Supplement recommendations often provide targeted nutrients that may be difficult to obtain through food alone, ensuring pets receive essential vitamins and minerals tailored to their specific health needs. Food-based interventions emphasize whole, balanced diets that support overall wellness and can address dietary deficiencies naturally while promoting better digestion and nutrient absorption. Combining both approaches can optimize a pet's nutritional status, enhancing health outcomes through complementary strategies.
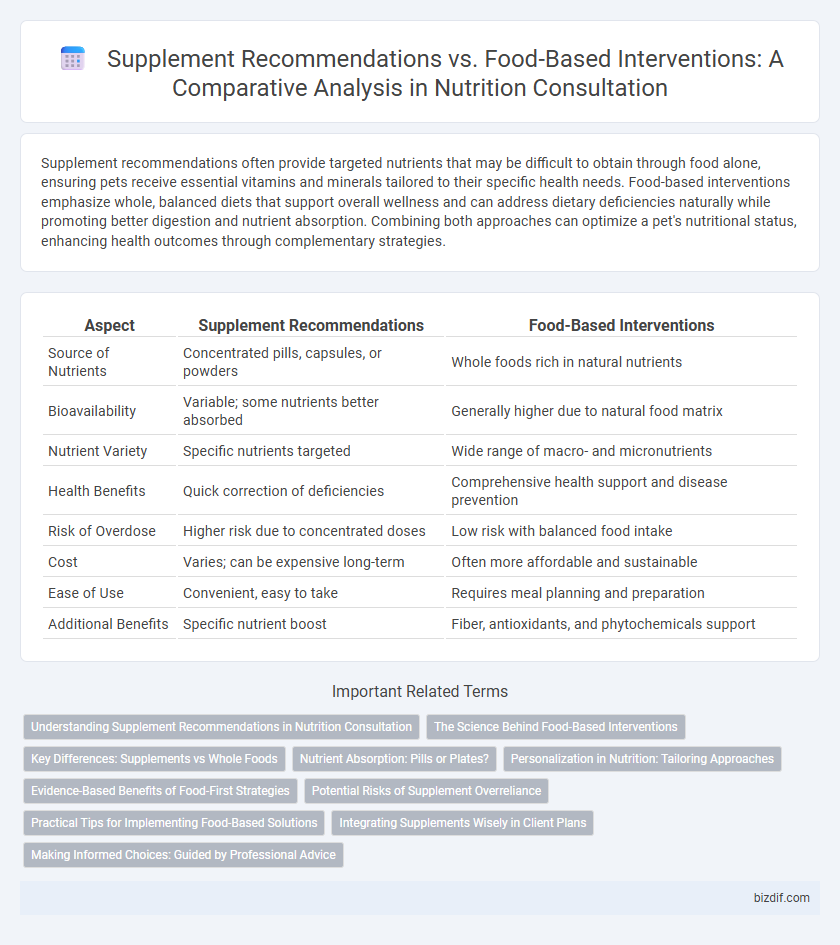
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Supplement Recommendations | Food-Based Interventions |
|---|---|---|
| Source of Nutrients | Concentrated pills, capsules, or powders | Whole foods rich in natural nutrients |
| Bioavailability | Variable; some nutrients better absorbed | Generally higher due to natural food matrix |
| Nutrient Variety | Specific nutrients targeted | Wide range of macro- and micronutrients |
| Health Benefits | Quick correction of deficiencies | Comprehensive health support and disease prevention |
| Risk of Overdose | Higher risk due to concentrated doses | Low risk with balanced food intake |
| Cost | Varies; can be expensive long-term | Often more affordable and sustainable |
| Ease of Use | Convenient, easy to take | Requires meal planning and preparation |
| Additional Benefits | Specific nutrient boost | Fiber, antioxidants, and phytochemicals support |
Understanding Supplement Recommendations in Nutrition Consultation
Understanding supplement recommendations in nutrition consultation involves evaluating individual dietary needs, health status, and potential nutrient deficiencies to tailor effective strategies. Registered dietitians assess factors like bioavailability, interactions, and dosage to ensure supplements complement food-based interventions without risking toxicity or imbalance. Emphasizing whole food sources remains fundamental, while supplements serve as targeted additions for addressing specific nutritional gaps or medical conditions.
