Interpretation involves converting spoken language in real-time, capturing tone and context to ensure accurate communication during live interactions. Translation deals with written texts, requiring precise rendering of meaning, style, and cultural nuances from one language to another. Both skills are essential in multilingual settings, but interpretation emphasizes immediacy while translation allows for careful revision.
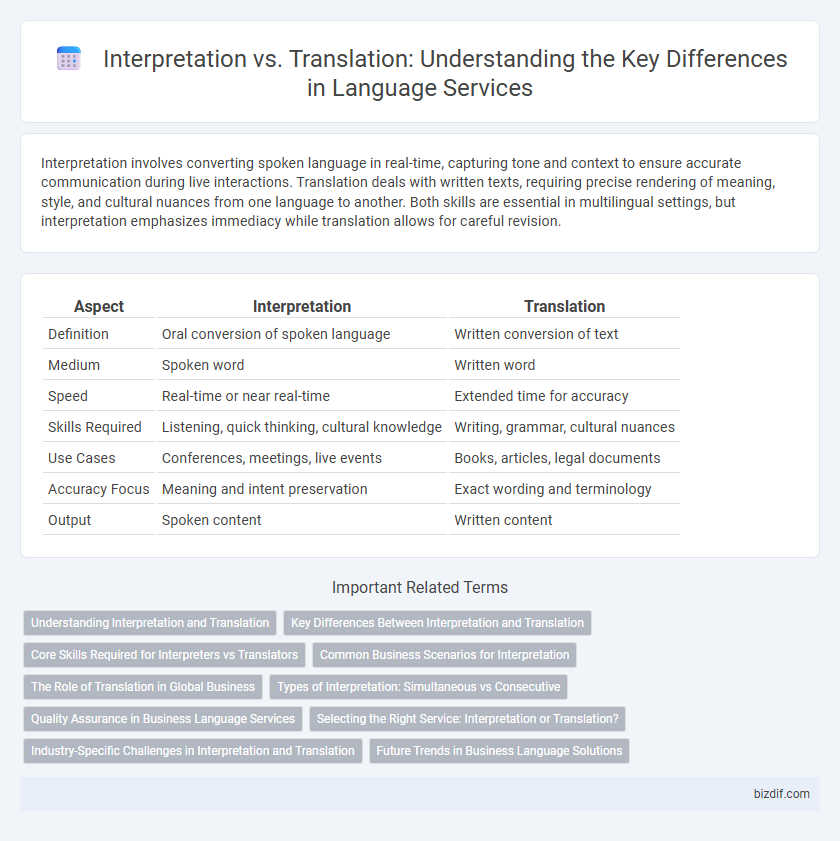
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Interpretation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Oral conversion of spoken language | Written conversion of text |
| Medium | Spoken word | Written word |
| Speed | Real-time or near real-time | Extended time for accuracy |
| Skills Required | Listening, quick thinking, cultural knowledge | Writing, grammar, cultural nuances |
| Use Cases | Conferences, meetings, live events | Books, articles, legal documents |
| Accuracy Focus | Meaning and intent preservation | Exact wording and terminology |
| Output | Spoken content | Written content |
Understanding Interpretation and Translation
Interpretation involves the oral conveyance of spoken language in real-time, requiring instant comprehension and expression of ideas between speakers. Translation refers to the process of converting written text from one language to another, emphasizing accuracy and context preservation. Both skills demand deep linguistic knowledge and cultural awareness but differ fundamentally in medium, immediacy, and cognitive approach.
Key Differences Between Interpretation and Translation
Interpretation involves orally conveying spoken language in real-time, while translation deals with converting written text from one language to another. Interpretation requires immediate comprehension and verbal delivery, making it essential in live settings like conferences or meetings. Translation allows for more time to ensure accuracy and involves understanding context, grammar, and cultural nuances in written documents.
Core Skills Required for Interpreters vs Translators
Interpreters require advanced listening, quick decision-making, and excellent oral communication skills to convey spoken language accurately in real-time. Translators need strong reading comprehension, writing expertise, and cultural knowledge to produce precise written texts. Both professions demand language proficiency, but interpreters excel in immediacy and verbal clarity, while translators focus on accuracy and nuance in writing.
Common Business Scenarios for Interpretation
Interpretation is essential in business meetings, conferences, and negotiations where real-time communication is critical, enabling participants to understand each other despite language barriers. Common business scenarios for interpretation include international sales presentations, legal depositions, and diplomatic discussions, where immediate and accurate oral communication ensures effective collaboration. Unlike translation, which deals with written text, interpretation demands quick thinking and fluency to convey meaning instantaneously.
The Role of Translation in Global Business
Translation in global business enables precise communication across diverse languages, ensuring accurate transfer of written content such as contracts, marketing materials, and technical documents. Interpretation facilitates real-time spoken communication, but translation provides a permanent, reviewed record essential for legal compliance and strategic planning. Effective translation enhances cross-border partnerships by maintaining cultural nuances and technical accuracy, driving international growth and minimizing costly misunderstandings.
Types of Interpretation: Simultaneous vs Consecutive
Simultaneous interpretation involves rendering the speaker's message in real-time, often used in conferences and international meetings to ensure immediate communication across languages. Consecutive interpretation requires the interpreter to wait for the speaker to pause before translating, which suits legal settings, medical consultations, and business negotiations where accuracy and detail are critical. Both types demand specialized skills, with simultaneous interpretation relying on rapid processing and advanced equipment, while consecutive interpretation emphasizes note-taking and memory retention.
Quality Assurance in Business Language Services
Quality assurance in business language services distinguishes interpretation from translation by emphasizing accuracy, cultural nuance, and context fidelity. Translation undergoes rigorous proofreading, terminology consistency checks, and software-assisted quality controls, ensuring precise written communication. Interpretation requires real-time accuracy, speaker intent comprehension, and ethical standards adherence to maintain message integrity during live interactions.
Selecting the Right Service: Interpretation or Translation?
Selecting the right language service depends on the communication context: interpretation is ideal for real-time spoken exchanges such as conferences, meetings, or medical consultations, while translation is suited for converting written documents like legal contracts, manuals, or websites. Interpreters require strong listening and verbal skills to convey tone and intent instantly, whereas translators focus on accuracy and cultural nuance in writing. Understanding these differences ensures effective communication tailored to the audience's needs.
Industry-Specific Challenges in Interpretation and Translation
Interpretation and translation face distinct industry-specific challenges, with interpretation requiring real-time language processing and cultural nuance adaptation in sectors like healthcare and legal services. Translation demands precise terminology management and consistency, particularly in technical fields such as engineering, pharmaceuticals, and finance. Both disciplines must address confidentiality, accuracy, and context sensitivity to meet professional standards and client expectations.
Future Trends in Business Language Solutions
Future trends in business language solutions emphasize increased integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning for real-time interpretation, enhancing accuracy and cultural nuance. Cloud-based platforms and hybrid models combining human expertise with automated translation tools are driving cost-efficiency and scalability. Emphasis on multilingual communication in global markets accelerates demand for seamless interpretation alongside traditional translation services.
Interpretation vs Translation Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com