Bench jewelry involves traditional handcrafting techniques that rely on the jeweler's skill to shape, solder, and polish each piece, offering unique artistry and tactile detail. CAD jewelry design utilizes advanced computer software to create precise 3D models, enabling intricate designs and streamlined production with high accuracy. Both methods complement each other in modern jewelry making, blending craftsmanship with technological innovation to produce exceptional jewelry.
Table of Comparison
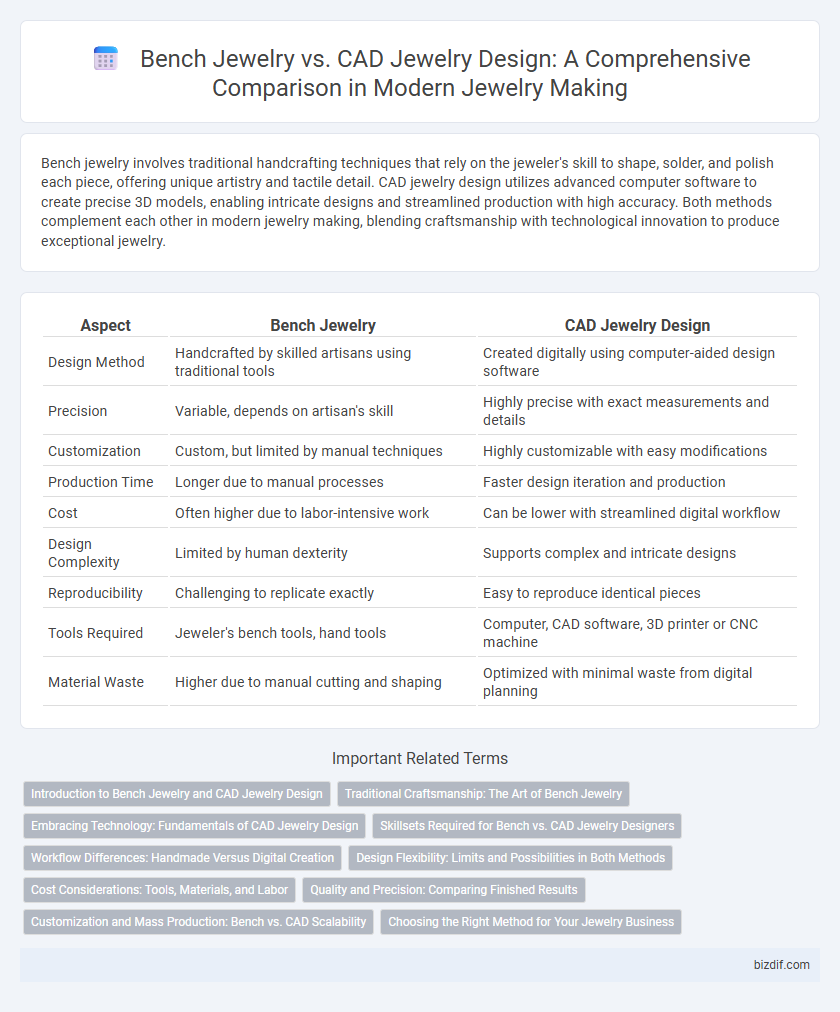
| Aspect | Bench Jewelry | CAD Jewelry Design |
|---|---|---|
| Design Method | Handcrafted by skilled artisans using traditional tools | Created digitally using computer-aided design software |
| Precision | Variable, depends on artisan's skill | Highly precise with exact measurements and details |
| Customization | Custom, but limited by manual techniques | Highly customizable with easy modifications |
| Production Time | Longer due to manual processes | Faster design iteration and production |
| Cost | Often higher due to labor-intensive work | Can be lower with streamlined digital workflow |
| Design Complexity | Limited by human dexterity | Supports complex and intricate designs |
| Reproducibility | Challenging to replicate exactly | Easy to reproduce identical pieces |
| Tools Required | Jeweler's bench tools, hand tools | Computer, CAD software, 3D printer or CNC machine |
| Material Waste | Higher due to manual cutting and shaping | Optimized with minimal waste from digital planning |
Introduction to Bench Jewelry and CAD Jewelry Design
Bench jewelry design involves handcrafted techniques such as sawing, filing, soldering, and stone setting directly on a jeweler's workbench, allowing for intricate customization and unique artistic expression. CAD jewelry design utilizes advanced computer software like Rhino, MatrixGold, and Blender to create precise 3D models that streamline the production process and enable complex geometries difficult to achieve by hand. Both methods play essential roles in modern jewelry making, with bench work offering tactile craftsmanship and CAD design providing efficiency and innovative capabilities.
