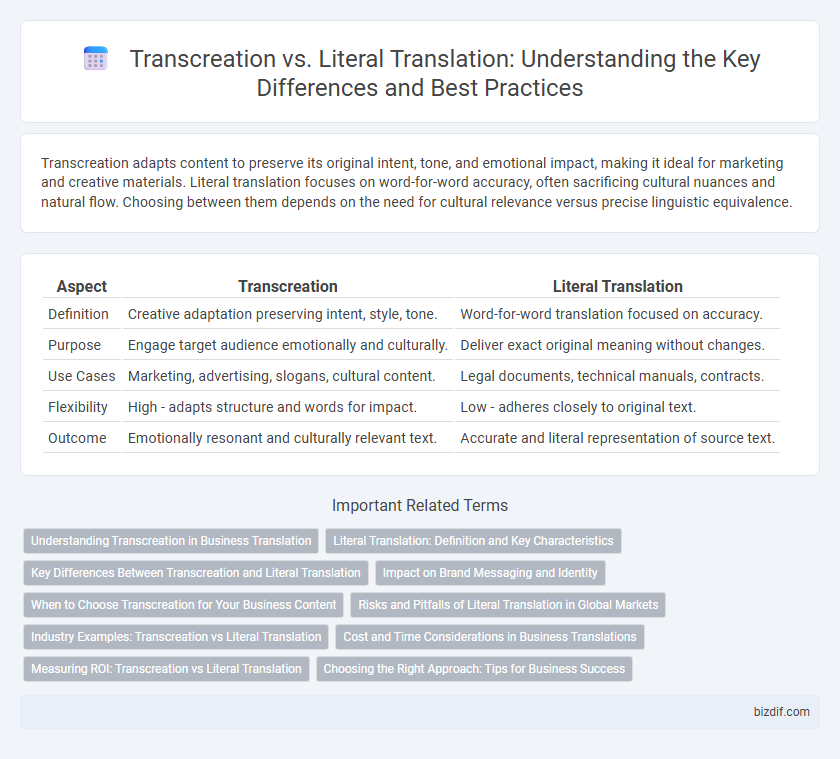
Transcreation adapts content to preserve its original intent, tone, and emotional impact, making it ideal for marketing and creative materials. Literal translation focuses on word-for-word accuracy, often sacrificing cultural nuances and natural flow. Choosing between them depends on the need for cultural relevance versus precise linguistic equivalence.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Transcreation | Literal Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Creative adaptation preserving intent, style, tone. | Word-for-word translation focused on accuracy. |
| Purpose | Engage target audience emotionally and culturally. | Deliver exact original meaning without changes. |
| Use Cases | Marketing, advertising, slogans, cultural content. | Legal documents, technical manuals, contracts. |
| Flexibility | High - adapts structure and words for impact. | Low - adheres closely to original text. |
| Outcome | Emotionally resonant and culturally relevant text. | Accurate and literal representation of source text. |
Understanding Transcreation in Business Translation
Transcreation in business translation involves adapting marketing content to resonate culturally and emotionally with the target audience while preserving the original message's intent. Unlike literal translation that focuses on word-for-word accuracy, transcreation requires creative reinterpretation to align with local market trends and consumer behavior. This approach enhances brand consistency and effectiveness across diverse global markets by prioritizing cultural relevance and audience engagement.
Literal Translation: Definition and Key Characteristics
Literal translation involves converting text word-for-word from the source language to the target language, preserving the original syntax and vocabulary as closely as possible. This method prioritizes semantic accuracy and linguistic fidelity, often at the expense of natural flow and cultural relevance. Literal translation is commonly used in technical documents, legal texts, and scientific materials where precise meaning and terminology are critical.
Key Differences Between Transcreation and Literal Translation
Transcreation adapts content to evoke the same emotions and cultural relevance in the target language, while literal translation focuses on word-for-word accuracy without cultural adaptation. Transcreation involves creative rewriting to maintain the original message's intent, tone, and style, essential for marketing and advertising content. Literal translation suits technical or legal documents where precise wording is critical, but it may miss nuances and cultural subtleties present in transcreated texts.
Impact on Brand Messaging and Identity
Transcreation enhances brand messaging by adapting content to resonate emotionally with the target audience, preserving the brand's voice and cultural relevance. Literal translation often risks diluting the brand identity due to a lack of contextual and cultural adaptation, resulting in messages that may feel disconnected or awkward. Effective transcreation strengthens brand loyalty and engagement by ensuring consistent, impactful communication across diverse markets.
When to Choose Transcreation for Your Business Content
Choose transcreation for your business content when conveying brand voice, cultural nuances, and emotional impact is crucial to engage target audiences effectively. This approach works best for marketing materials, advertising campaigns, and slogans that require adaptation beyond literal word-for-word translation. Prioritizing transcreation ensures messaging resonates authentically across different languages, enhancing customer connection and driving conversion rates.
Risks and Pitfalls of Literal Translation in Global Markets
Literal translation poses significant risks in global markets by failing to capture cultural nuances, leading to misinterpretations and brand misalignment. It often results in awkward phrasing or errors that diminish message clarity and reduce consumer trust. Transcreation mitigates these pitfalls by adapting content to resonate authentically within target cultures, enhancing engagement and market effectiveness.
Industry Examples: Transcreation vs Literal Translation
In advertising, transcreation is essential for brands like Coca-Cola, where emotional resonance and cultural relevance are prioritized over direct word-for-word translation. Literal translation works well in technical manuals or legal documents, ensuring precise and unambiguous communication. Companies in the gaming and entertainment industries rely heavily on transcreation to adapt humor, idioms, and cultural nuances that cannot be conveyed through literal translation.
Cost and Time Considerations in Business Translations
Transcreation typically demands higher costs and longer turnaround times than literal translation due to its creative adaptation and cultural tailoring requirements. Businesses investing in transcreation ensure messages resonate locally, enhancing brand impact despite increased expenses and extended deadlines. Literal translation offers faster, more affordable solutions but risks losing nuanced meaning and emotional connection essential for effective marketing.
Measuring ROI: Transcreation vs Literal Translation
Measuring ROI in transcreation versus literal translation involves comparing the effectiveness of culturally adapted content against direct translation in engaging target audiences and driving conversions. Transcreation often yields higher ROI by enhancing brand relevance and emotional connection, which increases customer engagement and loyalty. Literal translation may reduce upfront costs but risks lower ROI due to potential miscommunication and less impactful messaging in diverse markets.
Choosing the Right Approach: Tips for Business Success
Transcreation adapts content to resonate culturally and emotionally with target audiences, making it ideal for marketing and branding materials where emotional impact drives engagement. Literal translation prioritizes accuracy and is best suited for technical documents and legal texts requiring precise information conveyance. Businesses should assess project goals, audience expectations, and content type to choose between transcreation and literal translation, ensuring effective communication and maximizing market success.
Transcreation vs Literal Translation Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com