Certified translation involves a professional translator attesting that the translation is accurate and complete, often required for official purposes but without legal authorization by a government entity. Sworn translation, also known as a notarized or official translation, is performed by a translator authorized by a governmental body, ensuring the document's legal validity in judicial and administrative processes. Understanding the distinction between certified and sworn translations is essential for selecting the appropriate service based on the document's intended use.
Table of Comparison
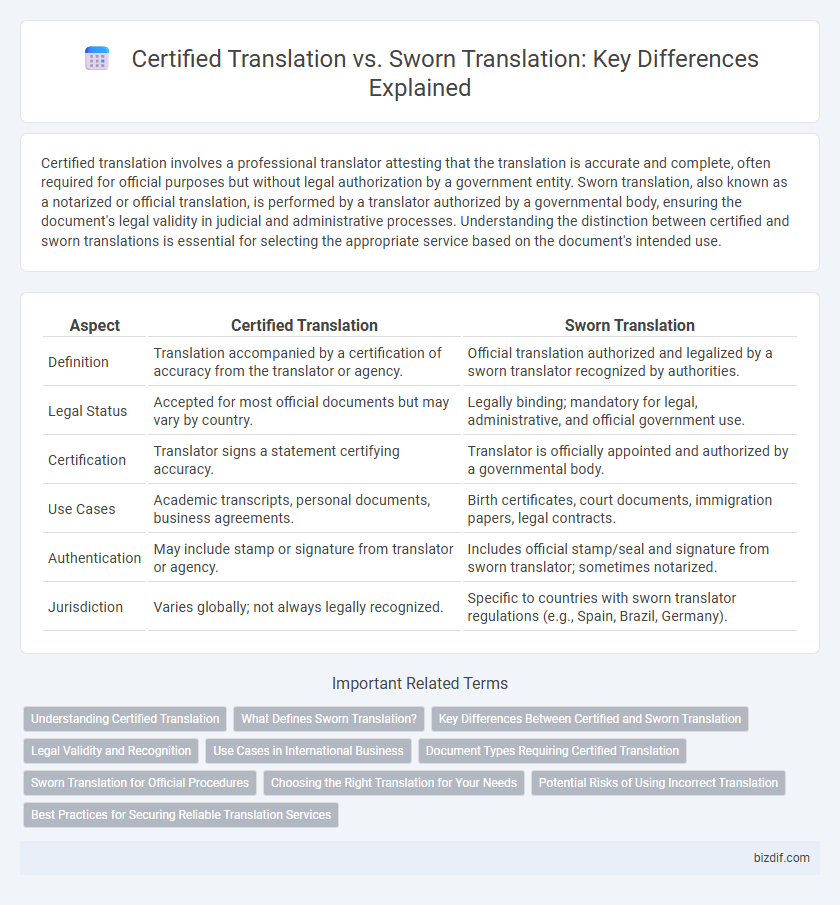
| Aspect | Certified Translation | Sworn Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Translation accompanied by a certification of accuracy from the translator or agency. | Official translation authorized and legalized by a sworn translator recognized by authorities. |
| Legal Status | Accepted for most official documents but may vary by country. | Legally binding; mandatory for legal, administrative, and official government use. |
| Certification | Translator signs a statement certifying accuracy. | Translator is officially appointed and authorized by a governmental body. |
| Use Cases | Academic transcripts, personal documents, business agreements. | Birth certificates, court documents, immigration papers, legal contracts. |
| Authentication | May include stamp or signature from translator or agency. | Includes official stamp/seal and signature from sworn translator; sometimes notarized. |
| Jurisdiction | Varies globally; not always legally recognized. | Specific to countries with sworn translator regulations (e.g., Spain, Brazil, Germany). |
Understanding Certified Translation
Certified translation involves a translator attesting that the translation is a true and accurate representation of the original document, often accompanied by a signed statement or certificate of authenticity. This type of translation is widely accepted for legal, academic, and official purposes in many countries, providing validation without requiring the translator to take an official oath. Certified translations differ from sworn translations, which typically require the translator to be officially authorized or sworn in by a government authority to guarantee the translation's legal binding status.
