Manual techniques in handicraft preserve traditional skills and offer unique, personalized creations that embody artisanal value and cultural heritage. Automated processes increase production efficiency and consistency, enabling mass production while potentially reducing the artistic uniqueness of each piece. Balancing manual craftsmanship with automation can optimize quality and scalability, meeting diverse market demands.
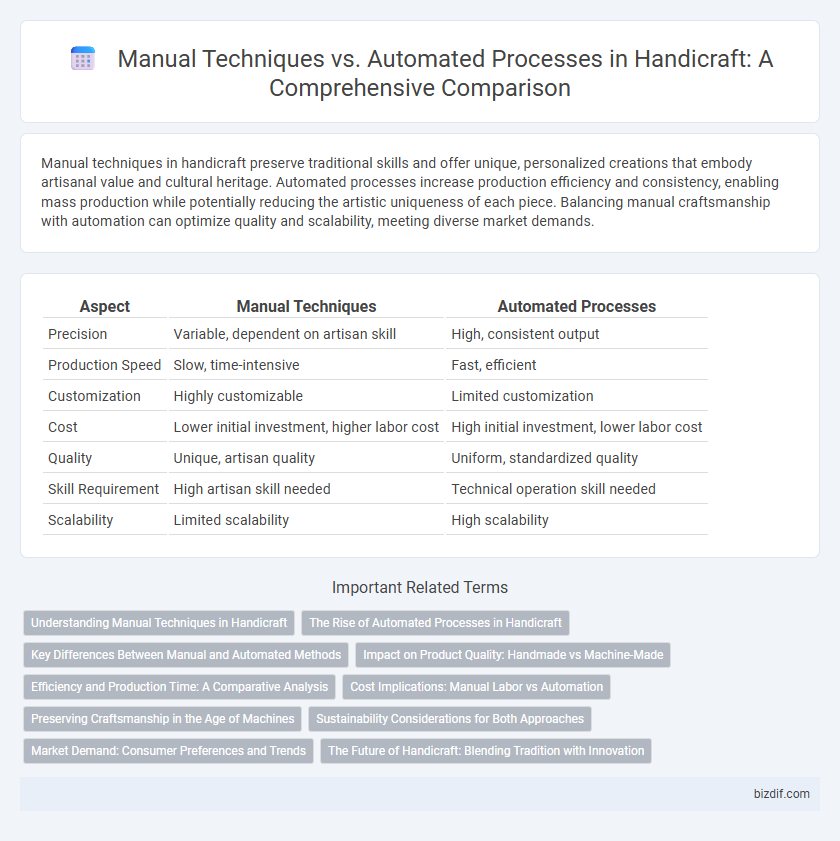
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Manual Techniques | Automated Processes |
|---|---|---|
| Precision | Variable, dependent on artisan skill | High, consistent output |
| Production Speed | Slow, time-intensive | Fast, efficient |
| Customization | Highly customizable | Limited customization |
| Cost | Lower initial investment, higher labor cost | High initial investment, lower labor cost |
| Quality | Unique, artisan quality | Uniform, standardized quality |
| Skill Requirement | High artisan skill needed | Technical operation skill needed |
| Scalability | Limited scalability | High scalability |
Understanding Manual Techniques in Handicraft
Manual techniques in handicraft emphasize skilled handwork, precision, and traditional methods that preserve cultural heritage. Artisans rely on tools like chisels, needles, and looms to create unique, detailed pieces that reflect individual craftsmanship. These techniques foster creativity and authenticity, often resulting in higher quality and more valued products compared to automated processes.
The Rise of Automated Processes in Handicraft
The rise of automated processes in handicraft has revolutionized production by increasing efficiency and consistency while reducing labor costs. CNC machines, laser cutters, and 3D printers enable intricate designs and precise replication previously unattainable through purely manual techniques. Despite automation's advances, the unique artistic value and cultural significance of handcrafted items continue to drive demand for skilled artisans.
Key Differences Between Manual and Automated Methods
Manual techniques in handicraft emphasize skilled handwork, intricate detailing, and unique, personalized creations, promoting artistic expression and craftsmanship. Automated processes rely on machinery and technology to produce consistent, high-volume outputs, prioritizing efficiency and uniformity over individual customization. The key differences lie in the level of human involvement, production speed, and the ability to create one-of-a-kind versus mass-produced items.
Impact on Product Quality: Handmade vs Machine-Made
Handmade handicrafts exhibit unique textures and intricate details due to manual techniques, often resulting in superior aesthetic quality and authenticity compared to machine-made products. Automated processes ensure consistent precision and uniformity, yet may lack the nuanced craftsmanship that defines handmade items. Quality in handmade products is largely influenced by the artisan's skill, while machine-made goods rely on programmed accuracy for standardized outcomes.
Efficiency and Production Time: A Comparative Analysis
Manual techniques in handicraft offer unique artistic detail but often require significantly more production time compared to automated processes. Automated machinery enhances efficiency by producing large quantities with consistent quality, reducing labor costs and turnaround times. However, the intricate precision and customization achievable through manual methods remain unmatched in niche artisan markets.
Cost Implications: Manual Labor vs Automation
Manual techniques in handicraft often involve higher labor costs due to the time-intensive nature of skilled craftsmanship and the reliance on artisans' expertise. Automated processes reduce production time and labor expenses, enabling lower unit costs and increased scalability, but initial investments in machinery and technology can be substantial. Cost implications vary significantly depending on product complexity, volume, and quality standards, with manual labor favoring bespoke items and automation suited for mass production.
Preserving Craftsmanship in the Age of Machines
Manual techniques in handicraft preserve the intricate skills and cultural heritage passed down through generations, ensuring each piece carries unique artistic value. Automated processes increase production speed and consistency but often lack the subtle imperfections that characterize authentic craftsmanship. Balancing mechanization with traditional handwork sustains artisanal identities while meeting modern market demands.
Sustainability Considerations for Both Approaches
Manual techniques in handicraft promote sustainability through low energy consumption and reduced waste, often utilizing locally sourced, biodegradable materials. Automated processes can increase efficiency and scalability but may rely on non-renewable resources and generate higher carbon footprints unless integrated with eco-friendly technologies. Evaluating both methods for sustainability involves balancing craftsmanship preservation with innovation in green manufacturing practices.
Market Demand: Consumer Preferences and Trends
Market demand for handicrafts increasingly reflects consumer preferences favoring unique, handmade products over mass-produced items, driving growth in manual techniques. Artisans leveraging traditional skills tap into trends valuing authenticity, sustainability, and cultural heritage, which automated processes often lack. Despite automation's efficiency, the emotional connection and perceived quality of handcrafted goods maintain strong appeal, sustaining niche markets and premium pricing.
The Future of Handicraft: Blending Tradition with Innovation
The future of handicraft lies in seamlessly blending manual techniques with automated processes to enhance precision and efficiency while preserving artisanal authenticity. Advanced technologies such as 3D printing and CNC machining complement traditional handcrafting skills, enabling bespoke designs and complex patterns that were previously unattainable. This hybrid approach not only sustains cultural heritage but also drives innovation, expanding market opportunities for handcrafted goods globally.
Manual Techniques vs Automated Processes Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com