Effective weight management in pets involves tailored nutrition plans that promote healthy weight loss or maintenance, reducing obesity-related risks. Disease management requires specialized diets that address specific health conditions such as diabetes, kidney disease, or allergies to improve overall well-being and prevent complications. Collaborating with a veterinary nutritionist ensures customized feeding strategies that support both weight regulation and disease control for optimal pet health.
Table of Comparison
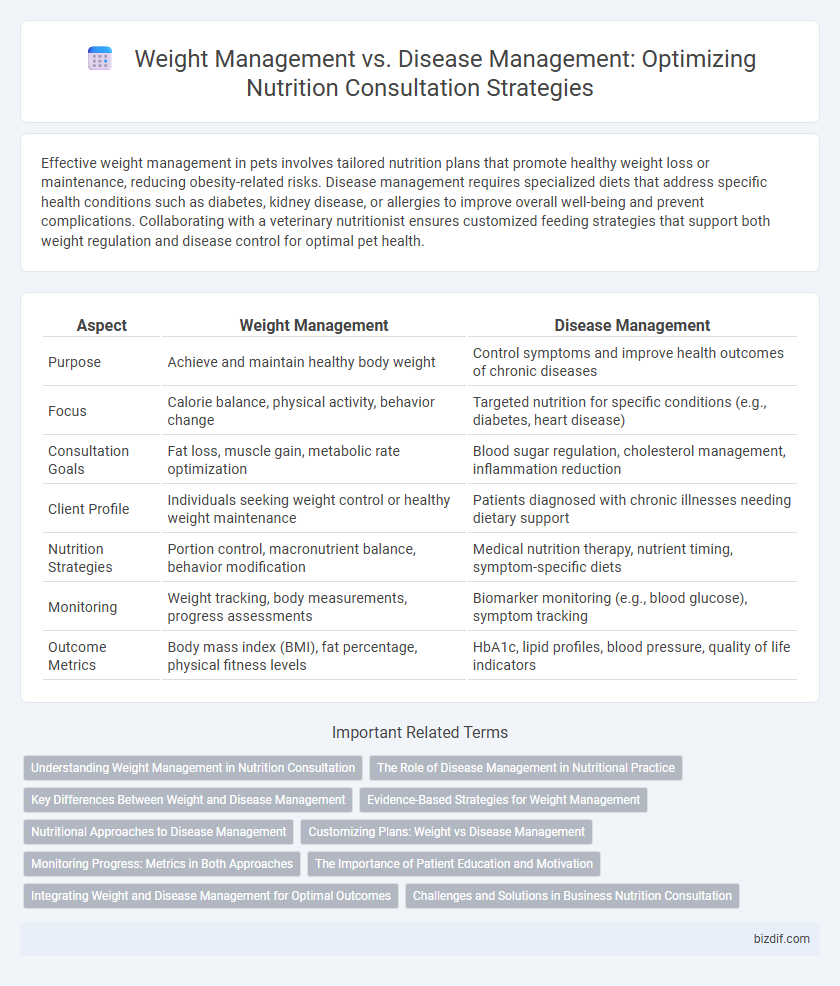
| Aspect | Weight Management | Disease Management |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Achieve and maintain healthy body weight | Control symptoms and improve health outcomes of chronic diseases |
| Focus | Calorie balance, physical activity, behavior change | Targeted nutrition for specific conditions (e.g., diabetes, heart disease) |
| Consultation Goals | Fat loss, muscle gain, metabolic rate optimization | Blood sugar regulation, cholesterol management, inflammation reduction |
| Client Profile | Individuals seeking weight control or healthy weight maintenance | Patients diagnosed with chronic illnesses needing dietary support |
| Nutrition Strategies | Portion control, macronutrient balance, behavior modification | Medical nutrition therapy, nutrient timing, symptom-specific diets |
| Monitoring | Weight tracking, body measurements, progress assessments | Biomarker monitoring (e.g., blood glucose), symptom tracking |
| Outcome Metrics | Body mass index (BMI), fat percentage, physical fitness levels | HbA1c, lipid profiles, blood pressure, quality of life indicators |
Understanding Weight Management in Nutrition Consultation
Weight management in nutrition consultation centers on balancing calorie intake with energy expenditure to achieve and maintain a healthy body weight. This approach includes personalized meal planning, behavior modification, and monitoring progress to prevent obesity-related complications. Effective weight management supports overall health by reducing the risk of chronic diseases such as diabetes, cardiovascular conditions, and metabolic syndrome.
