. Machine-woven products offer high uniformity and faster production rates driven by automated processes, enabling mass production with consistent texture and pattern precision. The choice between hand-looming and machine-weaving impacts quality, customization, environmental footprint, and price, as hand-loomed fabric tends to be more sustainable but costlier compared to efficient yet resource-intensive machine weaving.
Impact on Artisans: Hand-looming vs Machine-weaving
Hand-looming preserves the traditional skills of artisans, providing sustainable livelihoods and fostering cultural heritage through intricate manual craftsmanship. Machine-weaving increases production efficiency but often leads to the displacement of skilled weavers, reducing opportunities for artisanal communities. The shift from hand-looming to machine-weaving significantly impacts economic stability and cultural preservation among artisans worldwide.
Quality and Durability: Comparing Hand-loomed and Machine-woven Textiles
Hand-loomed textiles exhibit superior quality with intricate patterns and unique textures achieved through skilled craftsmanship, resulting in durable fabrics that age gracefully. Machine-woven fabrics provide uniformity and higher production speed but often lack the artisanal detail and long-lasting strength found in hand-loomed materials. The natural fibers used in hand-looming further enhance durability, making these textiles ideal for premium, sustainable applications.
Sustainability: Environmental Effects of Hand-looming and Machine-weaving
Hand-looming significantly reduces energy consumption compared to machine-weaving, relying on human power rather than electricity, which lowers the carbon footprint associated with textile production. The manual process produces minimal waste and uses natural fibers more efficiently, contributing to less environmental pollution and chemical runoff. In contrast, machine-weaving often depends on synthetic materials and industrial power sources, resulting in higher greenhouse gas emissions and greater resource depletion.
Market Demand and Consumer Preferences
Hand-loomed textiles attract a niche market that values artisanal craftsmanship, cultural heritage, and sustainability, appealing to consumers seeking unique and eco-friendly products. Machine-woven fabrics dominate mass markets due to their cost efficiency and faster production rates, catering to consumers prioritizing affordability and uniformity. Increasing consumer awareness about ethical fashion and quality artisanship is gradually shifting demand toward hand-loomed goods in premium market segments.
Cost Analysis: Production and Pricing Comparison
Hand-looming involves higher labor costs due to manual craftsmanship, resulting in longer production times and premium pricing for unique, artisanal textiles. Machine-weaving significantly reduces production costs by automating weaving processes, enabling mass production with lower prices but less customization. Pricing differences reflect the value placed on hand-woven quality and exclusivity versus the affordability and efficiency of machine-made fabrics.
Future Trends in Hand-looming and Machine-weaving
Future trends in hand-looming emphasize sustainable practices, customization, and the revival of traditional techniques, driven by increasing consumer demand for eco-friendly and artisanal products. Machine-weaving is advancing through automation, AI integration, and high-speed production to meet global-scale demands and improve fabric consistency. Hybrid models combining hand-loom craftsmanship with machine precision are emerging, reflecting a growing market for innovative, high-quality textiles that balance tradition and technology.
Choosing Between Hand-loomed and Machine-woven Handicrafts
Choosing between hand-loomed and machine-woven handicrafts involves evaluating factors such as uniqueness, craftsmanship, and production scale. Hand-loomed textiles offer intricate designs and cultural authenticity, reflecting skilled artisanship, while machine-woven products provide consistency, affordability, and faster production rates. Preference depends on the value placed on traditional aesthetics versus mass-market accessibility in handicraft selection.
Hand-looming vs Machine-weaving Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com