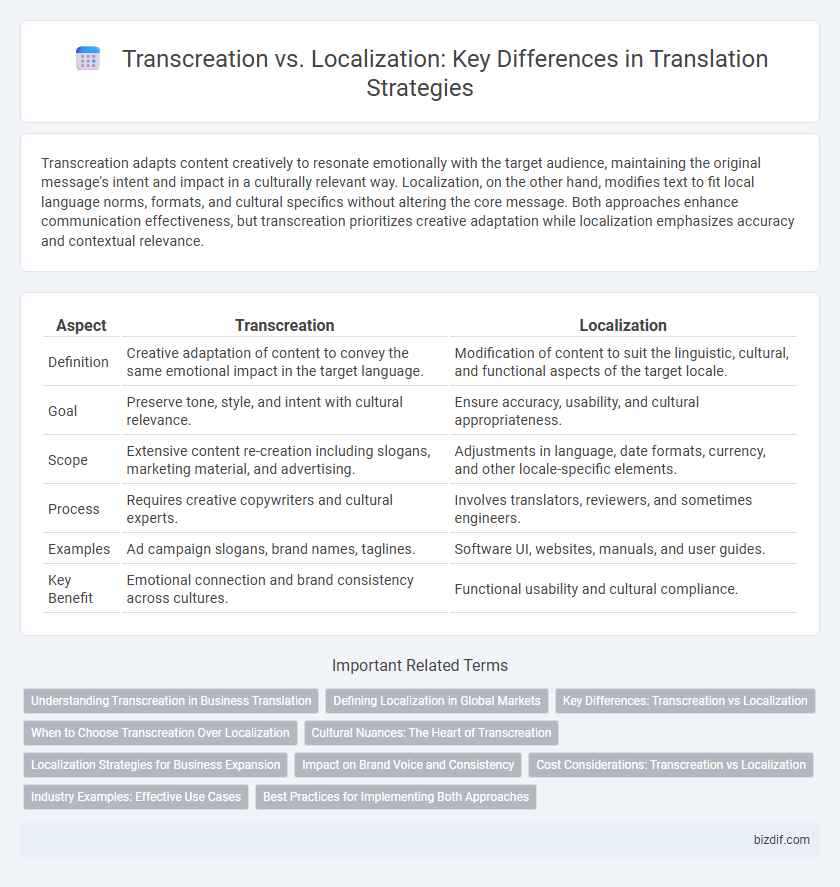
Transcreation adapts content creatively to resonate emotionally with the target audience, maintaining the original message's intent and impact in a culturally relevant way. Localization, on the other hand, modifies text to fit local language norms, formats, and cultural specifics without altering the core message. Both approaches enhance communication effectiveness, but transcreation prioritizes creative adaptation while localization emphasizes accuracy and contextual relevance.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Transcreation | Localization |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Creative adaptation of content to convey the same emotional impact in the target language. | Modification of content to suit the linguistic, cultural, and functional aspects of the target locale. |
| Goal | Preserve tone, style, and intent with cultural relevance. | Ensure accuracy, usability, and cultural appropriateness. |
| Scope | Extensive content re-creation including slogans, marketing material, and advertising. | Adjustments in language, date formats, currency, and other locale-specific elements. |
| Process | Requires creative copywriters and cultural experts. | Involves translators, reviewers, and sometimes engineers. |
| Examples | Ad campaign slogans, brand names, taglines. | Software UI, websites, manuals, and user guides. |
| Key Benefit | Emotional connection and brand consistency across cultures. | Functional usability and cultural compliance. |
Understanding Transcreation in Business Translation
Transcreation in business translation involves adapting content to resonate culturally and emotionally with the target audience, going beyond literal translation to preserve the original message's impact. It requires creative skills and deep cultural insight to ensure marketing materials, slogans, and brand messages evoke the same response across different markets. Unlike localization, which focuses on language and regional adjustments, transcreation emphasizes maintaining the essence and persuasive power of the content in a way that feels native to the target culture.