The Role of Disease Management in Nutritional Practice
Disease management plays a critical role in nutritional practice by tailoring individualized dietary plans that address specific health conditions such as diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and chronic kidney disease. Effective nutritional intervention in disease management improves patient outcomes by controlling symptoms, preventing complications, and enhancing quality of life. Integrating evidence-based guidelines with patient-centered care ensures optimal management of both the disease and overall nutritional status.
Key Differences Between Weight and Disease Management
Weight management focuses on achieving and maintaining a healthy body weight primarily through calorie control, physical activity, and behavioral changes to prevent obesity-related conditions. Disease management targets specific chronic conditions such as diabetes, hypertension, or cardiovascular disease by tailoring nutrition plans to control symptoms, improve metabolic function, and reduce complications. While weight management emphasizes prevention and overall well-being, disease management requires individualized dietary interventions based on medical needs and clinical outcomes.
Evidence-Based Strategies for Weight Management
Evidence-based strategies for weight management emphasize personalized nutrition plans, behavioral therapy, and physical activity to achieve sustainable fat loss and improve metabolic health. Clinical studies support interventions such as calorie restriction, macronutrient composition adjustments, and meal timing to optimize energy balance and reduce obesity-related risks. Integrating these approaches with continuous monitoring and support enhances adherence and long-term success in weight management.
Nutritional Approaches to Disease Management
Nutritional approaches to disease management prioritize tailored dietary interventions to control symptoms and improve patient outcomes in conditions like diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and chronic kidney disease. Emphasis is placed on nutrient-dense foods, balanced macronutrient distribution, and restriction of harmful substances such as sodium, added sugars, and saturated fats. Unlike general weight management, these strategies target disease-specific metabolic pathways and inflammatory processes to support long-term health and reduce complication risks.
Customizing Plans: Weight vs Disease Management
Customizing nutrition plans for weight management prioritizes caloric balance, macronutrient ratios, and sustainable lifestyle habits to achieve targeted fat loss or muscle gain. In contrast, disease management requires tailored nutrient adjustments that address specific medical conditions, such as limiting sodium for hypertension or controlling carbohydrate intake for diabetes. Both approaches rely on individualized assessments and continuous monitoring to optimize health outcomes effectively.
Monitoring Progress: Metrics in Both Approaches
Monitoring progress in weight management primarily involves tracking body weight, body mass index (BMI), and body composition changes, such as fat percentage and muscle mass. In disease management, key metrics include blood glucose levels for diabetes, blood pressure for hypertension, and cholesterol profiles, along with anthropometric measurements. Both approaches benefit from regular assessments through digital health tools and wearable devices that provide continuous data for personalized nutrition adjustments.
The Importance of Patient Education and Motivation
Effective weight management and disease management rely heavily on comprehensive patient education and sustained motivation to achieve lasting health outcomes. Educating patients about balanced nutrition, portion control, and personalized dietary adjustments empowers them to make informed decisions, while motivation fosters adherence to lifestyle changes crucial for preventing chronic conditions like diabetes and cardiovascular diseases. Continuous support from nutrition consultants enhances patient engagement, resulting in improved metabolic markers and overall well-being.
Integrating Weight and Disease Management for Optimal Outcomes
Integrating weight management with disease management enhances overall health outcomes by addressing the root causes of chronic conditions such as diabetes, hypertension, and cardiovascular disease. Personalized nutrition consultations promote sustainable weight loss while simultaneously managing disease-specific dietary needs, improving metabolic function and reducing medication dependency. This holistic approach supports long-term wellness by balancing caloric intake, nutrient density, and physical activity tailored to individual health profiles.
Challenges and Solutions in Business Nutrition Consultation
Weight management in business nutrition consultation presents challenges such as client motivation variability and the need for personalized intervention plans that adapt to diverse lifestyles and metabolic responses. Disease management requires precise nutritional protocols addressing chronic conditions, demanding continuous monitoring and collaboration with healthcare providers to ensure compliance and effectiveness. Solutions include integrating digital health tools for real-time tracking, employing data-driven personalization, and fostering interdisciplinary teamwork to enhance client outcomes and business scalability.
Weight Management vs Disease Management Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com