Choosing between iOS and Android for app development involves considering user demographics, platform customization, and development costs. iOS offers a streamlined ecosystem with higher revenue potential due to a dedicated user base, while Android provides broader market reach with extensive device variety and flexible app approval processes. Developers must balance these factors to optimize app performance and profitability across both platforms.
Table of Comparison
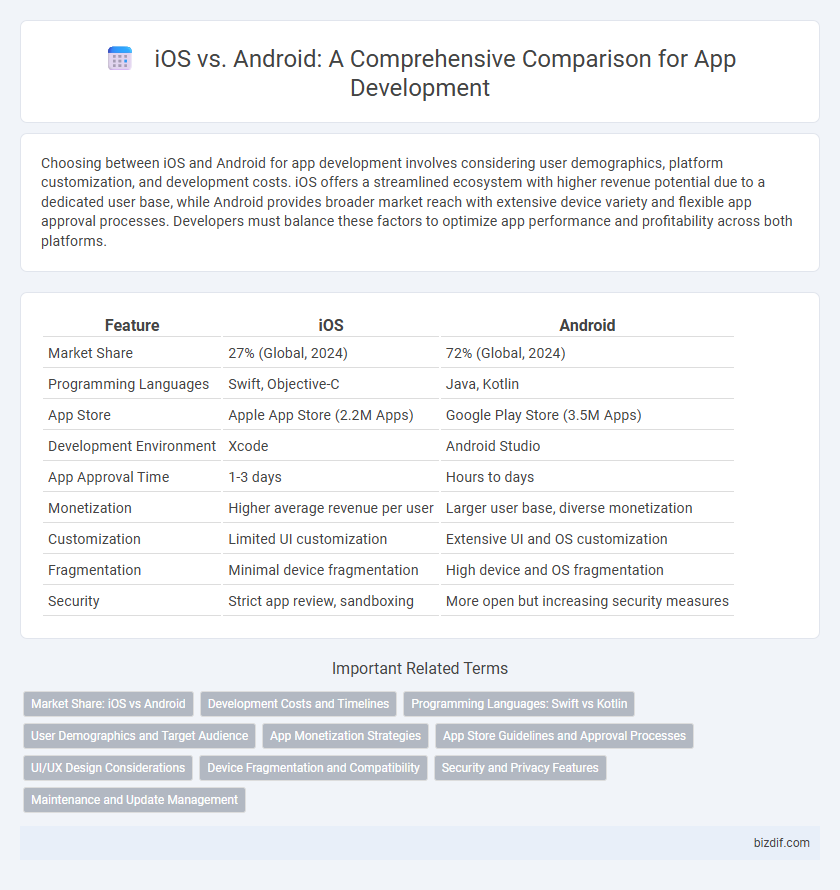
| Feature | iOS | Android |
|---|---|---|
| Market Share | 27% (Global, 2024) | 72% (Global, 2024) |
| Programming Languages | Swift, Objective-C | Java, Kotlin |
| App Store | Apple App Store (2.2M Apps) | Google Play Store (3.5M Apps) |
| Development Environment | Xcode | Android Studio |
| App Approval Time | 1-3 days | Hours to days |
| Monetization | Higher average revenue per user | Larger user base, diverse monetization |
| Customization | Limited UI customization | Extensive UI and OS customization |
| Fragmentation | Minimal device fragmentation | High device and OS fragmentation |
| Security | Strict app review, sandboxing | More open but increasing security measures |
Market Share: iOS vs Android
Android commands approximately 72% of the global smartphone market share, making it the dominant platform for app developers aiming at a broad audience. iOS holds around 27%, favored in high-spending markets like the United States and Western Europe, attracting developers targeting premium users. Understanding these market share dynamics is crucial for optimizing app development strategies and maximizing revenue potential.
Development Costs and Timelines
Development costs for iOS apps are generally lower due to a more streamlined ecosystem and fewer device variations, which reduces testing and optimization time. Android development often requires longer timelines and higher budgets because of the wide range of devices and OS versions that demand extensive compatibility checks. Efficient project management and clear requirements can help mitigate these cost and timeline disparities in both platforms.
Programming Languages: Swift vs Kotlin
Swift, the primary language for iOS development, offers seamless integration with Apple's ecosystem, optimized performance, and a concise syntax that enhances developer productivity. Kotlin, endorsed by Google for Android development, provides interoperability with Java, null safety, and modern language features that simplify complex programming tasks. Both languages support robust app performance and developer efficiency but are tailored to their respective platform architectures and frameworks.
User Demographics and Target Audience
iOS users typically represent a higher-income demographic with a strong presence in North America and Western Europe, making it ideal for apps targeting premium customers and affluent markets. Android dominates globally with a larger, more diverse user base, particularly popular in emerging markets across Asia, Africa, and South America, offering extensive reach for apps requiring mass adoption. Understanding these user demographics and regional preferences is crucial for developers to tailor app features, design, and marketing strategies effectively.
App Monetization Strategies
iOS app monetization strategies often emphasize premium pricing and in-app purchases due to a higher spending user base, resulting in greater revenue per user. Android developers typically leverage ad-based monetization and freemium models, expanding reach through a larger global install base. Understanding platform-specific user behavior and market demographics is crucial for optimizing revenue generation in mobile app development.
App Store Guidelines and Approval Processes
iOS and Android differ significantly in their App Store Guidelines and approval processes, impacting app development strategies. Apple's App Store enforces stringent, clear-cut guidelines emphasizing user privacy, security, and content quality, with a typically longer, more rigorous review process that can take days to weeks. In contrast, Google Play offers more flexible policies and a faster approval timeline, enabling quicker app updates but potentially leading to less consistent quality control.
UI/UX Design Considerations
iOS UI/UX design prioritizes consistency with Apple's Human Interface Guidelines, emphasizing simplicity, intuitive navigation, and gesture-based interactions for seamless user experiences. Android design allows more customization with Material Design principles, enabling adaptable interfaces tailored to diverse device types and user preferences. Understanding platform-specific typography, spacing, and touch target standards is crucial to optimize usability and engagement across both operating systems.
Device Fragmentation and Compatibility
Device fragmentation significantly impacts Android app development due to the wide variety of screen sizes, hardware capabilities, and OS versions across numerous manufacturers, demanding extensive testing and optimization. In contrast, iOS offers a more controlled environment with fewer device models and consistent operating system updates, facilitating greater compatibility and streamlined development processes. Ensuring app functionality across diverse Android devices requires sophisticated adaptability strategies, whereas iOS developers benefit from standardized APIs and uniform user interface guidelines.
Security and Privacy Features
iOS offers robust security through its tightly controlled app ecosystem, regular updates, and features like App Tracking Transparency, which limits cross-app data sharing. Android provides flexibility with granular permission controls and enhanced sandboxing in recent versions, but fragmentation can lead to inconsistent security across devices. Both platforms prioritize privacy, yet iOS consistently ranks higher in user data protection due to its stringent app review process and hardware-based security measures like the Secure Enclave.
Maintenance and Update Management
iOS offers streamlined maintenance and update management through its uniform hardware and software ecosystem, allowing developers to push timely updates with minimal compatibility issues. Android requires more extensive testing across diverse devices and OS versions, increasing maintenance complexity and update rollout times. Efficient update management on iOS results in faster bug fixes and feature releases, enhancing user experience compared to the fragmented Android environment.
iOS vs Android Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com