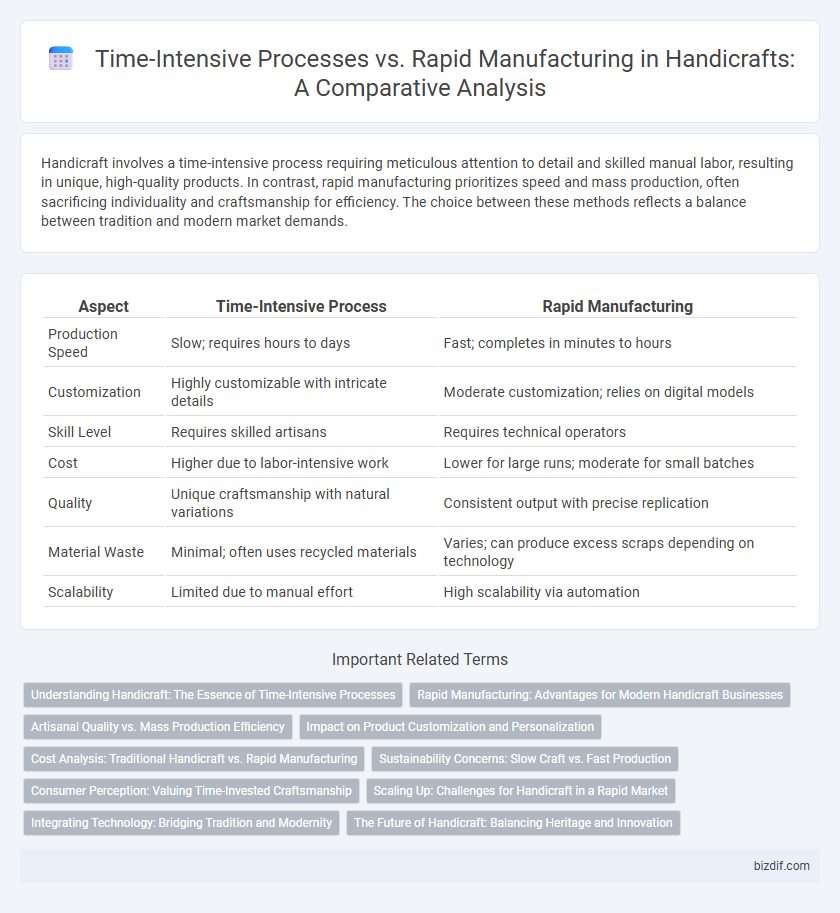
Handicraft involves a time-intensive process requiring meticulous attention to detail and skilled manual labor, resulting in unique, high-quality products. In contrast, rapid manufacturing prioritizes speed and mass production, often sacrificing individuality and craftsmanship for efficiency. The choice between these methods reflects a balance between tradition and modern market demands.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Time-Intensive Process | Rapid Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|
| Production Speed | Slow; requires hours to days | Fast; completes in minutes to hours |
| Customization | Highly customizable with intricate details | Moderate customization; relies on digital models |
| Skill Level | Requires skilled artisans | Requires technical operators |
| Cost | Higher due to labor-intensive work | Lower for large runs; moderate for small batches |
| Quality | Unique craftsmanship with natural variations | Consistent output with precise replication |
| Material Waste | Minimal; often uses recycled materials | Varies; can produce excess scraps depending on technology |
| Scalability | Limited due to manual effort | High scalability via automation |
Understanding Handicraft: The Essence of Time-Intensive Processes
Handicraft embodies a time-intensive process that prioritizes meticulous attention to detail and skilled manual techniques, resulting in unique, high-quality products unattainable through rapid manufacturing. The essence of handicraft lies in its patient craftsmanship, where artisans invest hours or days perfecting each piece, enhancing authenticity and cultural value. Unlike mass production, this labor-intensive approach fosters sustainability and preserves traditional skills, emphasizing quality over quantity.
Rapid Manufacturing: Advantages for Modern Handicraft Businesses
Rapid manufacturing significantly accelerates production time, enabling modern handicraft businesses to meet increasing consumer demand efficiently. This approach reduces labor costs and minimizes material waste through precise digital fabrication techniques like 3D printing and CNC machining. The integration of rapid manufacturing allows artisans to scale operations, customize designs easily, and maintain high-quality output without sacrificing craftsmanship.
