Supplement recommendations in pet nutrition provide targeted support for specific health concerns but should complement, not replace, a diet rich in whole foods. Whole food emphasis ensures pets receive balanced, natural nutrients that promote overall wellness and reduce the risk of deficiencies. Prioritizing whole foods while using supplements strategically optimizes pet health outcomes and supports long-term vitality.
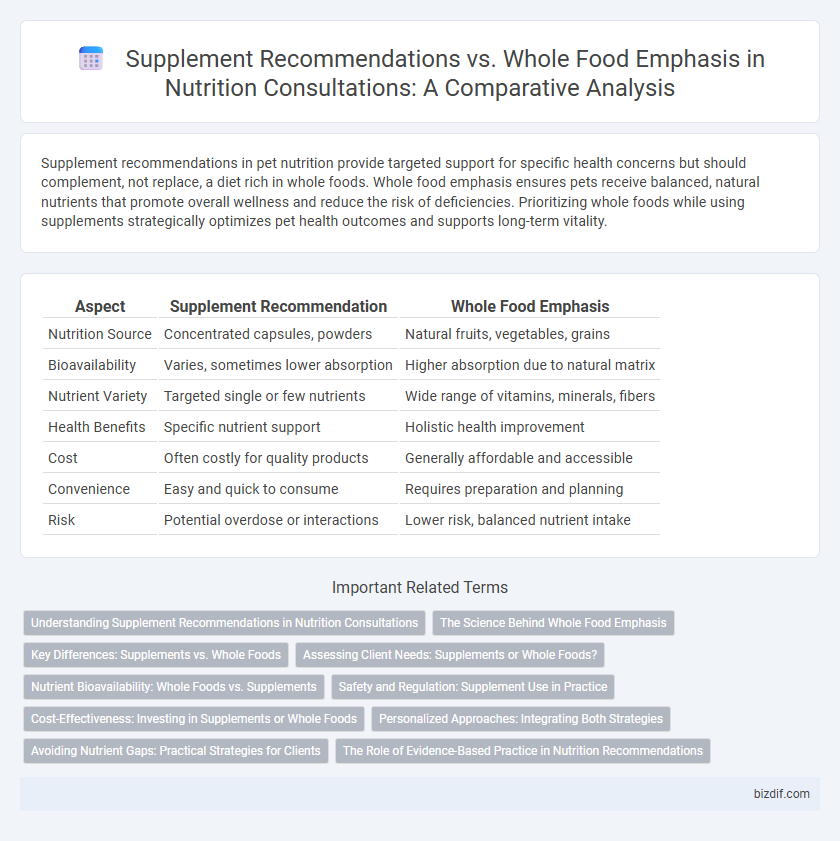
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Supplement Recommendation | Whole Food Emphasis |
|---|---|---|
| Nutrition Source | Concentrated capsules, powders | Natural fruits, vegetables, grains |
| Bioavailability | Varies, sometimes lower absorption | Higher absorption due to natural matrix |
| Nutrient Variety | Targeted single or few nutrients | Wide range of vitamins, minerals, fibers |
| Health Benefits | Specific nutrient support | Holistic health improvement |
| Cost | Often costly for quality products | Generally affordable and accessible |
| Convenience | Easy and quick to consume | Requires preparation and planning |
| Risk | Potential overdose or interactions | Lower risk, balanced nutrient intake |
Understanding Supplement Recommendations in Nutrition Consultations
Nutrition consultations emphasize personalized supplement recommendations based on individual dietary gaps, health conditions, and lifestyle factors to optimize nutrient intake effectively. Whole food emphasis remains critical for providing a broad spectrum of vitamins, minerals, fiber, and phytochemicals that supplements alone cannot replicate. Understanding supplement recommendations helps balance targeted nutrient support with the benefits of nutrient-rich whole foods, promoting overall wellness and preventing nutrient imbalances.
