Transcreation involves adapting content to preserve its intent, style, and emotional impact, making it ideal for marketing and creative materials. Direct translation focuses on converting text word-for-word, ensuring accuracy but often missing cultural nuances. Choosing between transcreation and direct translation depends on the purpose and target audience of the content.
Table of Comparison
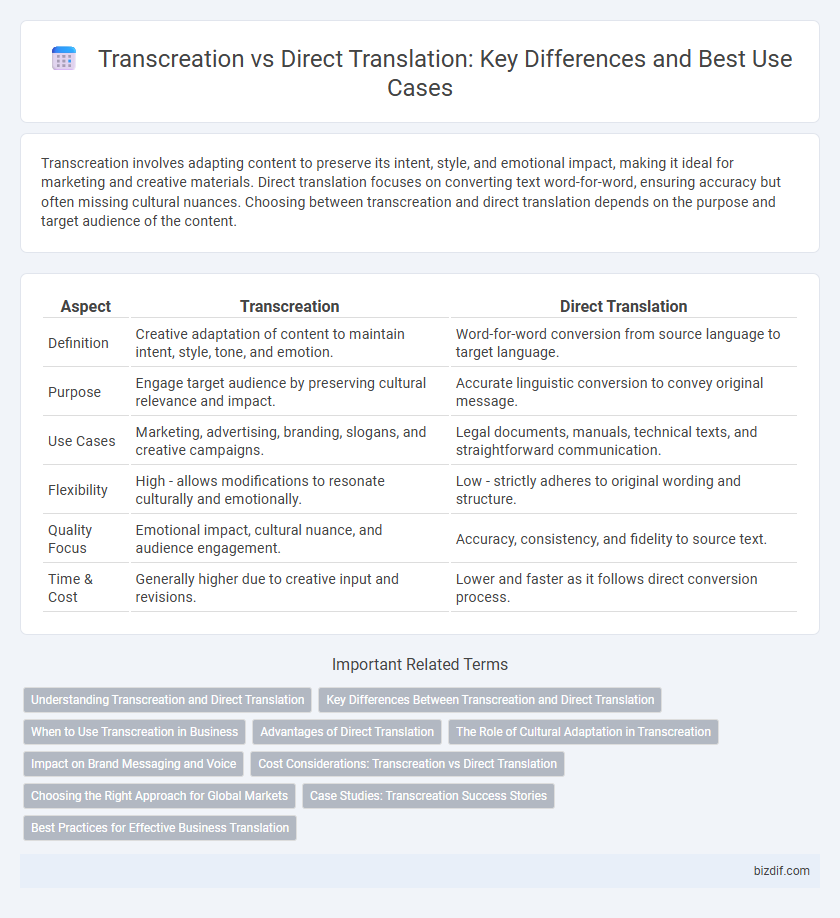
| Aspect | Transcreation | Direct Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Creative adaptation of content to maintain intent, style, tone, and emotion. | Word-for-word conversion from source language to target language. |
| Purpose | Engage target audience by preserving cultural relevance and impact. | Accurate linguistic conversion to convey original message. |
| Use Cases | Marketing, advertising, branding, slogans, and creative campaigns. | Legal documents, manuals, technical texts, and straightforward communication. |
| Flexibility | High - allows modifications to resonate culturally and emotionally. | Low - strictly adheres to original wording and structure. |
| Quality Focus | Emotional impact, cultural nuance, and audience engagement. | Accuracy, consistency, and fidelity to source text. |
| Time & Cost | Generally higher due to creative input and revisions. | Lower and faster as it follows direct conversion process. |
Understanding Transcreation and Direct Translation
Transcreation involves adapting content to resonate culturally and emotionally with the target audience, ensuring the original message's intent, style, tone, and context are preserved creatively. Direct translation focuses on rendering text word-for-word from the source language to the target language, prioritizing linguistic accuracy over cultural adaptation. Understanding the distinction helps businesses choose the right approach for marketing, literature, or technical documents to achieve effective communication.
