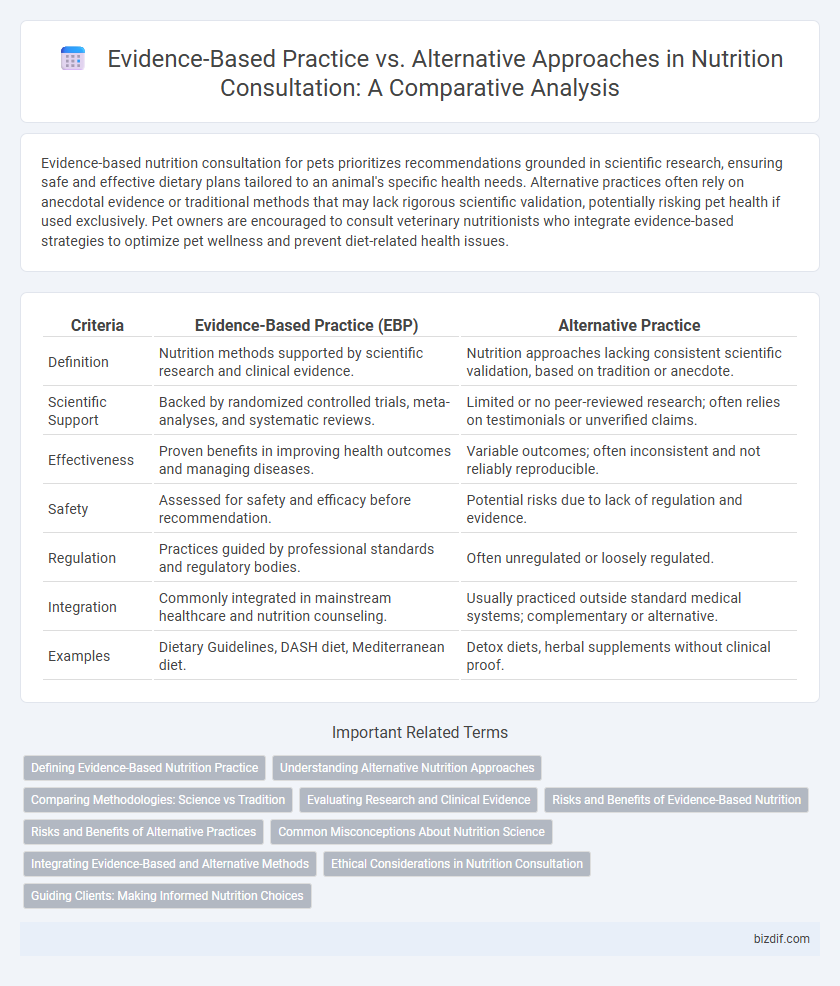
Evidence-based nutrition consultation for pets prioritizes recommendations grounded in scientific research, ensuring safe and effective dietary plans tailored to an animal's specific health needs. Alternative practices often rely on anecdotal evidence or traditional methods that may lack rigorous scientific validation, potentially risking pet health if used exclusively. Pet owners are encouraged to consult veterinary nutritionists who integrate evidence-based strategies to optimize pet wellness and prevent diet-related health issues.
Table of Comparison
| Criteria | Evidence-Based Practice (EBP) | Alternative Practice |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Nutrition methods supported by scientific research and clinical evidence. | Nutrition approaches lacking consistent scientific validation, based on tradition or anecdote. |
| Scientific Support | Backed by randomized controlled trials, meta-analyses, and systematic reviews. | Limited or no peer-reviewed research; often relies on testimonials or unverified claims. |
| Effectiveness | Proven benefits in improving health outcomes and managing diseases. | Variable outcomes; often inconsistent and not reliably reproducible. |
| Safety | Assessed for safety and efficacy before recommendation. | Potential risks due to lack of regulation and evidence. |
| Regulation | Practices guided by professional standards and regulatory bodies. | Often unregulated or loosely regulated. |
| Integration | Commonly integrated in mainstream healthcare and nutrition counseling. | Usually practiced outside standard medical systems; complementary or alternative. |
| Examples | Dietary Guidelines, DASH diet, Mediterranean diet. | Detox diets, herbal supplements without clinical proof. |
Defining Evidence-Based Nutrition Practice
Evidence-based nutrition practice relies on integrating the best available scientific research, clinical expertise, and patient values to guide dietary recommendations and interventions. This approach emphasizes the use of rigorously tested, peer-reviewed studies and meta-analyses to ensure safety and efficacy in nutritional counseling. Alternative practices often lack consistent empirical support, relying instead on anecdotal evidence or unproven theories, which may compromise outcome reliability in nutrition consultation.
