Traditional handicraft methods emphasize skilled manual labor and cultural heritage, preserving unique techniques passed down through generations. Modern techniques incorporate advanced tools and technology to increase efficiency and precision, often enabling mass production while maintaining quality. Balancing these approaches fosters innovation while respecting the artisanal value of handcrafted products.
Table of Comparison
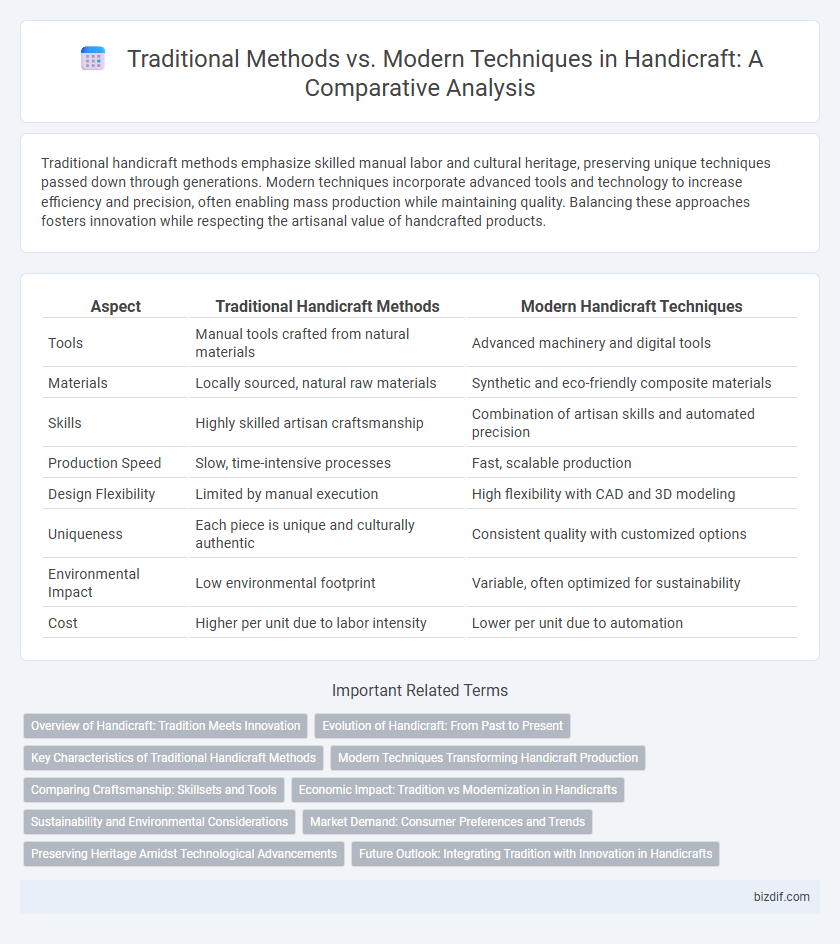
| Aspect | Traditional Handicraft Methods | Modern Handicraft Techniques |
|---|---|---|
| Tools | Manual tools crafted from natural materials | Advanced machinery and digital tools |
| Materials | Locally sourced, natural raw materials | Synthetic and eco-friendly composite materials |
| Skills | Highly skilled artisan craftsmanship | Combination of artisan skills and automated precision |
| Production Speed | Slow, time-intensive processes | Fast, scalable production |
| Design Flexibility | Limited by manual execution | High flexibility with CAD and 3D modeling |
| Uniqueness | Each piece is unique and culturally authentic | Consistent quality with customized options |
| Environmental Impact | Low environmental footprint | Variable, often optimized for sustainability |
| Cost | Higher per unit due to labor intensity | Lower per unit due to automation |
Overview of Handicraft: Tradition Meets Innovation
Traditional handicraft methods emphasize skilled manual techniques, cultural heritage, and the use of natural materials, preserving authenticity and unique artistic expressions. Modern techniques incorporate advanced tools, digital design, and sustainable materials, enhancing efficiency, precision, and scalability in production. The fusion of tradition and innovation in handicraft enables artisans to honor cultural roots while embracing contemporary trends and market demands.
