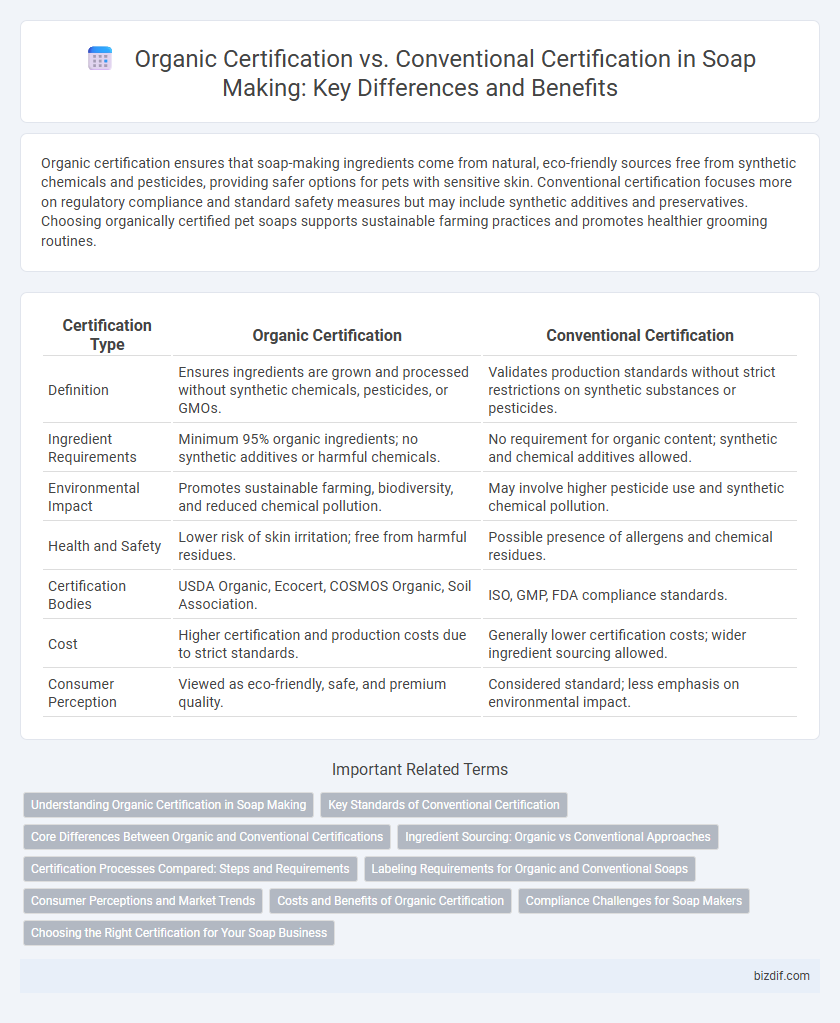
Organic certification ensures that soap-making ingredients come from natural, eco-friendly sources free from synthetic chemicals and pesticides, providing safer options for pets with sensitive skin. Conventional certification focuses more on regulatory compliance and standard safety measures but may include synthetic additives and preservatives. Choosing organically certified pet soaps supports sustainable farming practices and promotes healthier grooming routines.
Table of Comparison
| Certification Type | Organic Certification | Conventional Certification |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Ensures ingredients are grown and processed without synthetic chemicals, pesticides, or GMOs. | Validates production standards without strict restrictions on synthetic substances or pesticides. |
| Ingredient Requirements | Minimum 95% organic ingredients; no synthetic additives or harmful chemicals. | No requirement for organic content; synthetic and chemical additives allowed. |
| Environmental Impact | Promotes sustainable farming, biodiversity, and reduced chemical pollution. | May involve higher pesticide use and synthetic chemical pollution. |
| Health and Safety | Lower risk of skin irritation; free from harmful residues. | Possible presence of allergens and chemical residues. |
| Certification Bodies | USDA Organic, Ecocert, COSMOS Organic, Soil Association. | ISO, GMP, FDA compliance standards. |
| Cost | Higher certification and production costs due to strict standards. | Generally lower certification costs; wider ingredient sourcing allowed. |
| Consumer Perception | Viewed as eco-friendly, safe, and premium quality. | Considered standard; less emphasis on environmental impact. |
Understanding Organic Certification in Soap Making
Organic certification in soap making ensures ingredients comply with strict agricultural and processing standards set by organizations like USDA or COSMOS, emphasizing natural, chemical-free sources. This certification verifies the use of organically grown oils, herbs, and botanicals, free from synthetic pesticides and fertilizers, promoting environmentally sustainable practices. Certified organic soaps typically provide consumers with transparency, higher product quality, and adherence to rigorous health and safety guidelines compared to conventional certification.