Traditional Craftsmanship: The Art of Bench Jewelry
Traditional bench jewelry embodies the artistry of handcrafting precious metals and gemstones using time-honored techniques such as soldering, stone setting, and engraving. Master jewelers rely on tactile skills and precision tools at the workbench to create unique, custom pieces that showcase individual craftsmanship and intricate detailing. Unlike CAD jewelry design, which uses digital modeling software for mass production, bench jewelry emphasizes personalized artistry and tangible, hands-on creation.
Embracing Technology: Fundamentals of CAD Jewelry Design
Embracing technology in jewelry making involves mastering CAD jewelry design fundamentals, which streamline precision and creativity compared to traditional bench jewelry techniques. CAD software allows jewelers to visualize intricate designs in 3D, enabling complex geometries and accurate measurements that are difficult to achieve manually. Integrating CAD technology enhances efficiency and innovation, transforming custom jewelry production with digital modeling and rapid prototyping.
Skillsets Required for Bench vs. CAD Jewelry Designers
Bench jewelry design demands exceptional manual dexterity, precision hand skills, and extensive experience with traditional tools to create intricate, custom pieces. CAD jewelry design requires proficiency in specialized software such as Rhino, Matrix, or JewelCAD, along with a strong understanding of 3D modeling, digital rendering, and technical specifications. Both disciplines benefit from a deep knowledge of gemstones, metals, and jewelry construction, but the emphasis shifts from hands-on craftsmanship to digital innovation in CAD design.
Workflow Differences: Handmade Versus Digital Creation
Bench jewelry involves hands-on craftsmanship where artisans physically shape metals and set stones, allowing for intricate, unique designs through direct manipulation and traditional tools. CAD jewelry design utilizes computer software to create precise 3D models, enabling efficient modifications, rapid prototyping, and seamless integration with CNC machines or 3D printers. The workflow for bench jewelry emphasizes manual skill and tactile feedback, while CAD design prioritizes digital accuracy, scalability, and streamlined production processes.
Design Flexibility: Limits and Possibilities in Both Methods
Bench jewelry allows artisans to create highly intricate and unique designs through hands-on techniques, offering unparalleled tactile control but limited by physical skill and time constraints. CAD jewelry design expands design flexibility by enabling complex geometries, precise modifications, and easy replication, though it may lack the organic spontaneity achieved at the bench. Both methods present distinct possibilities: bench work excels in bespoke, artisan-crafted details, while CAD enables innovative designs that push the boundaries of traditional jewelry making.
Cost Considerations: Tools, Materials, and Labor
Bench jewelry making involves traditional tools and hands-on labor, which typically results in variable material waste and higher upfront costs for skilled craftsmanship. CAD jewelry design relies on digital software and precise 3D printing or milling technologies, reducing material waste and often lowering labor costs through automation. While bench work requires investment in specialized hand tools and a bench setup, CAD design demands expenses for software licenses and hardware, influencing overall budgeting for jewelry production.
Quality and Precision: Comparing Finished Results
Bench jewelry offers handcrafted uniqueness and artisan detail, resulting in rich textures and organic imperfections that appeal to collectors valuing traditional craftsmanship. CAD jewelry design excels in precision and consistency, utilizing advanced software to create intricate, flawless patterns that can be replicated with exact measurements for mass production. The finished CAD pieces often achieve higher dimensional accuracy and uniformity, while bench-made jewelry provides a one-of-a-kind, tactile quality that machines cannot fully replicate.
Customization and Mass Production: Bench vs. CAD Scalability
Bench jewelry offers unparalleled customization through hands-on craftsmanship, allowing artisans to tailor each piece with intricate, unique details that reflect personal artistry. CAD jewelry design excels in mass production scalability by enabling precise replication of digital models, which accelerates manufacturing and maintains consistent quality across large quantities. Combining the tactile flexibility of bench work with the efficiency of CAD technology can optimize both bespoke customization and large-scale production needs.
Choosing the Right Method for Your Jewelry Business
Bench jewelry design offers hands-on craftsmanship and the ability to create one-of-a-kind pieces with intricate detailing, ideal for artisans prioritizing traditional techniques. CAD jewelry design leverages advanced software to produce highly precise, repeatable designs, streamlining production and enabling complex geometries suitable for scaling a business. Selecting the right method depends on your brand's focus, production volume, and the balance between bespoke artistry and mass customization.
Bench jewelry vs CAD jewelry design Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com