Artisanal Quality vs. Mass Production Efficiency
Handicraft embodies a time-intensive process where artisans meticulously create unique, high-quality products that showcase individual skill and cultural heritage. In contrast, rapid manufacturing emphasizes mass production efficiency, enabling large-scale output with consistent standards but often sacrificing the distinctiveness and intricate details found in handmade goods. The artisanal quality of handcrafted items appeals to consumers seeking authenticity and personalized craftsmanship over the uniformity of mass-produced products.
Impact on Product Customization and Personalization
Time-intensive handicraft processes enable a high degree of product customization and personalization, allowing artisans to infuse unique cultural elements and individual craftsmanship into each item. Rapid manufacturing techniques, such as 3D printing and automated assembly, significantly reduce production time but often sacrifice the depth of customization and the distinctiveness associated with handcrafted goods. The choice between these methods impacts consumer experience, with time-intensive crafts appealing to niche markets valuing exclusivity and rapid manufacturing meeting mass demand for affordable, customizable products.
Cost Analysis: Traditional Handicraft vs. Rapid Manufacturing
Traditional handicraft involves a time-intensive process that significantly increases labor costs and limits production volume, resulting in higher per-unit expenses. In contrast, rapid manufacturing leverages automation and streamlined workflows to reduce labor time, lowering costs and enabling economies of scale. Cost analysis shows rapid manufacturing offers greater affordability and efficiency, while traditional methods justify premium pricing through artisanal quality and uniqueness.
Sustainability Concerns: Slow Craft vs. Fast Production
Handicraft's time-intensive process often ensures higher sustainability by minimizing waste and using eco-friendly materials, contrasting with the rapid manufacturing's mass production that frequently leads to resource depletion and excessive pollution. Slow craft supports circular economy principles by emphasizing durability and repairability, whereas fast production promotes disposable culture with short product lifecycles and increased landfill contributions. Prioritizing sustainable handicrafts can significantly reduce carbon footprints and foster ethical consumerism in the global marketplace.
Consumer Perception: Valuing Time-Invested Craftsmanship
Consumers often associate time-intensive handicraft with superior quality and unique artistry, perceiving it as a valuable investment in authenticity and skill. Rapid manufacturing may offer affordability and speed but lacks the personalized touch that artisans imbue through meticulous, time-consuming techniques. The growing consumer demand for ethically produced, handcrafted goods reflects a preference for products that signify time-invested craftsmanship and cultural heritage.
Scaling Up: Challenges for Handicraft in a Rapid Market
Handicraft production involves a time-intensive process requiring skilled artisans and detailed manual labor, which limits scalability in a rapid manufacturing market dominated by automated systems. Rapid manufacturing technologies enable mass production with consistent quality and shorter lead times, challenging traditional handicraft businesses to maintain competitiveness. Scaling up handicraft operations faces challenges such as increased costs, maintaining authenticity, and preserving craftsmanship without compromising production speed.
Integrating Technology: Bridging Tradition and Modernity
Integrating advanced technology in handicraft production enhances efficiency while preserving the unique artistry of time-intensive processes, creating a harmonious blend of tradition and modernity. Digital tools like 3D printing and computer-aided design (CAD) enable rapid manufacturing without compromising handcrafted detail and cultural authenticity. This synergy between cutting-edge innovation and artisanal craftsmanship fosters sustainable growth and opens new markets for traditional handicrafts worldwide.
The Future of Handicraft: Balancing Heritage and Innovation
Handicraft embodies a time-intensive process that preserves cultural heritage through meticulous, skilled artistry, contrasting sharply with rapid manufacturing's efficiency-driven production. The future of handicraft demands a balance where innovation integrates advanced tools and digital techniques without compromising traditional craftsmanship's authenticity. Embracing technology alongside heritage ensures sustainable growth, enabling artisans to meet modern market demands while safeguarding timeless cultural expressions.
Time-intensive Process vs Rapid Manufacturing Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com