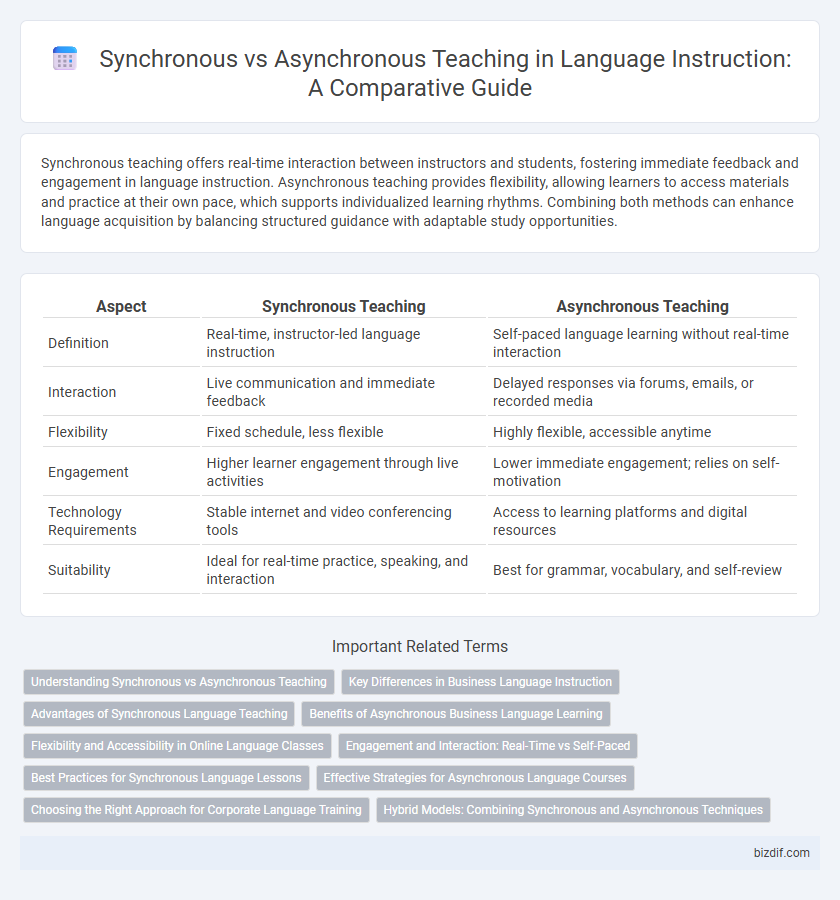
Synchronous teaching offers real-time interaction between instructors and students, fostering immediate feedback and engagement in language instruction. Asynchronous teaching provides flexibility, allowing learners to access materials and practice at their own pace, which supports individualized learning rhythms. Combining both methods can enhance language acquisition by balancing structured guidance with adaptable study opportunities.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Synchronous Teaching | Asynchronous Teaching |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Real-time, instructor-led language instruction | Self-paced language learning without real-time interaction |
| Interaction | Live communication and immediate feedback | Delayed responses via forums, emails, or recorded media |
| Flexibility | Fixed schedule, less flexible | Highly flexible, accessible anytime |
| Engagement | Higher learner engagement through live activities | Lower immediate engagement; relies on self-motivation |
| Technology Requirements | Stable internet and video conferencing tools | Access to learning platforms and digital resources |
| Suitability | Ideal for real-time practice, speaking, and interaction | Best for grammar, vocabulary, and self-review |
Understanding Synchronous vs Asynchronous Teaching
Synchronous teaching requires real-time interaction between instructors and students, utilizing tools like video conferencing and live chats to facilitate immediate feedback and engagement. Asynchronous teaching offers flexibility by allowing learners to access materials, lectures, and assignments on their own schedule through platforms such as learning management systems and recorded videos. Understanding the distinct advantages of synchronous methods for direct communication and asynchronous formats for accommodating diverse learning paces is crucial for optimizing instructional design.
