Effective document retention balances the necessity of keeping important records for legal, financial, and personal reference with the need to securely dispose of outdated or irrelevant documents to prevent clutter and protect sensitive information. Establishing clear guidelines for document retention periods helps professional organizers ensure clients maintain only essential paperwork, reducing stress and enhancing organization. Proper document destruction methods, such as shredding, safeguard against identity theft and maintain client confidentiality in a professional organizing environment.
Table of Comparison
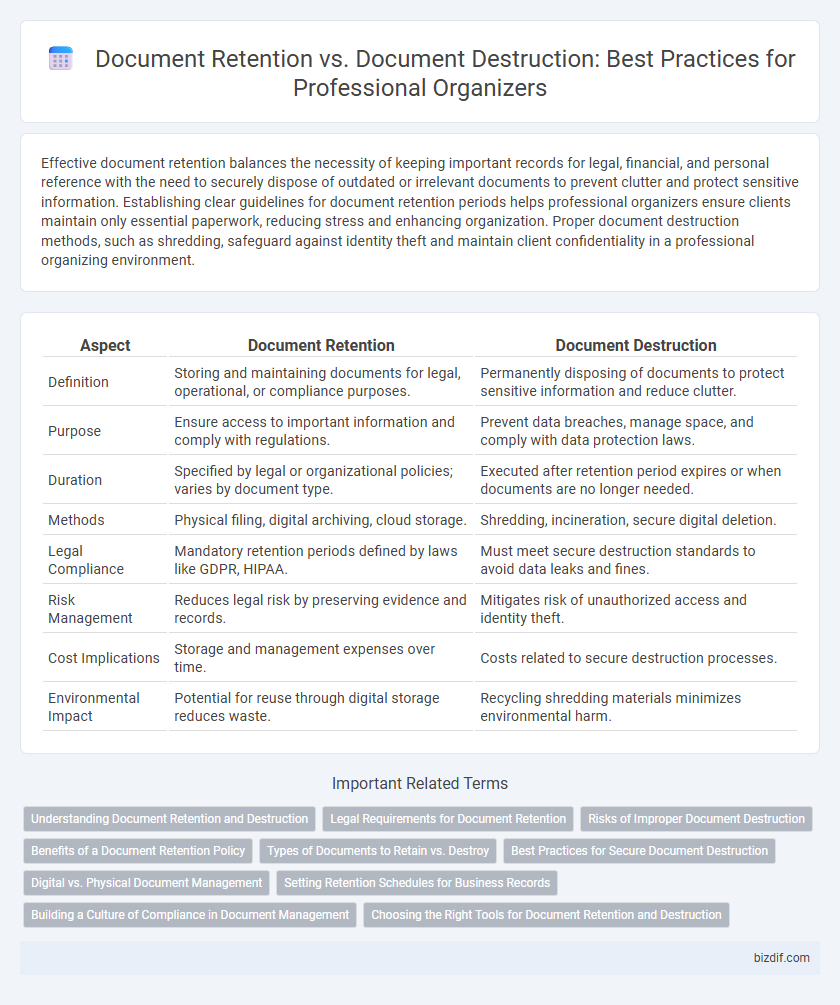
| Aspect | Document Retention | Document Destruction |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Storing and maintaining documents for legal, operational, or compliance purposes. | Permanently disposing of documents to protect sensitive information and reduce clutter. |
| Purpose | Ensure access to important information and comply with regulations. | Prevent data breaches, manage space, and comply with data protection laws. |
| Duration | Specified by legal or organizational policies; varies by document type. | Executed after retention period expires or when documents are no longer needed. |
| Methods | Physical filing, digital archiving, cloud storage. | Shredding, incineration, secure digital deletion. |
| Legal Compliance | Mandatory retention periods defined by laws like GDPR, HIPAA. | Must meet secure destruction standards to avoid data leaks and fines. |
| Risk Management | Reduces legal risk by preserving evidence and records. | Mitigates risk of unauthorized access and identity theft. |
| Cost Implications | Storage and management expenses over time. | Costs related to secure destruction processes. |
| Environmental Impact | Potential for reuse through digital storage reduces waste. | Recycling shredding materials minimizes environmental harm. |
Understanding Document Retention and Destruction
Document retention involves systematically keeping important records for legal, financial, and operational purposes, ensuring compliance with regulations such as GDPR or HIPAA. Document destruction refers to the secure disposal of papers and digital files once their retention period expires, preventing identity theft and data breaches. Understanding the balance between these processes is crucial for effective professional organizing, minimizing clutter while safeguarding sensitive information.