The Science Behind Food-Based Interventions
Food-based interventions leverage the complex matrix of nutrients, phytochemicals, and fiber found naturally in whole foods, which work synergistically to enhance bioavailability and metabolic responses. Research demonstrates that nutrients consumed through food sources are more effectively absorbed and utilized by the body compared to isolated supplements, leading to improved health outcomes and reduced risk of chronic diseases. Clinical studies also highlight the role of diverse dietary patterns, such as the Mediterranean diet, in modulating inflammation and supporting gut microbiota balance, underpinning the scientific rationale for prioritizing food-based approaches in nutrition consultation.
Key Differences: Supplements vs Whole Foods
Supplements provide concentrated doses of specific nutrients, targeting deficiencies quickly but often lack the complex matrix of vitamins, minerals, fiber, and phytochemicals found in whole foods. Whole foods deliver a synergistic blend of nutrients that support overall health and promote better digestion, absorption, and long-term disease prevention. Nutrition consultation emphasizes individualized supplement recommendations when dietary intake is insufficient while encouraging whole food-based interventions for sustainable nutrient balance and enhanced metabolic health.
Nutrient Absorption: Pills or Plates?
Nutrient absorption varies significantly between supplement recommendations and food-based interventions, with whole foods providing synergistic compounds like fiber and phytochemicals that enhance bioavailability. Supplements, often isolated nutrients in pill form, may lack the natural cofactors needed for optimal absorption, sometimes leading to reduced efficacy. Emphasizing nutrient-rich foods ensures comprehensive nutrient uptake and supports overall digestive health more effectively than relying solely on supplements.
Personalization in Nutrition: Tailoring Approaches
Personalization in nutrition involves tailoring supplement recommendations and food-based interventions to an individual's unique genetic, metabolic, and lifestyle factors. Nutrigenomic testing and continuous dietary assessments enable precise adjustments, optimizing nutrient intake for health conditions and personal goals. Emphasizing personalized strategies enhances efficacy, minimizes risks, and supports sustainable dietary adherence.
Evidence-Based Benefits of Food-First Strategies
Food-based interventions provide a diverse array of nutrients, phytochemicals, and fiber that supplements often lack, fostering synergistic health benefits supported by extensive clinical research. Evidence indicates that whole foods improve nutrient bioavailability and reduce chronic disease risk more effectively than isolated supplements, particularly in cardiovascular health and metabolic regulation. Prioritizing a food-first strategy aligns with dietary guidelines and emphasizes sustainable, long-term wellness outcomes grounded in evidence-based nutrition science.
Potential Risks of Supplement Overreliance
Relying heavily on supplements instead of food-based interventions can lead to nutrient imbalances and toxicity, particularly with fat-soluble vitamins like A, D, E, and K. Supplements often lack the synergistic compounds found in whole foods that enhance nutrient absorption and overall health benefits. Excessive supplement intake may also mask underlying dietary deficiencies, delaying proper nutritional diagnosis and comprehensive dietary improvements.
Practical Tips for Implementing Food-Based Solutions
Emphasizing whole foods over supplements enhances nutrient bioavailability and supports overall health through synergistic effects. Practical tips include incorporating a variety of colorful fruits and vegetables to maximize vitamin and antioxidant intake, using herbs and spices for added micronutrients and flavor, and planning balanced meals rich in lean proteins, healthy fats, and complex carbohydrates. Encouraging clients to prepare meals at home fosters mindful eating habits and improves long-term adherence to nutrient-rich, food-based dietary patterns.
Integrating Supplements Wisely in Client Plans
Integrating supplements wisely in client nutrition plans involves assessing individual dietary gaps and health goals to prioritize food-based interventions while using supplements as targeted support. Emphasizing whole foods rich in essential nutrients ensures sustainable nutrient intake, with supplements serving to address specific deficiencies or therapeutic needs. This balanced approach enhances overall client outcomes by optimizing nutrient bioavailability and minimizing reliance on isolated nutrients alone.
Making Informed Choices: Guided by Professional Advice
Professional nutrition consultations emphasize making informed choices by evaluating supplement recommendations alongside food-based interventions to optimize health outcomes. Registered dietitians assess individual dietary needs, potential nutrient interactions, and bioavailability to tailor plans that prioritize natural food sources while considering supplements when necessary. Aligning supplementation with whole-food strategies ensures balanced nutrient intake, reduces risks of excess or deficiency, and supports sustainable wellness goals.
Supplement Recommendations vs Food-Based Interventions Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com