Flipped classroom models empower language learners by shifting content delivery outside of class, enabling interactive practice and personalized feedback during in-class sessions. Direct instruction remains effective for foundational language skills, providing clear explanations and structured guidance critical for beginners. Combining both methods can enhance engagement and mastery by leveraging the strengths of active learning and explicit teaching.
Table of Comparison
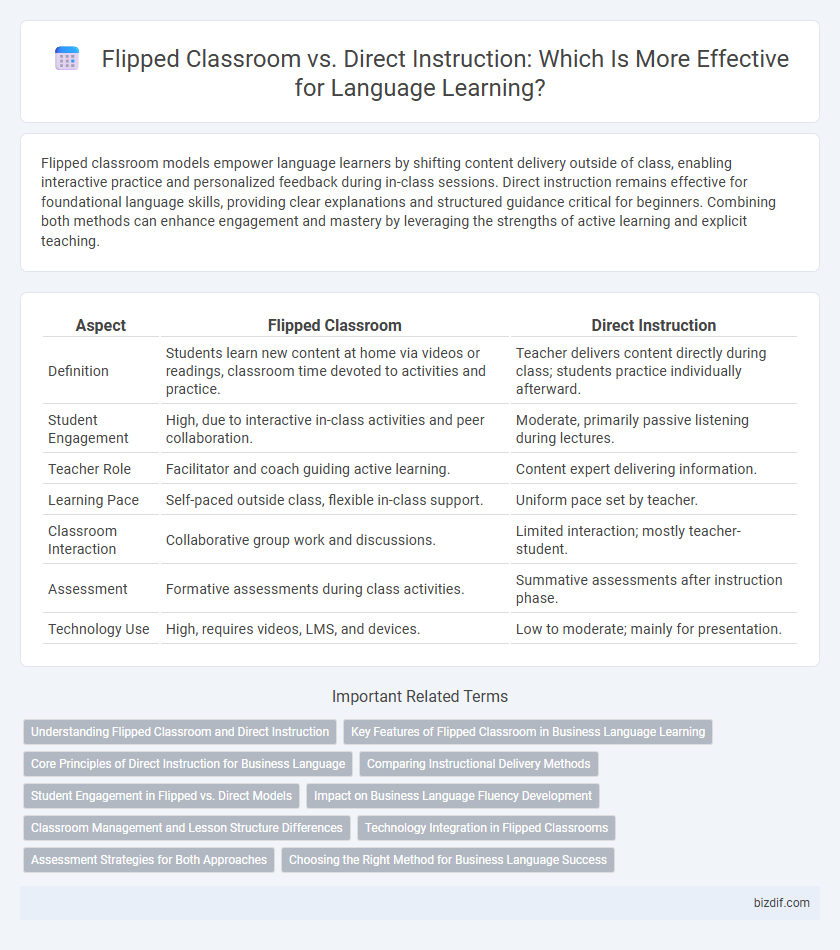
| Aspect | Flipped Classroom | Direct Instruction |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Students learn new content at home via videos or readings, classroom time devoted to activities and practice. | Teacher delivers content directly during class; students practice individually afterward. |
| Student Engagement | High, due to interactive in-class activities and peer collaboration. | Moderate, primarily passive listening during lectures. |
| Teacher Role | Facilitator and coach guiding active learning. | Content expert delivering information. |
| Learning Pace | Self-paced outside class, flexible in-class support. | Uniform pace set by teacher. |
| Classroom Interaction | Collaborative group work and discussions. | Limited interaction; mostly teacher-student. |
| Assessment | Formative assessments during class activities. | Summative assessments after instruction phase. |
| Technology Use | High, requires videos, LMS, and devices. | Low to moderate; mainly for presentation. |
Understanding Flipped Classroom and Direct Instruction
Flipped classroom reverses traditional teaching by delivering instructional content online outside of class, freeing up in-class time for active learning and personalized support. Direct instruction involves teacher-led, structured lessons focusing on clear, step-by-step teaching of language concepts with immediate feedback. Understanding these methods highlights how flipped classrooms promote learner autonomy and engagement, while direct instruction emphasizes teacher control and explicit teaching.