Key Differences in Business Language Instruction
Synchronous teaching in business language instruction involves live, real-time interaction between instructors and learners, fostering immediate feedback and dynamic conversation practice essential for professional communication skills. Asynchronous teaching offers flexible, self-paced learning through recorded lectures and digital resources, allowing busy professionals to balance language study with work commitments efficiently. The choice between synchronous and asynchronous methods significantly impacts learner engagement, retention, and the development of practical business communication competencies.
Advantages of Synchronous Language Teaching
Synchronous language teaching offers real-time interaction, allowing immediate feedback and clarification that enhance learner comprehension and engagement. This method supports dynamic speaking and listening practice, crucial for language acquisition and fluency development. It also fosters a sense of community through live discussions, promoting motivation and accountability among students.
Benefits of Asynchronous Business Language Learning
Asynchronous business language learning offers unparalleled flexibility, allowing professionals to study at their own pace and revisit complex material as needed, which enhances comprehension and retention. It supports a diverse range of multimedia resources, including interactive exercises, video lessons, and real-world case studies, fostering deeper engagement and practical application. This method accommodates varying time zones and schedules, making it ideal for global teams and busy executives seeking efficient, self-directed skill development.
Flexibility and Accessibility in Online Language Classes
Synchronous teaching in online language classes offers real-time interaction, promoting immediate feedback and active participation but requires users to adhere to fixed schedules. Asynchronous teaching provides greater flexibility, allowing students to access materials and complete exercises at their own pace, accommodating diverse time zones and personal commitments. Combining both methods enhances accessibility, catering to various learning preferences and maximizing language acquisition opportunities.
Engagement and Interaction: Real-Time vs Self-Paced
Synchronous teaching fosters high engagement through real-time interaction, enabling immediate feedback and dynamic discussions that enhance learning motivation. Asynchronous teaching offers flexibility with self-paced learning, allowing students to reflect deeply and access materials anytime, though it may reduce spontaneous interaction. Balancing live participation and independent study optimizes learner engagement and accommodates diverse communication preferences.
Best Practices for Synchronous Language Lessons
Synchronous language lessons thrive on real-time interaction, fostering immediate feedback and natural conversational practice essential for language acquisition. Best practices include utilizing clear audio-visual tools, integrating breakout rooms for small group discussions, and employing interactive materials such as polls or quizzes to maintain student engagement. Scheduling consistent session times and encouraging active participation optimize learner motivation and language retention in synchronous environments.
Effective Strategies for Asynchronous Language Courses
Effective strategies for asynchronous language courses include utilizing multimedia resources such as videos, audio recordings, and interactive quizzes to enhance comprehension and engagement. Incorporating regular formative assessments and providing timely, personalized feedback supports learner progress and retention. Establishing clear guidelines, flexible pacing, and opportunities for peer interaction through discussion forums fosters a collaborative and autonomous learning environment.
Choosing the Right Approach for Corporate Language Training
Synchronous teaching in corporate language training offers real-time interaction, fostering immediate feedback and dynamic discussions that enhance employee engagement and language retention. Asynchronous teaching allows learners to access materials at their convenience, accommodating diverse schedules and enabling self-paced progress suitable for global teams. Selecting the right approach depends on aligning training goals with workforce availability, learning preferences, and the need for collaborative versus individual learning experiences.
Hybrid Models: Combining Synchronous and Asynchronous Techniques
Hybrid models in language instruction integrate synchronous teaching, offering real-time interaction, with asynchronous techniques that provide flexible, self-paced learning. This combination enhances student engagement by catering to diverse learning styles and schedules, while promoting deeper comprehension through varied instructional methods. Effective hybrid language programs leverage digital platforms to synchronize live sessions with accessible online resources, optimizing both collaboration and independent practice.
Synchronous teaching vs asynchronous teaching Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com