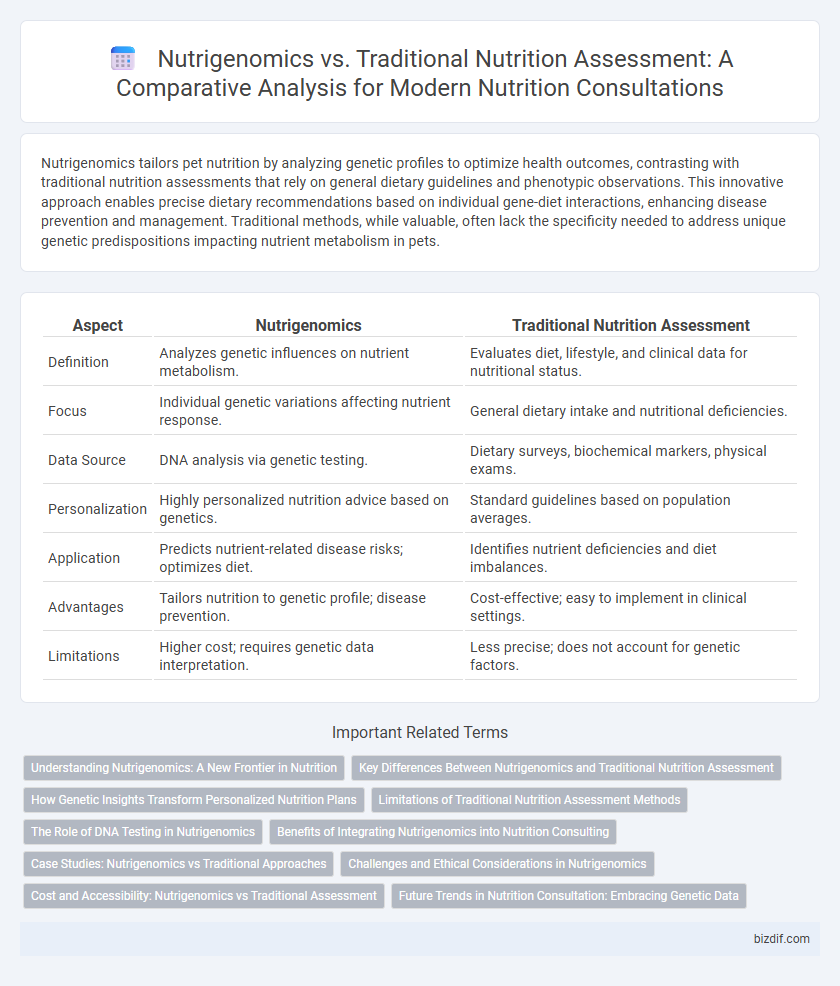
Nutrigenomics tailors pet nutrition by analyzing genetic profiles to optimize health outcomes, contrasting with traditional nutrition assessments that rely on general dietary guidelines and phenotypic observations. This innovative approach enables precise dietary recommendations based on individual gene-diet interactions, enhancing disease prevention and management. Traditional methods, while valuable, often lack the specificity needed to address unique genetic predispositions impacting nutrient metabolism in pets.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Nutrigenomics | Traditional Nutrition Assessment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Analyzes genetic influences on nutrient metabolism. | Evaluates diet, lifestyle, and clinical data for nutritional status. |
| Focus | Individual genetic variations affecting nutrient response. | General dietary intake and nutritional deficiencies. |
| Data Source | DNA analysis via genetic testing. | Dietary surveys, biochemical markers, physical exams. |
| Personalization | Highly personalized nutrition advice based on genetics. | Standard guidelines based on population averages. |
| Application | Predicts nutrient-related disease risks; optimizes diet. | Identifies nutrient deficiencies and diet imbalances. |
| Advantages | Tailors nutrition to genetic profile; disease prevention. | Cost-effective; easy to implement in clinical settings. |
| Limitations | Higher cost; requires genetic data interpretation. | Less precise; does not account for genetic factors. |
Understanding Nutrigenomics: A New Frontier in Nutrition
Nutrigenomics explores the relationship between an individual's genetic makeup and their nutritional response, offering personalized dietary recommendations based on DNA analysis. Unlike traditional nutrition assessments that rely on general dietary guidelines and phenotypic data, nutrigenomics enables targeted interventions by identifying gene-nutrient interactions affecting metabolism and disease risk. This innovative approach enhances precision in nutrition planning, optimizing health outcomes through customized nutrient intake tailored to genetic profiles.
