Local markets for handicrafts emphasize cultural authenticity and community support, offering artisans direct engagement with consumers who value traditional craftsmanship. Export markets demand products with consistent quality, scalable production, and compliance with international standards, often requiring adaptations in design to suit global tastes. Balancing these markets enables artisans to preserve heritage while expanding economic opportunities.
Table of Comparison
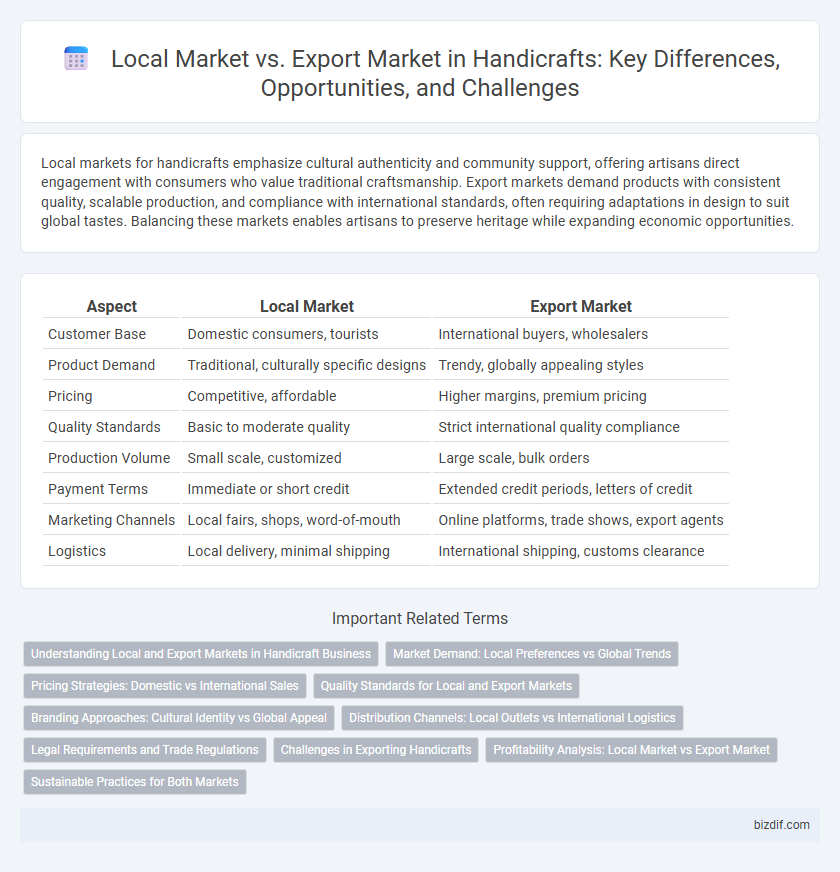
| Aspect | Local Market | Export Market |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Base | Domestic consumers, tourists | International buyers, wholesalers |
| Product Demand | Traditional, culturally specific designs | Trendy, globally appealing styles |
| Pricing | Competitive, affordable | Higher margins, premium pricing |
| Quality Standards | Basic to moderate quality | Strict international quality compliance |
| Production Volume | Small scale, customized | Large scale, bulk orders |
| Payment Terms | Immediate or short credit | Extended credit periods, letters of credit |
| Marketing Channels | Local fairs, shops, word-of-mouth | Online platforms, trade shows, export agents |
| Logistics | Local delivery, minimal shipping | International shipping, customs clearance |
Understanding Local and Export Markets in Handicraft Business
Understanding local and export markets in the handicraft business requires analyzing consumer preferences, purchasing power, and cultural trends. Local markets often demand traditional designs reflecting cultural heritage, while export markets seek unique, high-quality, and trendy products aligned with global demand. Price sensitivity, certification standards, and logistics also differ significantly between local sales and international exports.
Market Demand: Local Preferences vs Global Trends
Local market demand for handicrafts often centers on traditional designs, cultural significance, and functional use, reflecting deep-rooted preferences and heritage values. Export market demand prioritizes innovative styles, contemporary aesthetics, and global trends, driven by diverse consumer tastes and international fashion influences. Understanding the divergence between local preferences and global market trends is essential for artisans to tailor products effectively and expand their market reach.
Pricing Strategies: Domestic vs International Sales
Pricing strategies for handicrafts differ significantly between local markets and export markets, driven by factors such as production costs, competition, and consumer purchasing power. Domestic sales often employ competitive pricing to attract local buyers and accommodate lower disposable incomes, while international sales tend to adopt premium pricing to reflect quality, uniqueness, and shipping expenses. Export market pricing also accounts for tariffs, exchange rates, and market demand, enabling artisans to maximize profit margins while maintaining cultural authenticity.
Quality Standards for Local and Export Markets
Local markets for handicrafts often prioritize traditional designs and cultural authenticity, with quality standards focused on durability and aesthetic appeal suited to local tastes. Export markets demand stringent quality controls, including standardized measurements, material certification, and compliance with international regulations to meet global consumer expectations. Meeting export quality standards involves rigorous inspection and certification processes that can enhance product value and open access to diverse international buyers.
Branding Approaches: Cultural Identity vs Global Appeal
Local markets in handicrafts emphasize branding rooted in cultural identity, showcasing traditional designs, indigenous materials, and artisan stories that resonate with regional consumers. Export markets prioritize global appeal by integrating contemporary aesthetics, universal themes, and standardized quality certifications to attract diverse international buyers. Balancing authenticity with market preferences enhances brand value and drives sustainable growth in both sectors.
Distribution Channels: Local Outlets vs International Logistics
Local handicraft markets rely heavily on direct distribution channels such as artisan shops, fairs, and community-based outlets that facilitate personalized customer interactions and immediate product feedback. Export markets depend on complex international logistics, including freight forwarding, customs clearance, and global retail partnerships, requiring robust supply chain coordination to maintain product quality and timely deliveries. Efficient management of distribution channels is critical for artisans to balance local market accessibility with international demand growth.
Legal Requirements and Trade Regulations
Local markets for handicrafts typically involve simpler legal requirements such as basic business licenses and local health or safety standards, facilitating easier market entry for artisans. Export markets demand stringent compliance with international trade regulations including customs documentation, product certification, labeling standards, and adherence to bilateral trade agreements. Understanding export-specific regulations like the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species (CITES) and quality control measures is crucial to avoid legal penalties and ensure smooth cross-border transactions.
Challenges in Exporting Handicrafts
Exporting handicrafts faces challenges like strict international quality standards, fluctuating global demand, and high shipping costs that often limit market access. Artisans struggle with intellectual property rights protection and adapting designs to meet diverse cultural preferences abroad. Limited access to efficient logistics and trade facilitation further complicates reaching competitive export markets compared to local market sales.
Profitability Analysis: Local Market vs Export Market
Profitability analysis reveals that the export market generally offers higher profit margins for handicrafts due to premium pricing and larger order volumes, despite increased logistics and compliance costs. Local markets provide quicker turnover and lower transportation expenses but often yield lower prices because of intense competition and limited purchasing power. Effective profitability depends on balancing export benefits with local market stability, considering factors like demand patterns, cost structures, and currency fluctuations.
Sustainable Practices for Both Markets
Sustainable practices in handicraft production focus on using eco-friendly materials and traditional techniques that minimize waste and conserve resources, benefiting both local and export markets. Local markets often emphasize community engagement and cultural preservation, while export markets demand compliance with international sustainability standards and certifications. Integrating sustainable sourcing and fair labor practices enhances the value and credibility of handicrafts globally, promoting long-term environmental and economic resilience.
Local Market vs Export Market Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com