Key Standards of Conventional Certification
Conventional certification in soap making primarily adheres to standards set by regulatory bodies such as the FDA and the EPA, ensuring product safety, proper labeling, and compliance with synthetic ingredient usage guidelines. Key standards include restrictions on toxic substances, mandatory stability testing, and adherence to good manufacturing practices (GMP) to guarantee product consistency and consumer safety. Unlike organic certification, conventional certification allows the use of synthetic detergents and preservatives while maintaining strict hygiene and quality control protocols.
Core Differences Between Organic and Conventional Certifications
Organic certification in soap making mandates the use of natural ingredients sourced from certified organic farms, ensuring products are free from synthetic pesticides, fertilizers, and harmful chemicals. Conventional certification allows for synthetic additives, chemical preservatives, and non-organic raw materials, focusing more on safety standards rather than ingredient source purity. The core difference lies in ingredient origin and processing standards, where organic certification prioritizes environmental sustainability and natural integrity, while conventional certification mainly ensures compliance with general safety and quality regulations.
Ingredient Sourcing: Organic vs Conventional Approaches
Organic certification requires sourcing ingredients from farms that avoid synthetic pesticides, fertilizers, and genetically modified organisms, ensuring purity and environmental sustainability in soap making. Conventional certification permits the use of synthetic chemicals and genetically modified ingredients, focusing on cost-efficiency and broader availability. Organic ingredient sourcing guarantees a higher standard for natural integrity, while conventional sourcing prioritizes scalability and affordability.
Certification Processes Compared: Steps and Requirements
Organic certification for soap making involves rigorous evaluation of ingredient sourcing, ensuring all components are derived from certified organic farms without synthetic chemicals or GMOs, alongside detailed documentation of production methods and regular on-site inspections. Conventional certification focuses primarily on compliance with safety and quality standards, requiring product testing and adherence to industry regulations but allows the use of synthetic additives and pesticides. Both certification processes demand thorough recordkeeping and third-party audits, but organic certification emphasizes sustainability and environmental impact throughout each step.
Labeling Requirements for Organic and Conventional Soaps
Organic certification for soaps mandates strict labeling requirements, including the percentage of organic ingredients used, certification logos, and clear disclosure of non-organic components. Conventional soap labeling generally requires compliance with basic ingredient listing and safety standards but lacks the detailed organic content transparency. These distinctions ensure consumers can make informed choices based on rigorous organic standards versus standard regulatory compliance.
Consumer Perceptions and Market Trends
Organic certification in soap making signals rigorous standards for natural ingredients and sustainable practices, appealing to eco-conscious consumers. Conventional certification often prioritizes safety and regulatory compliance, attracting buyers focused on affordability and accessibility. Market trends reveal a growing consumer preference for organically certified soaps, driven by increased awareness of environmental impact and health concerns.
Costs and Benefits of Organic Certification
Organic certification in soap making typically involves higher upfront costs due to rigorous standards for sourcing natural ingredients and compliance with organic farming practices. These costs are offset by premium pricing potential, increased consumer trust, and access to eco-conscious markets valuing sustainability and chemical-free products. Conventional certification demands less investment but may limit market differentiation and appeal to health-conscious buyers seeking organic guarantees.
Compliance Challenges for Soap Makers
Organic certification for soap makers demands strict adherence to natural ingredient sourcing, absence of synthetic chemicals, and rigorous documentation, posing compliance challenges compared to conventional certification which allows broader ingredient use. Navigating complex USDA Organic standards requires detailed record-keeping and supply chain transparency, often increasing production costs and time-intensive audits. Conventional certification processes focus on safety and quality but present fewer hurdles in ingredient restrictions, making compliance more straightforward for soap makers.
Choosing the Right Certification for Your Soap Business
Choosing the right certification for your soap business depends on market demand, target customers, and compliance costs. Organic certification verifies the use of natural, sustainably sourced ingredients free from synthetic chemicals, appealing to health-conscious consumers and premium markets. Conventional certification ensures adherence to general safety and quality standards but allows synthetic additives, often resulting in lower certification fees and broader market access.
Organic Certification vs Conventional Certification Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com