Key Differences Between Nutrigenomics and Traditional Nutrition Assessment
Nutrigenomics analyzes individual genetic profiles to tailor dietary recommendations based on gene-diet interactions, while traditional nutrition assessment primarily relies on dietary intake, lifestyle, and biochemical data without genetic considerations. Nutrigenomics enables personalized nutrition strategies targeting metabolic pathways influenced by specific gene variants, contrasting with the general guidelines used in traditional assessments. This genetic-focused approach improves precision in managing nutrition-related health risks and optimizing dietary interventions.
How Genetic Insights Transform Personalized Nutrition Plans
Genetic insights enable nutrigenomics to tailor personalized nutrition plans by analyzing individual DNA variations that affect nutrient metabolism and dietary response. Unlike traditional nutrition assessments relying on generalized dietary guidelines and phenotypic data, nutrigenomics integrates genetic profiles to predict optimal nutrient intake and potential sensitivities. This precision approach enhances effectiveness in managing chronic diseases, optimizing health outcomes, and preventing nutrition-related disorders.
Limitations of Traditional Nutrition Assessment Methods
Traditional nutrition assessment methods often rely on generalized dietary guidelines and biochemical markers that fail to capture individual genetic variability affecting nutrient metabolism. These methods lack the ability to identify gene-nutrient interactions, limiting personalized dietary recommendations and potentially reducing efficacy in disease prevention and management. Consequently, traditional assessments may overlook critical genetic factors that influence nutrient absorption, utilization, and overall health outcomes.
The Role of DNA Testing in Nutrigenomics
DNA testing in nutrigenomics enables personalized nutrition plans based on an individual's genetic profile, optimizing nutrient intake and reducing disease risk more effectively than traditional nutrition assessments. Unlike conventional methods that rely on generalized dietary guidelines, nutrigenomics evaluates genetic variants affecting metabolism, nutrient absorption, and food sensitivities. This precision approach enhances dietary recommendations by integrating genotype-specific data, offering tailored strategies for improved health outcomes.
Benefits of Integrating Nutrigenomics into Nutrition Consulting
Integrating nutrigenomics into nutrition consulting enhances personalized dietary recommendations by analyzing individual genetic profiles to optimize nutrient intake and prevent diet-related diseases. This approach offers more precise intervention strategies compared to traditional nutrition assessments, which rely on generalized dietary guidelines and phenotypic data. Utilizing nutrigenomic data improves patient outcomes by tailoring nutrition plans to genetic predispositions affecting metabolism, nutrient absorption, and response to foods.
Case Studies: Nutrigenomics vs Traditional Approaches
Case studies comparing nutrigenomics and traditional nutrition assessment reveal that nutrigenomics offers personalized dietary recommendations based on genetic profiles, improving outcomes in managing conditions like obesity and diabetes. Traditional assessments rely on generalized dietary guidelines and biochemical markers, often resulting in less targeted interventions. Evidence from clinical trials shows nutrigenomics can enhance metabolic response and patient adherence by addressing individual genetic variations in nutrient metabolism.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations in Nutrigenomics
Nutrigenomics faces significant challenges including limited genetic data interpretation, the complexity of gene-diet interactions, and variability in individual responses, which complicate personalized nutrition plans. Ethical considerations involve privacy concerns, informed consent for genetic testing, and potential discrimination based on genetic information. Unlike traditional nutrition assessment, which relies on observable dietary habits and biomarkers, nutrigenomics demands careful management of sensitive genetic data to ensure confidentiality and equitable access.
Cost and Accessibility: Nutrigenomics vs Traditional Assessment
Nutrigenomics offers personalized dietary recommendations based on genetic information but often comes with higher costs and limited availability due to specialized testing requirements and technology. Traditional nutrition assessments rely on dietary surveys and physical measurements, making them more affordable and widely accessible in clinical and community settings. The choice between the two depends on budget constraints and the need for individualized versus general nutrition guidance.
Future Trends in Nutrition Consultation: Embracing Genetic Data
Future trends in nutrition consultation emphasize integrating nutrigenomics to tailor dietary recommendations based on individual genetic profiles, enhancing precision and effectiveness compared to traditional nutrition assessments relying on generalized dietary guidelines. Advances in genetic testing technologies enable real-time analysis of nutrient-gene interactions, allowing nutritionists to address personalized metabolic responses and optimize nutrient intake. This shift toward genomics-driven consultations promises improved outcomes in disease prevention and personalized health management by leveraging genetic data for customized nutrition strategies.
Nutrigenomics vs Traditional Nutrition Assessment Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com