Defining Localization in Global Markets
Localization adapts content to meet the linguistic, cultural, and functional expectations of target global markets, ensuring relevance beyond mere language translation. It involves modifying elements such as date formats, currency, imagery, and user interface to fit local preferences and regulatory requirements. Effective localization enhances user experience and drives engagement by resonating authentically with regional audiences.
Key Differences: Transcreation vs Localization
Transcreation involves creatively adapting content to resonate culturally and emotionally with the target audience, often altering tone, style, and context to preserve intent and impact, whereas localization focuses on conventional translation and format adjustments such as language, date, currency, and units to fit the target market. Transcreation is essential for marketing campaigns and brand messaging that require a fresh, culturally relevant voice, while localization suits software, websites, and technical manuals needing accurate, functional language adaptation. Key differences include the level of creative freedom, the purpose of adaptation, and the scope of cultural customization.
When to Choose Transcreation Over Localization
Choose transcreation over localization when your content requires cultural adaptation and emotional resonance, such as marketing campaigns, brand slogans, or creative advertisements. Transcreation ensures that messages maintain their original intent, tone, and impact across different cultures by reinventing content rather than simply translating it. Localization is more appropriate for technical documents, product manuals, or websites where accuracy and functionality are paramount.
Cultural Nuances: The Heart of Transcreation
Transcreation centers on adapting content with deep cultural nuances, ensuring the message resonates authentically with the target audience beyond literal translation. Unlike localization, which mainly adjusts language and format for regional preferences, transcreation reshapes ideas, idioms, and emotional undertones to preserve brand voice and cultural relevance. This nuanced approach enhances engagement, making transcreation essential for marketing campaigns that demand cultural sensitivity and impact.
Localization Strategies for Business Expansion
Localization strategies for business expansion involve adapting products and content to meet the cultural, linguistic, and regulatory nuances of target markets. Effective localization goes beyond translation by incorporating local customs, consumer behavior, and market preferences to ensure relevance and engagement. Implementing comprehensive localization techniques can significantly enhance brand perception and drive global growth.
Impact on Brand Voice and Consistency
Transcreation involves creatively adapting marketing content to preserve brand voice and emotional impact across different cultures, ensuring consistent messaging that resonates deeply with target audiences. Localization focuses on modifying language and cultural references to enhance clarity and relevance, which supports brand consistency by maintaining tone and style in a contextually appropriate manner. Balancing transcreation and localization is essential for sustaining a cohesive brand identity while effectively engaging diverse global markets.
Cost Considerations: Transcreation vs Localization
Transcreation involves higher costs due to its creative process, requiring skilled linguists to adapt content emotionally and culturally, beyond direct translation. Localization typically incurs lower expenses by focusing on adapting text for language and regional preferences without significant changes to the original message. Budget decisions should consider project goals, with transcreation favored for marketing campaigns demanding cultural nuance and localization suited for software, websites, or technical materials.
Industry Examples: Effective Use Cases
Transcreation and localization serve distinct roles in global marketing strategies, with transcreation often employed by advertising agencies for culturally resonant campaigns like Coca-Cola's "Share a Coke" initiative, which adapts slogans to evoke local emotions. Localization is commonly used by software companies such as Microsoft to adapt user interfaces and documentation, ensuring linguistic accuracy and functional relevance across markets. Brands like Netflix utilize both by transcreating promotional content for emotional impact while localizing subtitles and UI elements to meet regional preferences and regulatory standards.
Best Practices for Implementing Both Approaches
Effective transcreation delivers culturally resonant messages by adapting content beyond literal translation, ensuring emotional impact and brand consistency. Localization customizes products or content to align with regional language, customs, and legal requirements, improving user experience and market relevance. Combining transcreation and localization through thorough market research, collaboration with native experts, and iterative quality checks optimizes global communication strategies.
Transcreation vs Localization Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com