Understanding Alternative Nutrition Approaches
Alternative nutrition approaches often lack rigorous scientific validation and rely on anecdotal evidence or traditional beliefs rather than randomized controlled trials. Nutrition consultation emphasizes understanding these practices' theoretical foundations and potential risks to provide balanced guidance. Evaluating the efficacy and safety of alternative methods ensures informed decision-making aligned with evidence-based standards.
Comparing Methodologies: Science vs Tradition
Evidence-based nutrition consultation employs rigorous scientific methodologies, including randomized controlled trials and systematic reviews, to ensure accuracy and reliability in dietary recommendations. Alternative practices often rely on traditional knowledge, anecdotal evidence, and holistic approaches that may lack empirical validation but emphasize personalized care. Comparing these methodologies highlights the contrast between data-driven interventions and culturally rooted practices in achieving optimal nutritional outcomes.
Evaluating Research and Clinical Evidence
Evaluating research and clinical evidence in nutrition consultation requires prioritizing evidence-based practices supported by rigorous scientific studies, randomized controlled trials, and meta-analyses to ensure safety and efficacy. Alternative practices often rely on anecdotal evidence, expert opinion, or preliminary data lacking robust clinical validation, making critical appraisal essential for distinguishing reliable interventions. Utilizing standardized tools and systematic reviews enhances the accuracy of translating research findings into practical nutritional recommendations.
Risks and Benefits of Evidence-Based Nutrition
Evidence-based nutrition utilizes scientifically validated data to optimize dietary recommendations, reducing risks such as nutrient deficiencies and misinformation compared to alternative practices. This approach enhances patient safety by relying on clinical trials and systematic reviews, ensuring interventions are effective and personalized. While alternative nutrition may offer novel insights, evidence-based nutrition remains the gold standard for balancing health benefits and minimizing potential harm.
Risks and Benefits of Alternative Practices
Alternative nutrition practices often lack rigorous scientific validation, increasing the risk of ineffective or harmful interventions such as nutrient imbalances or delayed treatment for serious conditions. Despite potential benefits like personalized approaches and holistic focus, these methods may lead to misinformation and unregulated supplement use. Evaluating alternative nutrition strategies requires cautious consideration of safety, efficacy, and integration with evidence-based protocols to minimize health risks.
Common Misconceptions About Nutrition Science
Evidence-based nutrition practice relies on rigorous scientific research, such as randomized controlled trials and systematic reviews, to develop dietary guidelines that optimize health outcomes. Common misconceptions in nutrition science include the belief that all natural or alternative diets are inherently safer or more effective, ignoring the lack of empirical support and potential risks associated with unproven methods. Understanding the distinction between evidence-based recommendations and alternative practices is essential for making informed decisions and avoiding misinformation in nutrition consultation.
Integrating Evidence-Based and Alternative Methods
Integrating evidence-based and alternative nutrition practices involves combining scientifically validated dietary guidelines with personalized, holistic approaches that respect individual preferences and cultural traditions. This synergy enhances patient outcomes by leveraging rigorous research alongside complementary therapies such as herbal supplementation and mindful eating. Nutrition professionals prioritize continuous evaluation of alternative methods through clinical trials and systematic reviews to ensure safety and efficacy within personalized nutrition plans.
Ethical Considerations in Nutrition Consultation
Ethical considerations in nutrition consultation require prioritizing evidence-based practice to ensure client safety, accuracy, and effectiveness of dietary recommendations. Nutrition professionals must critically evaluate alternative practices, recognizing potential risks, lack of scientific support, and the possibility of misinformation that could harm client health. Upholding informed consent and transparency fosters trust and respects client autonomy while reinforcing professional integrity and accountability.
Guiding Clients: Making Informed Nutrition Choices
Guiding clients in nutrition consultation requires emphasizing evidence-based practice, which relies on scientifically validated data from reputable sources like peer-reviewed journals and clinical guidelines to inform dietary recommendations. Alternative practices, often lacking rigorous scientific support, may present unproven benefits or risks, making client education about credible evidence essential for informed decision-making. Nutrition professionals should prioritize transparent communication about the effectiveness and safety of interventions to help clients choose nutrition strategies that optimize health outcomes.
Evidence-Based Practice vs Alternative Practice Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com