Legal Requirements for Document Retention
Legal requirements for document retention vary by industry and jurisdiction, often mandating that businesses keep financial records, tax documents, and contracts for a specific number of years, typically between 3 to 7 years. Compliance with laws such as the Sarbanes-Oxley Act or the IRS guidelines ensures that documents are preserved to support audits, legal claims, and regulatory reviews. Failure to adhere to these retention policies risks penalties, legal disputes, and loss of critical evidence, making professional organization systems essential for timely document destruction and secure storage.
Risks of Improper Document Destruction
Improper document destruction poses significant risks including identity theft, legal penalties, and loss of sensitive information, undermining both personal and business security. Failure to comply with federally mandated retention schedules can lead to costly audits and litigation. Secure shredding and data destruction protocols must be rigorously followed to mitigate these hazards and ensure regulatory compliance.
Benefits of a Document Retention Policy
A well-defined document retention policy ensures compliance with legal requirements and reduces the risk of data breaches by securely managing the lifespan of sensitive records. It enhances office efficiency by minimizing clutter and streamlining access to essential documents, saving valuable time for professionals. Implementing retention guidelines lowers storage costs and supports environmental sustainability through timely, responsible document destruction.
Types of Documents to Retain vs. Destroy
Critical documents such as tax records, legal contracts, and financial statements should be retained for specified periods mandated by law or business needs, often ranging from three to seven years. Personal records like utility bills, expired warranties, or junk mail can generally be destroyed promptly to reduce clutter and enhance organization. Proper assessment of document types ensures compliance, security, and efficient space management in professional organizing.
Best Practices for Secure Document Destruction
Secure document destruction ensures the protection of sensitive information by following best practices such as shredding paper documents using cross-cut shredders and employing professional services that guarantee compliance with data privacy regulations like HIPAA and GDPR. Digital files should be permanently deleted using software that offers multiple overwrites or encryption-based erasure to prevent data recovery. Regular audits and clear retention schedules help organizations balance document retention requirements with secure disposal, minimizing the risk of data breaches and identity theft.
Digital vs. Physical Document Management
Effective professional organizing of documents requires clear differentiation between document retention and document destruction practices in both digital and physical formats. Digital document management benefits from automated retention schedules, secure encryption, and compliance with data privacy regulations, whereas physical documents demand proper labeling, secure storage, and timely shredding to reduce clutter and mitigate information risks. Implementing centralized digital systems alongside organized physical filing ensures optimal accessibility while adhering to legal and operational retention guidelines.
Setting Retention Schedules for Business Records
Setting retention schedules for business records ensures compliance with legal requirements and optimizes office efficiency by specifying how long documents must be kept before destruction. Properly defined schedules reduce the risk of retaining unnecessary paperwork while protecting critical records for audits, tax purposes, and litigation. Implementing systematic document retention policies streamlines access to essential data and supports sustainable records management practices.
Building a Culture of Compliance in Document Management
Building a culture of compliance in document management requires clear policies on document retention versus document destruction that align with legal regulations and industry standards. Implementing systematic audits and employee training ensures that sensitive information is securely stored while obsolete records are properly destroyed to reduce risk. Consistent adherence to these practices enhances organizational accountability and protects against data breaches and regulatory penalties.
Choosing the Right Tools for Document Retention and Destruction
Selecting appropriate tools for document retention and destruction is crucial to maintaining an organized and compliant workspace. Digital solutions like secure cloud storage and document management software facilitate efficient categorization and long-term retention, while shredders and certified destruction services ensure sensitive information is irreversibly disposed of. Utilizing these specialized tools aligns with regulatory requirements such as GDPR and HIPAA, minimizing legal risks and enhancing data security.
document retention vs document destruction Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com