The Science Behind Whole Food Emphasis
Whole food emphasis in nutrition consultation is backed by robust scientific evidence highlighting improved bioavailability and synergistic nutrient interactions that supplements often lack. Studies show that vitamins and minerals consumed through whole foods are absorbed more efficiently, supporting better metabolic functions and reducing risks of chronic diseases. Clinical trials consistently demonstrate that whole food-based diets promote long-term health outcomes more effectively than isolated supplement use.
Key Differences: Supplements vs. Whole Foods
Nutritional consultations emphasize the key differences between supplement recommendations and whole food consumption, highlighting that whole foods provide a complex matrix of nutrients, fiber, and bioactive compounds essential for optimal health. Supplements offer concentrated doses of specific nutrients, useful for addressing targeted deficiencies or health conditions but lack the synergistic benefits found in whole foods. Effective nutrition plans prioritize whole food intake while strategically incorporating supplements when necessary to enhance overall nutrient status.
Assessing Client Needs: Supplements or Whole Foods?
Assessing client needs for nutrition consultation involves evaluating dietary gaps, health goals, and lifestyle factors to determine whether supplements or whole foods offer optimal nutrient delivery. Whole foods provide complex matrices of vitamins, minerals, fiber, and phytochemicals that support overall health and nutrient bioavailability, while supplements address specific deficiencies or targeted outcomes more efficiently. Personalized plans prioritize nutrient interactions, absorption rates, and client adherence to maximize the effectiveness of either supplements or whole food-based strategies.
Nutrient Bioavailability: Whole Foods vs. Supplements
Whole foods provide nutrients in complex matrices that enhance bioavailability, ensuring better absorption and utilization by the body compared to isolated supplements. Supplements often contain nutrients in isolated or synthetic forms, which can lead to lower bioavailability and reduced efficacy. Emphasizing whole foods in nutrition consultation supports optimal nutrient intake and metabolic synergy, promoting overall health more effectively than relying solely on supplements.
Safety and Regulation: Supplement Use in Practice
Supplement recommendations in nutrition consultations prioritize safety by adhering to regulations set by agencies such as the FDA and EFSA, ensuring product quality and accurate labeling. Whole food emphasis provides a natural matrix of nutrients and bioactive compounds, reducing risks associated with isolated supplement overconsumption. Practitioners carefully evaluate individual health status, potential interactions, and dosage to optimize efficacy while minimizing adverse effects.
Cost-Effectiveness: Investing in Supplements or Whole Foods
Choosing whole foods over supplements often provides better cost-effectiveness due to nutrient density and bioavailability, leading to improved long-term health outcomes. Supplements can address specific nutritional deficiencies but may incur higher recurring expenses without the additional benefits of fiber and phytochemicals found in whole foods. Prioritizing a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains maximizes nutrient absorption while minimizing overall dietary costs.
Personalized Approaches: Integrating Both Strategies
Personalized nutrition consultations integrate supplement recommendations with whole food emphasis to tailor strategies based on individual health needs and lifestyle factors. Utilizing clinical data and dietary assessments, practitioners can identify nutrient gaps, optimizing bioavailability through targeted supplements while encouraging nutrient-dense whole foods for balanced intake. This hybrid approach maximizes efficacy by addressing specific deficiencies and supporting overall dietary quality.
Avoiding Nutrient Gaps: Practical Strategies for Clients
Emphasizing whole foods ensures clients receive a diverse array of essential vitamins, minerals, and phytonutrients that supplements alone may not provide. Practical strategies include creating balanced meal plans rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins to naturally fill nutrient gaps. When supplementation is necessary, personalized recommendations based on dietary assessments and blood work optimize nutrient absorption and overall health outcomes.
The Role of Evidence-Based Practice in Nutrition Recommendations
Evidence-based practice prioritizes whole food consumption over supplement reliance by emphasizing nutrient bioavailability and synergistic effects inherent in natural foods. Clinical studies consistently show improved health outcomes when nutrition recommendations focus on balanced diets rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains rather than isolated supplement use. Integrating current scientific research ensures personalized and effective nutrition strategies that optimize metabolic function and reduce chronic disease risk.
Supplement Recommendation vs Whole Food Emphasis Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com