Key Differences Between Transcreation and Direct Translation
Transcreation involves adapting content creatively to maintain the original message's intent, tone, and cultural relevance, while direct translation focuses on accurately converting text from one language to another without significant modification. Transcreation is essential for marketing and advertising materials where emotional impact and cultural nuances drive engagement, whereas direct translation suits technical documents requiring precise terminology. Key differences include the scope of adaptation, creative freedom, and the emphasis on cultural and emotional resonance.
When to Use Transcreation in Business
Transcreation is essential in business when marketing campaigns require cultural adaptation to resonate emotionally with target audiences, ensuring brand messaging retains its impact across different languages. It is ideal for advertising slogans, product names, and promotional content where literal direct translation might fail to convey nuances or evoke the desired response. Choosing transcreation over direct translation enhances brand consistency and engagement in global markets by aligning with local idioms, humor, and cultural references.
Advantages of Direct Translation
Direct translation ensures linguistic accuracy by maintaining the original text's precise meaning and structure, which is essential for technical manuals, legal documents, and scientific papers. It significantly reduces the risk of misinterpretation, preserving the source material's integrity across different languages. This method is usually faster and more cost-effective than transcreation, making it ideal for content requiring strict fidelity to the source text.
The Role of Cultural Adaptation in Transcreation
Cultural adaptation in transcreation ensures that marketing messages resonate deeply with the target audience by reflecting local customs, idioms, and values, which direct translation often overlooks. This process involves reimagining content to maintain emotional impact and brand voice while making it culturally relevant and engaging. Effective transcreation drives stronger connections and higher engagement rates by bridging linguistic and cultural gaps beyond literal word-for-word translation.
Impact on Brand Messaging and Voice
Transcreation enhances brand messaging by adapting content to resonate culturally and emotionally with target audiences, preserving the original tone and intent more effectively than direct translation. Direct translation risks losing nuanced brand voice and emotional impact, leading to misinterpretation or dilution of key messages. Effective transcreation ensures consistent brand identity across markets while maintaining engagement and authenticity.
Cost Considerations: Transcreation vs Direct Translation
Transcreation typically incurs higher costs than direct translation due to the extensive creative process involved, requiring skilled linguists with cultural expertise. Direct translation is more cost-effective for straightforward, technical, or informational content where literal accuracy is prioritized over localization. Businesses should evaluate project goals and budget constraints to determine whether investing in transcreation's higher expense justifies the enhanced cultural relevance and emotional impact.
Choosing the Right Approach for Global Markets
Choosing between transcreation and direct translation depends on the target market's cultural nuances and the brand's communication goals. Transcreation adapts content creatively to resonate emotionally and culturally, making it ideal for marketing campaigns in diverse global regions. Direct translation suits technical or straightforward content where accuracy and consistency outweigh emotional appeal, ensuring clarity and uniformity across languages.
Case Studies: Transcreation Success Stories
Transcreation adapts marketing content by preserving emotional impact and cultural relevance, as demonstrated in Coca-Cola's "Share a Coke" campaign, which personalized names for local markets, boosting engagement significantly. Nike's transcreated slogans maintained brand voice while resonating authentically across diverse languages, resulting in higher regional sales and brand loyalty. These case studies highlight how transcreation outperforms direct translation by delivering tailored messages that connect deeply with target audiences.
Best Practices for Effective Business Translation
Transcreation involves adapting content to resonate culturally and emotionally with the target audience, ensuring brand voice and intent remain intact, while direct translation focuses on converting text word-for-word. Best practices for effective business translation emphasize collaboration with native-speaking experts who understand industry-specific terminology and cultural nuances, enhancing customer engagement and brand consistency. Combining thorough market research with iterative feedback loops optimizes accuracy and relevance, preventing misinterpretation and fostering trust in global markets.
Transcreation vs Direct Translation Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com