Evolution of Handicraft: From Past to Present
Traditional methods of handicraft emphasize manual skills, natural materials, and time-honored techniques passed down through generations, preserving cultural heritage and unique artisanal quality. Modern techniques integrate advanced tools, digital design, and innovative materials, enhancing precision, efficiency, and scalability while still respecting artistic expression. The evolution of handicraft reflects a dynamic blend of heritage and innovation, enabling artisans to adapt to contemporary markets without losing the essence of traditional craftsmanship.
Key Characteristics of Traditional Handicraft Methods
Traditional handicraft methods emphasize manual skills, intricate detailing, and cultural authenticity, often passed down through generations. These techniques rely on natural materials and handcrafted tools, which result in unique, one-of-a-kind products reflecting regional heritage. The slower production pace and individual artisan involvement highlight the value of craftsmanship over mass production.
Modern Techniques Transforming Handicraft Production
Modern techniques in handicraft production leverage digital tools like 3D printing and laser cutting to enhance precision and scalability while preserving artisanal quality. Integration of computer-aided design (CAD) software allows artisans to create intricate patterns and prototypes rapidly, reducing material waste and production time. These innovations transform traditional craftsmanship by enabling mass customization and expanding market accessibility without compromising the authenticity of handmade products.
Comparing Craftsmanship: Skillsets and Tools
Traditional handicraft methods emphasize artisanal skillsets honed over generations, using hand tools such as chisels, looms, and carving knives that demand precision and tactile expertise. In contrast, modern techniques incorporate advanced machinery like CNC routers, laser cutters, and computer-aided design software, enhancing efficiency and repeatability while requiring technical knowledge. The craftsmanship in traditional methods showcases individual artistry and cultural heritage, whereas modern techniques focus on scalability and innovation within the production process.
Economic Impact: Tradition vs Modernization in Handicrafts
Traditional handicraft methods often rely on skilled labor and locally sourced materials, supporting small-scale artisans and preserving cultural heritage, which fosters sustainable economic development in rural areas. Modern techniques enhance productivity through automation and innovative tools, enabling mass production and broader market access, but can lead to the displacement of traditional craftsmen and loss of unique cultural attributes. Balancing tradition and modernization in handicrafts is crucial for maximizing economic benefits while maintaining cultural identity and employment opportunities in the sector.
Sustainability and Environmental Considerations
Traditional handicraft methods prioritize sustainability by using natural, biodegradable materials and low-energy processes that minimize environmental impact. Modern techniques often incorporate eco-friendly technologies and recycled materials to enhance resource efficiency and reduce waste. Combining the strengths of both approaches can lead to innovative, sustainable production practices that support environmental conservation.
Market Demand: Consumer Preferences and Trends
Traditional handcrafted products appeal to niche markets valuing authenticity, cultural heritage, and unique artistry, often commanding higher prices among collectors and enthusiasts. Modern techniques enable mass production, meeting large-scale consumer demand for affordability, consistency, and trend-driven designs in home decor and fashion accessories. Market trends increasingly show a hybrid preference where consumers seek sustainable, handmade qualities combined with contemporary aesthetics and faster delivery times.
Preserving Heritage Amidst Technological Advancements
Traditional handicraft methods emphasize manual skills, cultural storytelling, and use of natural materials, preserving the authenticity and heritage of craft forms passed down through generations. Modern techniques incorporate digital tools, mechanization, and innovative materials, enhancing production efficiency and design possibilities while risking the dilution of cultural significance. Balancing these approaches ensures the preservation of intangible cultural heritage alongside embracing technological advancements for sustainable craft innovation.
Future Outlook: Integrating Tradition with Innovation in Handicrafts
Future outlook in handicrafts emphasizes the integration of time-honored traditional methods with cutting-edge modern techniques to create products that honor cultural heritage while appealing to contemporary markets. Artisans are increasingly adopting digital tools, sustainable materials, and innovative design processes to enhance craftsmanship quality and operational efficiency. This fusion ensures the preservation of artistic legacy and drives economic growth through expanded global reach and diversified product offerings.
Traditional methods vs Modern techniques Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com