Single-tenant architecture offers dedicated resources and enhanced security by isolating each user's data within a separate environment, making it ideal for apps requiring strict compliance and customization. Multi-tenant architecture maximizes resource efficiency and scalability by sharing infrastructure among multiple users while maintaining logical data separation, enabling cost-effective app development and simplified maintenance. Choosing between the two depends on factors like security needs, scalability requirements, and budget constraints for the pet app's user base.
Table of Comparison
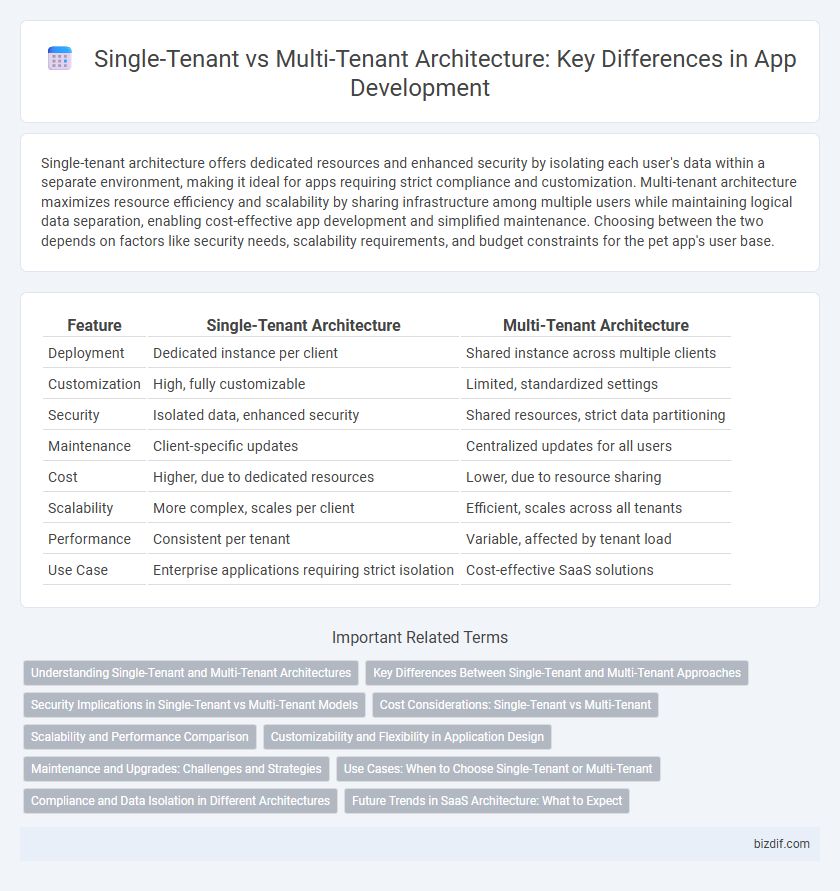
| Feature | Single-Tenant Architecture | Multi-Tenant Architecture |
|---|---|---|
| Deployment | Dedicated instance per client | Shared instance across multiple clients |
| Customization | High, fully customizable | Limited, standardized settings |
| Security | Isolated data, enhanced security | Shared resources, strict data partitioning |
| Maintenance | Client-specific updates | Centralized updates for all users |
| Cost | Higher, due to dedicated resources | Lower, due to resource sharing |
| Scalability | More complex, scales per client | Efficient, scales across all tenants |
| Performance | Consistent per tenant | Variable, affected by tenant load |
| Use Case | Enterprise applications requiring strict isolation | Cost-effective SaaS solutions |
Understanding Single-Tenant and Multi-Tenant Architectures
Single-tenant architecture provides a dedicated instance of software for each user or organization, ensuring customized security and performance isolation. Multi-tenant architecture hosts multiple users on a shared instance while maintaining data separation through logical isolation. Choosing between these architectures impacts scalability, cost-efficiency, and application maintenance strategies in app development.