Key Features of Flipped Classroom in Business Language Learning
The flipped classroom in business language learning emphasizes learner-centered activities, where students review lecture materials before class and engage in interactive exercises during sessions, enhancing language acquisition through practical application. This model promotes autonomous learning, allowing professionals to control pacing while maximizing classroom time for real-world communication practice and immediate feedback. Key features include the use of digital resources for pre-class preparation, collaborative tasks during face-to-face sessions, and a focus on business-specific terminology and scenarios to improve fluency and confidence in professional contexts.
Core Principles of Direct Instruction for Business Language
Direct instruction in business language emphasizes clear, structured lessons with explicit teaching of vocabulary and grammar essential for professional communication. Core principles include modeling correct language use, providing guided practice with immediate feedback, and ensuring mastery through repetitive drills and assessments tailored to workplace scenarios. This method enhances efficiency in acquiring precise skills needed for effective business interactions and reduces ambiguity common in less structured approaches.
Comparing Instructional Delivery Methods
Flipped classroom models enhance language instruction by shifting content delivery outside the classroom, allowing in-class time for interactive practice and personalized feedback, which increases student engagement and retention. Direct instruction relies on teacher-led presentations for introducing new language concepts, promoting structured learning but often limiting active student participation during the lesson. Studies show flipped classrooms improve speaking and listening skills through collaborative activities, while direct instruction remains effective for foundational grammar and vocabulary acquisition.
Student Engagement in Flipped vs. Direct Models
Student engagement in flipped classrooms often surpasses that in direct instruction models, as learners actively interact with multimedia content before class and participate in collaborative activities during sessions. This approach fosters deeper cognitive involvement and motivation, enhancing language retention and practical usage. In contrast, direct instruction typically emphasizes teacher-led explanations, which may result in passive learning and reduced opportunities for student interaction and engagement.
Impact on Business Language Fluency Development
Flipped classroom models enhance business language fluency by promoting active learner engagement and real-world application through pre-class preparation and in-class practice. Direct instruction provides structured, expert-led explanations that ensure foundational grammar and vocabulary are clearly understood but may limit spontaneous communication opportunities. Studies show flipped classrooms lead to improved verbal proficiency and confidence in business contexts due to increased exposure to interactive speaking scenarios.
Classroom Management and Lesson Structure Differences
Flipped classroom models shift initial content delivery outside of class, requiring learners to engage with materials independently, which demands strong classroom management strategies to ensure accountability and participation during in-class activities. Direct instruction relies on teacher-led explanations and demonstrations in real-time, emphasizing structured lesson pacing and immediate feedback within a controlled classroom environment. These differences affect lesson structure, where flipped classrooms prioritize collaborative problem-solving and personalized support, and direct instruction focuses on sequential teaching and whole-group engagement.
Technology Integration in Flipped Classrooms
Flipped classrooms leverage technology to enhance language instruction by allowing students to access digital content and interactive materials outside of class, thereby maximizing face-to-face time for practice and personalized support. This approach integrates multimedia resources, such as video lectures and language apps, which foster greater student engagement and accommodate diverse learning styles compared to traditional direct instruction. Research indicates that technology integration in flipped classrooms improves language acquisition efficiency, learner autonomy, and overall classroom interaction.
Assessment Strategies for Both Approaches
Flipped classroom assessment strategies emphasize formative evaluations such as frequent quizzes and peer assessments, allowing students to demonstrate comprehension before class and instructors to tailor in-person activities. Direct instruction relies heavily on summative assessments, including standardized tests and final exams, focusing on measuring student retention and mastery after explicit teaching. Both approaches benefit from integrating real-time feedback mechanisms to enhance language acquisition and ensure continuous progress monitoring.
Choosing the Right Method for Business Language Success
Choosing the right method between flipped classroom and direct instruction depends on business language learners' specific needs, such as time constraints and preferred learning pace. Flipped classrooms promote active engagement and practical application by delivering content outside class, ideal for self-motivated professionals. Direct instruction offers structured guidance and immediate feedback, beneficial for foundational language acquisition and beginners in corporate communication.
Flipped classroom vs direct instruction Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com