What Defines Sworn Translation?
Sworn translation is defined by its legal validity, where a certified translator, often authorized by a government or judicial body, takes an oath to provide accurate and faithful translations of official documents. This type of translation carries a sworn statement, making it legally binding for use in courts, government agencies, and official records. Unlike certified translation, which confirms accuracy without formal legal endorsement, sworn translation ensures that the translated document holds official recognition and authenticity.
Key Differences Between Certified and Sworn Translation
Certified translation involves a professional translator attesting to the accuracy and completeness of the document, usually accompanied by a signed statement or certificate. Sworn translation, also known as notarized translation, is performed by a translator authorized by a legal authority or court, who officially guarantees the translation's authenticity and legal validity. Key differences include the level of legal recognition, with sworn translations often required for official government or legal use, while certified translations are generally accepted for administrative or academic purposes.
Legal Validity and Recognition
Certified translation is officially recognized for general legal purposes and usually includes a translator's declaration of accuracy, whereas sworn translation carries legal authority granted by government-appointed translators, making it mandatory for official documents such as court submissions and notarized papers. The legal validity of sworn translations is higher in jurisdictions requiring an oath-bound translator, ensuring acceptance by governmental bodies without the need for further authentication. Certified translations are suitable for administrative use, but sworn translations guarantee formal recognition in legal proceedings and official certifications.
Use Cases in International Business
Certified translation ensures document accuracy for legal, immigration, and business contracts requiring official validation, often accepted by courts and government agencies. Sworn translation, performed by authorized translators who legally attest to the translation's authenticity, is essential in international business for notarized documents like trade agreements, patents, and financial statements. Both translation types facilitate cross-border communication, but sworn translations carry higher legal weight in regulatory compliance and dispute resolution.
Document Types Requiring Certified Translation
Certified translation is typically required for official documents such as birth certificates, marriage certificates, academic transcripts, and legal contracts to ensure accuracy and acceptance by government agencies or institutions. Sworn translation, on the other hand, is mandatory for legal documents that must be officially recognized in a foreign jurisdiction, including court documents, notarized papers, and immigration files. Certified translations guarantee that the translation is true and accurate, while sworn translations carry legal validity conferred by a sworn translator's signature and seal.
Sworn Translation for Official Procedures
Sworn translation is a legally recognized process where certified translators, authorized by government bodies, provide official translations accepted by courts, government agencies, and public institutions. This type of translation includes a signed declaration or stamp guaranteeing authenticity, essential for birth certificates, legal contracts, immigration papers, and academic documents. Certified translation, while accurate and performed by professional translators, may lack the official endorsement required for legal and administrative procedures, making sworn translation indispensable for official documentation.
Choosing the Right Translation for Your Needs
Certified translation requires a professional translator to attest that the translation is accurate and complete, often needed for official documents such as academic transcripts or immigration papers. Sworn translation is a specialized form performed by authorized translators who are legally recognized by a government body to produce translations that hold legal validity in courts and administrative procedures. Choosing the right translation depends on the specific requirements of the receiving institution or legal system, where certified translation serves general official use and sworn translation is essential for legally binding documents.
Potential Risks of Using Incorrect Translation
Using incorrect translation in certified or sworn documents can lead to significant legal complications, including contract disputes, fines, or invalidation of official paperwork. Incorrect translations may result in misunderstandings that affect immigration status, court rulings, or financial transactions, causing delays and financial losses. Ensuring accuracy through qualified translators mitigates risks associated with misinterpretation and non-compliance with regulatory standards.
Best Practices for Securing Reliable Translation Services
Certified translation requires a professional translator to attest that the document is an accurate and complete translation of the original, often accompanied by a certificate of accuracy. Sworn translation involves a legally authorized translator, sworn before a judicial authority, who produces translations with official validity in legal and administrative matters. To secure reliable translation services, verify the translator's certification or sworn status, review client testimonials, and confirm adherence to industry standards and confidentiality protocols.
Certified Translation vs Sworn Translation Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com