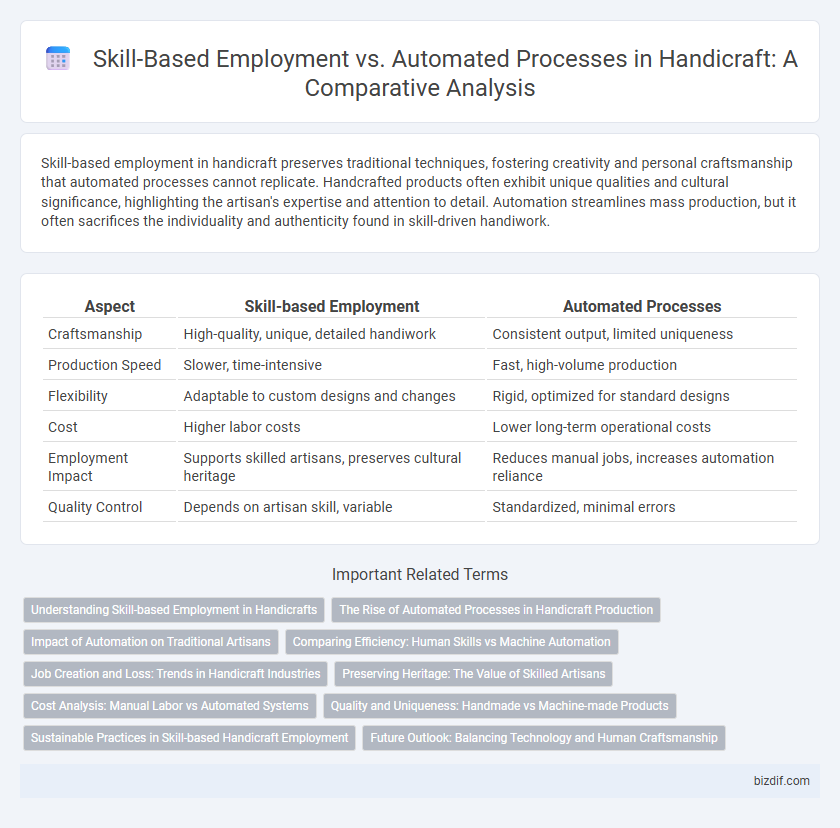
Skill-based employment in handicraft preserves traditional techniques, fostering creativity and personal craftsmanship that automated processes cannot replicate. Handcrafted products often exhibit unique qualities and cultural significance, highlighting the artisan's expertise and attention to detail. Automation streamlines mass production, but it often sacrifices the individuality and authenticity found in skill-driven handiwork.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Skill-based Employment | Automated Processes |
|---|---|---|
| Craftsmanship | High-quality, unique, detailed handiwork | Consistent output, limited uniqueness |
| Production Speed | Slower, time-intensive | Fast, high-volume production |
| Flexibility | Adaptable to custom designs and changes | Rigid, optimized for standard designs |
| Cost | Higher labor costs | Lower long-term operational costs |
| Employment Impact | Supports skilled artisans, preserves cultural heritage | Reduces manual jobs, increases automation reliance |
| Quality Control | Depends on artisan skill, variable | Standardized, minimal errors |
Understanding Skill-based Employment in Handicrafts
Skill-based employment in handicrafts emphasizes manual dexterity, creativity, and cultural knowledge that machines cannot replicate, resulting in unique, high-quality products. Artisans develop specialized techniques passed down through generations, contributing to cultural heritage preservation and local economies. This human-centered approach fosters job opportunities in communities where automation is limited or unsuitable.
The Rise of Automated Processes in Handicraft Production
The rise of automated processes in handicraft production has significantly increased efficiency and output while reducing manual labor costs. Advanced technologies like 3D printing and CNC machines enable precise replication of intricate designs, challenging traditional skill-based employment models. Despite automation's growth, skilled artisans remain essential for customization and quality control in handcrafted products.
Impact of Automation on Traditional Artisans
Automation has significantly transformed the handicraft sector by reducing demand for manual skill-based employment traditionally held by artisans. While automated processes increase production efficiency and lower costs, they often compromise the cultural authenticity and intricate craftsmanship unique to hand-made products. This shift challenges traditional artisans to adapt by emphasizing customization, quality, and heritage preservation to maintain relevance in a technology-driven market.
Comparing Efficiency: Human Skills vs Machine Automation
Handicraft industries relying on skilled artisans deliver intricate, customizable products with unique cultural value, whereas automated processes offer faster production speeds and consistent quality at scale. Human skills excel in tasks requiring creativity, fine motor precision, and adaptability, which machines often struggle to replicate despite advances in robotics and AI. Efficiency in handicraft versus automation depends heavily on product complexity and demand volume, with artisans thriving in bespoke markets and machines dominating mass production environments.
Job Creation and Loss: Trends in Handicraft Industries
Skill-based employment in the handicraft industry fosters job creation by leveraging artisanal expertise and preserving traditional craftsmanship, which cannot be easily replicated by automated processes. Automated techniques lead to increased production efficiency but often result in significant job losses, especially for low-skilled workers in this sector. Current trends show a growing demand for niche, handcrafted products that supports employment, while mass-produced items created through automation continue to dominate mainstream markets.
Preserving Heritage: The Value of Skilled Artisans
Skilled artisans play a crucial role in preserving cultural heritage through handcrafts that automated processes cannot replicate due to their intricate techniques and unique artistic expressions. Handcrafted items often carry historical significance and cultural stories, making skill-based employment vital for maintaining these traditions. Investing in artisan skills ensures the continuation of heritage crafts, supporting both cultural identity and sustainable local economies.
Cost Analysis: Manual Labor vs Automated Systems
Manual labor in handicraft industries often involves higher variable costs due to wages, training, and longer production times compared to automated systems that require significant upfront capital investment but lower per-unit costs over time. Automated processes increase efficiency and consistency, reducing labor costs and minimizing material waste, which can lead to overall lower production expenses in large-scale operations. However, skill-based employment supports intricate craftsmanship and customization that machines struggle to replicate, often commanding premium pricing despite higher labor costs.
Quality and Uniqueness: Handmade vs Machine-made Products
Handicraft products showcase exceptional quality and uniqueness due to skilled artisans' meticulous attention to detail, which automated processes often cannot replicate. Skill-based employment fosters creativity, enables customization, and preserves cultural heritage through distinctive designs and intricate craftsmanship. Machine-made products prioritize uniformity and efficiency but lack the personalized touch and artistic value inherent in handmade goods.
Sustainable Practices in Skill-based Handicraft Employment
Skill-based handicraft employment promotes sustainable practices by utilizing traditional techniques that minimize environmental impact and reduce waste compared to automated processes. Artisans often use locally sourced, natural materials which support eco-friendly production and preserve cultural heritage. This approach fosters economic resilience within communities by creating jobs that emphasize craftsmanship and sustainable resource management.
Future Outlook: Balancing Technology and Human Craftsmanship
Skill-based employment in handicraft preserves cultural heritage and offers unique, high-quality products that automated processes cannot replicate. Emerging technologies can enhance productivity and precision without fully replacing the artisan's creativity and expertise. Future outlook emphasizes a symbiotic relationship where human craftsmanship and automation coexist, driving innovation and sustainability in the industry.
Skill-based Employment vs Automated Processes Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com