Key Differences Between Single-Tenant and Multi-Tenant Approaches
Single-tenant architecture allocates dedicated resources and databases to each client, enhancing security and customization while increasing operational costs. Multi-tenant architecture shares resources across multiple clients within a single instance, optimizing scalability and reducing maintenance overhead but limiting individual customization. Key differences include data isolation, cost efficiency, scalability, and customization capabilities tailored to client requirements.
Security Implications in Single-Tenant vs Multi-Tenant Models
Single-tenant architecture offers enhanced security by isolating data and applications on dedicated servers, reducing the risk of cross-tenant data breaches common in multi-tenant models. Multi-tenant architecture shares resources among users, creating potential vulnerabilities due to shared access and increased attack surfaces. Enterprises prioritizing sensitive data protection often prefer single-tenant solutions despite higher costs, whereas multi-tenant environments require robust encryption and access controls to mitigate security risks.
Cost Considerations: Single-Tenant vs Multi-Tenant
Single-tenant architecture often incurs higher costs due to dedicated resources and individualized maintenance, resulting in increased infrastructure and operational expenses. Multi-tenant architecture reduces overall costs by sharing resources among multiple users, leading to efficient scalability and lower per-user expenses. Organizations must weigh the upfront and ongoing financial implications, factoring in customization needs and security requirements when choosing between these models.
Scalability and Performance Comparison
Single-tenant architecture offers dedicated resources for each client, ensuring consistent performance and easier scaling tailored to individual needs, but often at higher infrastructure costs. Multi-tenant architecture shares resources among multiple clients, providing efficient use of infrastructure and easier horizontal scaling, though it may introduce performance variability under high load. Scalability in multi-tenant systems relies heavily on optimized resource allocation and tenant isolation mechanisms to maintain performance, while single-tenant systems benefit from predictable workloads and simplified scaling strategies.
Customizability and Flexibility in Application Design
Single-tenant architecture provides superior customizability and flexibility in application design by allowing dedicated resources and tailored configurations for each client, enabling unique feature development and personalized user experiences. Multi-tenant architecture, while cost-effective and easier to scale, limits customization due to shared resources and uniform application instances across users. Developers prioritize single-tenant models when specific client requirements demand deep customization and isolated data environments.
Maintenance and Upgrades: Challenges and Strategies
Single-tenant architecture isolates each client's data and application instance, simplifying maintenance and enabling tailored upgrades without impacting other users, but it increases resource requirements and operational costs. Multi-tenant architecture centralizes maintenance and updates, allowing efficient, simultaneous upgrades across all clients, yet challenges arise in ensuring backward compatibility and minimizing service disruptions. Strategies for multi-tenant systems include automated testing, versioning, and phased rollouts to manage complexity and maintain system stability during upgrades.
Use Cases: When to Choose Single-Tenant or Multi-Tenant
Single-tenant architecture is ideal for businesses requiring enhanced security, customization, and dedicated resources, such as healthcare providers or financial institutions handling sensitive data. Multi-tenant architecture suits SaaS applications targeting startups or SMEs seeking cost efficiency, scalability, and simplified maintenance. Choosing between the two depends on factors like compliance requirements, budget constraints, and the need for personalized user experiences.
Compliance and Data Isolation in Different Architectures
Single-tenant architecture provides enhanced compliance capabilities by isolating data and applications for each client, ensuring strict adherence to industry-specific regulations such as GDPR and HIPAA. Multi-tenant architecture shares resources among multiple clients, which can introduce challenges in data isolation but benefits from centralized security controls and streamlined updates. Data isolation in single-tenant setups reduces cross-tenant vulnerability risks, while multi-tenant environments rely heavily on logical segmentation and access controls to maintain compliance.
Future Trends in SaaS Architecture: What to Expect
Future trends in SaaS architecture emphasize scalability and security enhancements within both single-tenant and multi-tenant models. Single-tenant architecture offers dedicated resources, promoting greater data isolation ideal for industries with stringent compliance requirements. Multi-tenant architecture advances through containerization and microservices, driving cost-efficiency and rapid deployment, which cater to evolving demands for flexible, scalable applications.
Single-Tenant Architecture vs Multi-Tenant Architecture Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com