Onscreen proofreading allows for quick edits and easy access to digital tools, making it efficient for spotting errors in text and formatting. Hardcopy proofreading offers a tactile experience that can help catch mistakes overlooked on screen, especially typographical and layout issues. Combining both methods enhances accuracy by leveraging the strengths of each approach in identifying subtle errors.
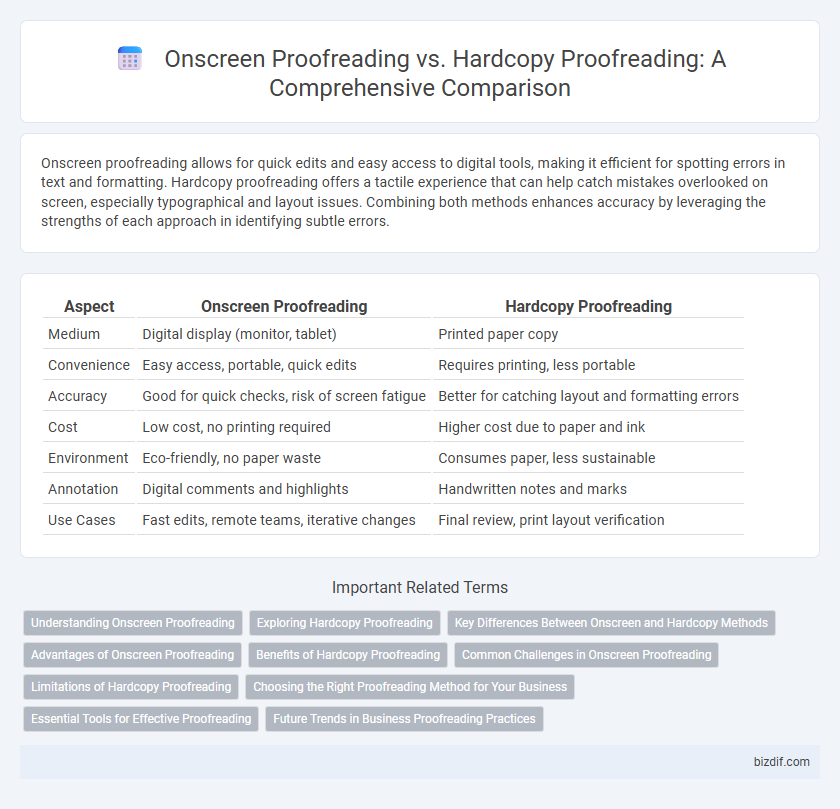
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Onscreen Proofreading | Hardcopy Proofreading |
|---|---|---|
| Medium | Digital display (monitor, tablet) | Printed paper copy |
| Convenience | Easy access, portable, quick edits | Requires printing, less portable |
| Accuracy | Good for quick checks, risk of screen fatigue | Better for catching layout and formatting errors |
| Cost | Low cost, no printing required | Higher cost due to paper and ink |
| Environment | Eco-friendly, no paper waste | Consumes paper, less sustainable |
| Annotation | Digital comments and highlights | Handwritten notes and marks |
| Use Cases | Fast edits, remote teams, iterative changes | Final review, print layout verification |
Understanding Onscreen Proofreading
Onscreen proofreading involves reviewing and editing digital text using specialized software or PDF viewers, offering real-time corrections and easy access to multiple document versions. This method enhances efficiency by allowing immediate annotation, highlighting, and comment insertion without the need for physical copies. Onscreen proofreading supports collaborative workflows and reduces paper waste, making it ideal for remote teams and fast-paced publishing environments.
Exploring Hardcopy Proofreading
Hardcopy proofreading involves reviewing a printed version of a document, allowing proofreaders to catch errors that might be overlooked on screens due to display limitations such as glare or scrolling. This method enhances accuracy by enabling easy annotation, margin notes, and the use of colored pens to highlight mistakes, which improves error detection in grammar, punctuation, and formatting. Despite digital advancements, hardcopy proofreading remains essential in publishing and legal industries where precision and physical document validation are critical.
Key Differences Between Onscreen and Hardcopy Methods
Onscreen proofreading involves reviewing content digitally on a screen, enabling quick edits with tools like track changes, while hardcopy proofreading requires marking physical paper copies, which can ease spotting layout or formatting errors. Onscreen methods enhance efficiency through features like zoom and search but may cause eye strain, whereas hardcopy proofreading provides a tactile experience that helps identify issues missed onscreen but can be time-consuming. Key differences lie in speed, error detection focus, and reviewer comfort, impacting the choice depending on project needs.
Advantages of Onscreen Proofreading
Onscreen proofreading offers significant advantages such as faster editing through digital tools, immediate access to search and replace functions, and the ability to zoom in for detailed inspection of text and images. It enhances collaboration by enabling multiple users to review and annotate simultaneously in real-time, reducing turnaround times. The environmental benefit of onscreen proofreading eliminates paper waste, making it a cost-effective and sustainable choice for editors and writers.
Benefits of Hardcopy Proofreading
Hardcopy proofreading offers tactile engagement with the text, enabling easier detection of errors like formatting inconsistencies, typographical mistakes, and punctuation issues that may be overlooked on screen. The physical format reduces eye strain and allows for natural annotation methods, improving accuracy in identifying and correcting mistakes. This method provides a reliable way to catch errors in print layout, color accuracy, and overall design that onscreen proofreading might miss.
Common Challenges in Onscreen Proofreading
Onscreen proofreading often presents challenges such as eye strain, limited ability to detect formatting errors, and distractions from multiple digital tools or notifications. The screen's resolution and glare can obscure subtle typos or inconsistencies that are easier to spot on hardcopy proofs. Moreover, the lack of physical interaction with text reduces tactile engagement, making it harder to catch nuanced errors like punctuation mistakes or line breaks.
Limitations of Hardcopy Proofreading
Hardcopy proofreading faces limitations such as difficulty in tracking changes and managing multiple revisions, often leading to inefficiencies in the editing process. Physical copies can be prone to damage, loss, and environmental waste, making them less sustainable than digital alternatives. Furthermore, hardcopy proofreading lacks the interactive capabilities of onscreen tools, such as real-time collaboration and automated error detection.
Choosing the Right Proofreading Method for Your Business
Selecting the appropriate proofreading method hinges on your business needs, budget, and project scale. Onscreen proofreading offers speed and easy tracking with digital tools, ideal for large-volume edits and collaborative environments. Hardcopy proofreading provides tactile accuracy for detailed design reviews and is preferred when layout and color fidelity are crucial.
Essential Tools for Effective Proofreading
Effective onscreen proofreading relies on essential digital tools such as advanced text editors with track changes, spell checkers, and annotation software, enabling quick identification and correction of errors. Hardcopy proofreading necessitates high-quality printed materials, red pens or markers for clear annotations, and good lighting to ensure accurate visual inspection of text. Both methods benefit from using style guides and checklists to maintain consistency and thoroughness in error detection.
Future Trends in Business Proofreading Practices
Onscreen proofreading is rapidly gaining traction in business due to advancements in digital annotation tools and AI-powered error detection, enabling faster turnaround and real-time collaboration. Hardcopy proofreading remains relevant for detailed tactile review, especially in high-stakes documents, but its use is expected to decline as digital workflows become more integrated and efficient. Emerging trends indicate a hybrid approach leveraging augmented reality (AR) and cloud-based platforms will shape the future of business proofreading practices.
Onscreen Proofreading vs Hardcopy Proofreading Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com