Post-editing involves refining machine-translated text to enhance accuracy and fluency, ensuring the final output meets linguistic standards. Pre-translation prepares source content by segmenting, cleaning, and aligning text to improve initial machine translation quality and reduce errors. Both techniques optimize translation workflows but target different phases of the process for maximum efficiency.
Table of Comparison
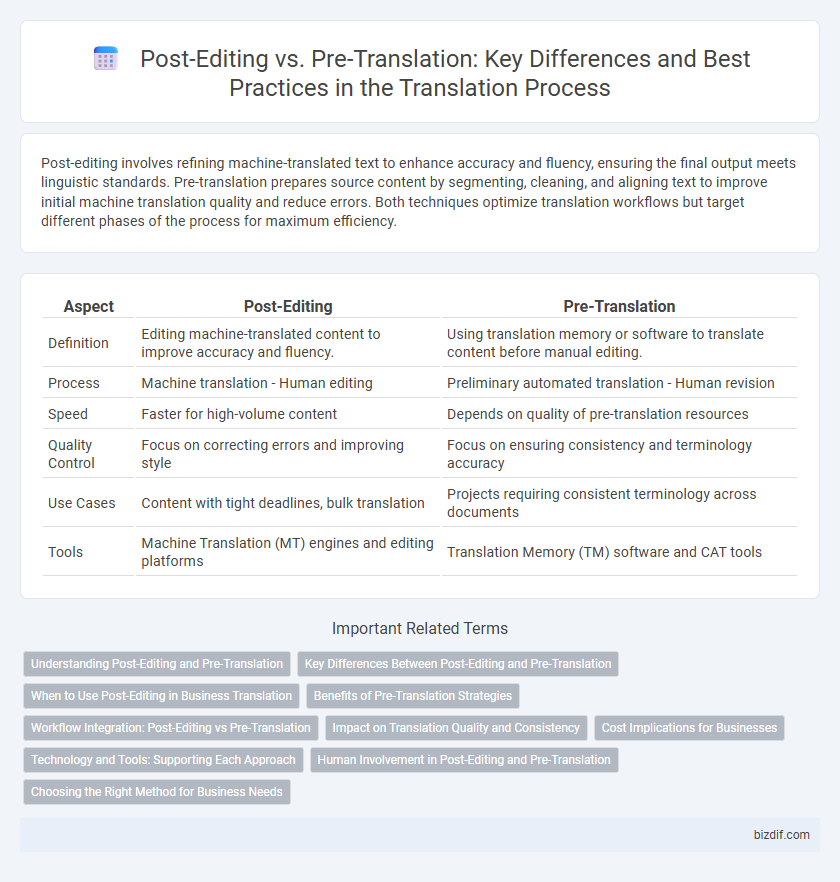
| Aspect | Post-Editing | Pre-Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Editing machine-translated content to improve accuracy and fluency. | Using translation memory or software to translate content before manual editing. |
| Process | Machine translation - Human editing | Preliminary automated translation - Human revision |
| Speed | Faster for high-volume content | Depends on quality of pre-translation resources |
| Quality Control | Focus on correcting errors and improving style | Focus on ensuring consistency and terminology accuracy |
| Use Cases | Content with tight deadlines, bulk translation | Projects requiring consistent terminology across documents |
| Tools | Machine Translation (MT) engines and editing platforms | Translation Memory (TM) software and CAT tools |
Understanding Post-Editing and Pre-Translation
Post-editing involves refining machine-translated content to improve accuracy, fluency, and context relevance, ensuring the final text meets quality standards. Pre-translation utilizes translation memory and glossaries to prepare source content, enhancing consistency and reducing translation time by leveraging previously translated segments. Both approaches optimize the translation workflow, with post-editing addressing machine output and pre-translation focusing on efficient content reuse.
Key Differences Between Post-Editing and Pre-Translation
Post-editing involves refining machine-translated content to meet quality standards, emphasizing human correction after initial automated output. Pre-translation utilizes translation memories or glossaries to convert source text prior to editing, focusing on improving consistency and efficiency from the start. The key differences lie in timing, workflow integration, and the balance between machine assistance and human intervention in the translation process.
When to Use Post-Editing in Business Translation
Post-editing is ideal for business translation when speed and cost-efficiency are prioritized, particularly for large volumes of content such as product descriptions, user manuals, and marketing materials. It leverages machine translation to generate initial drafts that human linguists then refine, ensuring both accuracy and cultural relevance. This method is especially effective when the source text is moderately complex and consistent, enabling faster turnaround without compromising quality.
Benefits of Pre-Translation Strategies
Pre-translation strategies enhance translation efficiency by leveraging machine translation outputs or bilingual glossaries to produce consistent and accurate initial drafts. These methods reduce human workload and turnaround time while maintaining terminology uniformity across large projects. Implementing pre-translation improves cost-effectiveness and accelerates project delivery without compromising quality.
Workflow Integration: Post-Editing vs Pre-Translation
Post-editing involves refining machine-translated content to enhance accuracy and fluency, seamlessly integrating into existing translation workflows by allowing human editors to improve initial output. Pre-translation utilizes translation memories or glossaries to automatically convert segments before human revision, accelerating the workflow while maintaining consistency with previous content. Effective workflow integration balances post-editing's quality control and pre-translation's efficiency to optimize translation project turnaround times and resource allocation.
Impact on Translation Quality and Consistency
Post-editing enhances translation quality by allowing human translators to refine machine-generated drafts, ensuring accurate terminology and natural phrasing while maintaining context relevance. Pre-translation leverages existing translation memories to improve consistency across large volumes of text, reducing variability in phraseology and terminology usage. Both methods significantly impact the overall quality and consistency of translations, with post-editing focusing on correctness and nuance, and pre-translation emphasizing uniformity and efficiency.
Cost Implications for Businesses
Post-editing machine translation often reduces initial costs by speeding up project turnaround and limiting reliance on human translators, making it a cost-effective option for businesses with large volumes of content. Pre-translation involves preparing source texts through terminology optimization and content simplification, which can increase upfront expenses but improve translation quality and reduce costly revisions later. Balancing post-editing and pre-translation strategies allows businesses to optimize translation budgets while maintaining accuracy and consistency.
Technology and Tools: Supporting Each Approach
Post-editing relies heavily on advanced machine translation engines combined with intuitive editing platforms that enable translators to refine automated outputs efficiently. Pre-translation utilizes translation memory (TM) systems and terminology management tools to preload and align consistent segments before the actual translation process begins. Both approaches leverage cloud-based platforms and AI-powered quality assurance tools to enhance accuracy, speed, and overall translation workflow.
Human Involvement in Post-Editing and Pre-Translation
Post-editing relies heavily on human involvement where translators review and correct machine-generated translations to enhance accuracy and contextual relevance. Pre-translation involves applying translation memories or glossaries before translation, minimizing human input initially but requiring expert intervention for final quality assurance. The degree of human engagement in post-editing is critical to achieving high-quality localization compared to the automated preparation in pre-translation processes.
Choosing the Right Method for Business Needs
Post-editing involves refining machine-translated content to enhance accuracy and fluency, making it ideal for businesses prioritizing speed and cost-efficiency. Pre-translation applies translation memories and glossaries upfront, ensuring consistency and terminology accuracy crucial for industries like legal or medical sectors. Selecting between post-editing and pre-translation depends on project complexity, quality requirements, and budget constraints, aligning linguistic precision with operational goals.
Post-Editing vs Pre-Translation Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com