Understanding the nuances between the source language and the target language is crucial for accurate translation. Cultural context, idiomatic expressions, and grammatical structures vary significantly, impacting meaning and readability. Effective translation requires adapting content to maintain intent while ensuring fluency and clarity in the target language.
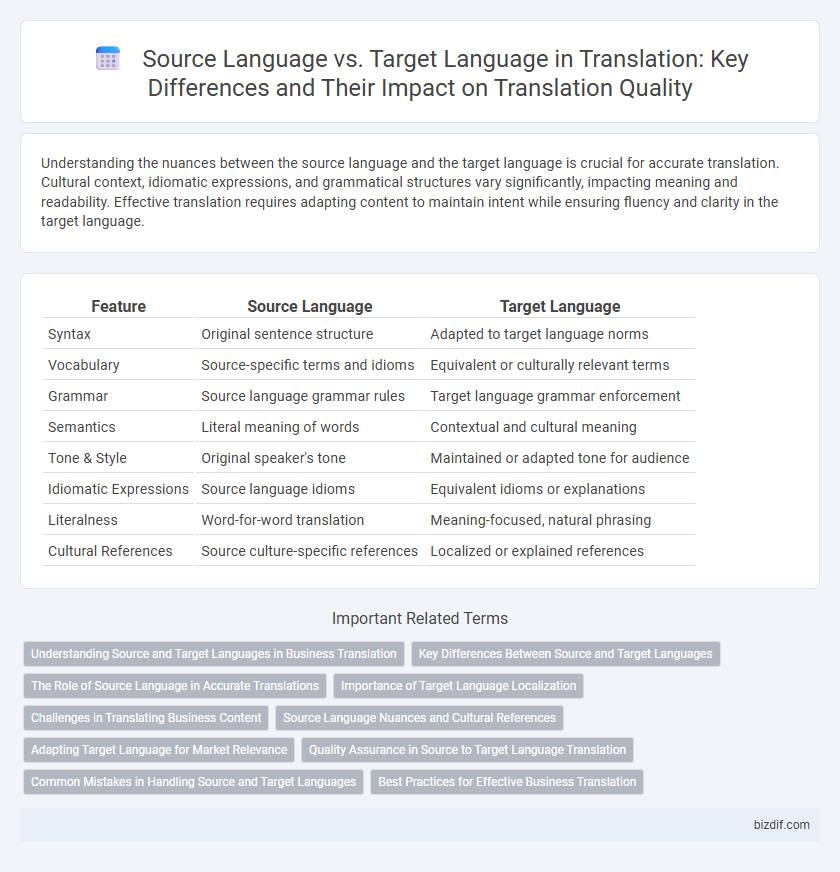
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Source Language | Target Language |
|---|---|---|
| Syntax | Original sentence structure | Adapted to target language norms |
| Vocabulary | Source-specific terms and idioms | Equivalent or culturally relevant terms |
| Grammar | Source language grammar rules | Target language grammar enforcement |
| Semantics | Literal meaning of words | Contextual and cultural meaning |
| Tone & Style | Original speaker's tone | Maintained or adapted tone for audience |
| Idiomatic Expressions | Source language idioms | Equivalent idioms or explanations |
| Literalness | Word-for-word translation | Meaning-focused, natural phrasing |
| Cultural References | Source culture-specific references | Localized or explained references |
Understanding Source and Target Languages in Business Translation
Accurate business translation hinges on deep understanding of both source and target languages, ensuring terminology and context align with industry standards. Mastery of the source language captures nuanced meanings, while fluency in the target language guarantees culturally appropriate and clear communication. Effective translation bridges linguistic gaps, enhancing global business interactions and maintaining brand integrity across markets.
Key Differences Between Source and Target Languages
Source languages serve as the original linguistic framework from which text or speech is translated, containing unique grammar, syntax, idiomatic expressions, and cultural references. Target languages require adaptation of these elements to maintain meaning, fluency, and relevance, often confronting structural differences such as word order, verb tense, and vocabulary nuances. Effective translation demands an in-depth understanding of both source and target languages to preserve intent, tone, and context while ensuring clarity and naturalness in the translated content.
The Role of Source Language in Accurate Translations
The source language serves as the foundation for accurate translations by providing the original meaning, context, and cultural nuances that must be preserved in the target language. Detailed understanding of the source language's syntax, semantics, and idiomatic expressions is essential to avoid mistranslations or loss of intent. Accurate translation outcomes rely heavily on the translator's expertise with the source language to ensure fidelity and clarity in the target language.
Importance of Target Language Localization
Effective target language localization ensures translations resonate culturally and contextually with the intended audience, enhancing clarity and engagement. Accurate adaptation reflects local idioms, customs, and legal norms, which prevents misunderstandings and increases user trust. Emphasizing localization over literal source language replication strengthens brand relevance and market penetration.
Challenges in Translating Business Content
Translating business content involves significant challenges due to cultural nuances and industry-specific terminology present in the source language that may not have direct equivalents in the target language. Differences in legal systems, marketing strategies, and financial terminologies require precise localization to maintain message accuracy and compliance. Ensuring consistency across multilingual business communications demands specialized knowledge in both the source and target languages, as well as expertise in the relevant business sector.
Source Language Nuances and Cultural References
Source language nuances and cultural references pose significant challenges in translation, requiring deep understanding to accurately convey meaning. Subtle idioms, humor, and culturally specific expressions often lack direct equivalents in the target language, demanding adaptive strategies. Effective translation preserves the original tone and intent while bridging linguistic and cultural gaps between the source and target languages.
Adapting Target Language for Market Relevance
Adapting the target language for market relevance involves tailoring translation to reflect cultural nuances, idiomatic expressions, and local preferences specific to the target audience. Effective localization ensures that marketing messages resonate authentically, increasing engagement and conversion rates in the target market. Understanding regional dialects and consumer behavior is crucial for achieving meaningful communication beyond literal source language translation.
Quality Assurance in Source to Target Language Translation
Ensuring quality assurance in source to target language translation requires rigorous accuracy checks to preserve the original meaning, tone, and context. Specialized tools like translation memory and glossary databases enhance consistency and reduce errors across the translation process. Engaging native speakers for review helps identify subtle nuances and cultural references, guaranteeing high-quality, reliable target language output.
Common Mistakes in Handling Source and Target Languages
Common mistakes in handling source and target languages include literal translations that ignore cultural nuances and context-specific meanings, leading to loss of intent and clarity. Translators often overlook idiomatic expressions and syntactic differences, resulting in awkward or inaccurate renditions in the target language. Failure to adapt tone, register, and style to the target audience can diminish the effectiveness and professionalism of the translated content.
Best Practices for Effective Business Translation
Prioritize thorough understanding of both the source language and target language to ensure accurate translation of business terminology and cultural nuances. Employ native speakers or professional translators with expertise in the target market to maintain contextual relevance and tone. Consistently use glossaries and style guides tailored to the target language for uniformity across all translated materials.
Source Language vs Target Language Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com