Gluten-free bakery products cater to individuals with gluten intolerance or celiac disease by using alternative flours such as almond, rice, or tapioca, ensuring safe and delicious options without compromising taste or texture. Conventional baked goods typically contain wheat flour, which provides elasticity and structure due to gluten proteins, resulting in classic chewy or fluffy textures that many consumers expect. Choosing between gluten-free and conventional bakery items depends on dietary needs and preference, with advances in gluten-free baking narrowing the quality gap.
Table of Comparison
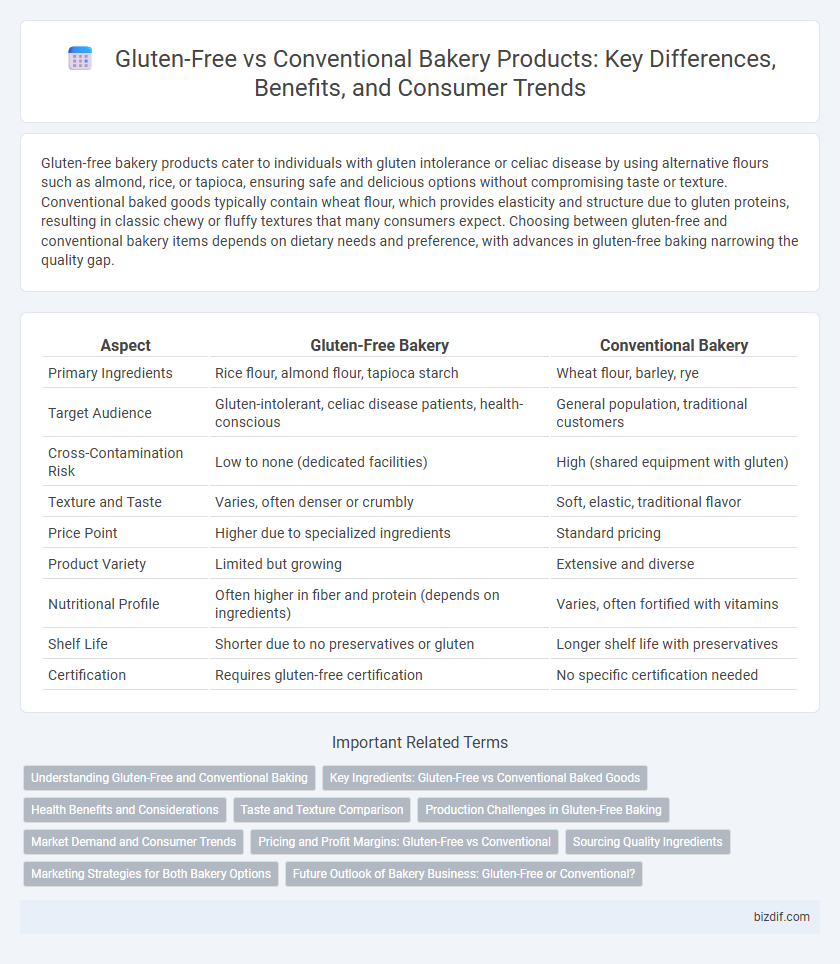
| Aspect | Gluten-Free Bakery | Conventional Bakery |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Ingredients | Rice flour, almond flour, tapioca starch | Wheat flour, barley, rye |
| Target Audience | Gluten-intolerant, celiac disease patients, health-conscious | General population, traditional customers |
| Cross-Contamination Risk | Low to none (dedicated facilities) | High (shared equipment with gluten) |
| Texture and Taste | Varies, often denser or crumbly | Soft, elastic, traditional flavor |
| Price Point | Higher due to specialized ingredients | Standard pricing |
| Product Variety | Limited but growing | Extensive and diverse |
| Nutritional Profile | Often higher in fiber and protein (depends on ingredients) | Varies, often fortified with vitamins |
| Shelf Life | Shorter due to no preservatives or gluten | Longer shelf life with preservatives |
| Certification | Requires gluten-free certification | No specific certification needed |
Understanding Gluten-Free and Conventional Baking
Gluten-free baking replaces wheat flour with alternative grains like rice, almond, or coconut flour to accommodate individuals with gluten intolerance or celiac disease, ensuring safe consumption without compromising texture and flavor. Conventional baking predominantly uses wheat-based flours containing gluten, a protein that provides dough elasticity and structure, resulting in traditional crumb and chewiness. Mastering gluten-free baking requires precise ingredient blends and techniques to mimic the elasticity and moisture retention inherent in conventional wheat-based recipes.
Key Ingredients: Gluten-Free vs Conventional Baked Goods
Gluten-free baked goods primarily use alternative flours such as almond, rice, or coconut flour to replace traditional wheat flour, which contains gluten. Conventional baked goods rely on wheat-based flours that provide elasticity and structure due to gluten proteins. The absence of gluten in gluten-free recipes necessitates the use of binding agents like xanthan gum or guar gum to mimic the texture and moisture retention found in conventional products.
Health Benefits and Considerations
Gluten-free bakery products cater to individuals with celiac disease or gluten sensitivity by eliminating wheat, barley, and rye, reducing the risk of digestive discomfort and inflammation. Conventional baked goods often contain essential nutrients like fiber, B vitamins, and iron but may trigger adverse reactions in sensitive individuals. Choosing gluten-free options requires attention to alternative grain sources and potential nutrient deficiencies to maintain a balanced diet.
Taste and Texture Comparison
Gluten-free baked goods often have a denser texture and a slightly crumbly bite compared to the airy, chewy texture of conventional wheat-based products. The absence of gluten affects the dough's elasticity, resulting in a different mouthfeel and sometimes a nuttier or earthier taste in gluten-free options. Many bakers use alternative flours like rice, almond, or tapioca to enhance flavor and improve texture, but conventional bread generally offers a more familiar taste and softer crumb.
Production Challenges in Gluten-Free Baking
Gluten-free baking presents unique production challenges such as achieving dough elasticity and structure without gluten, often requiring alternative flours like rice or almond combined with binders like xanthan gum. Maintaining consistent texture and moisture is difficult due to the absence of gluten's network-forming properties, leading to variations in product quality. Cross-contamination risks demand stringent cleaning protocols and dedicated equipment to comply with gluten-free standards in commercial bakeries.
Market Demand and Consumer Trends
Gluten-free bakery products have experienced a significant surge in market demand, driven by rising consumer awareness of gluten intolerance, celiac disease, and a growing preference for healthier lifestyle choices. Conventional baked goods continue to dominate overall sales, but the gluten-free segment is expanding rapidly, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 9% projected through 2028. Consumer trends reveal a shift towards clean-label ingredients and transparency, further fueling the popularity of gluten-free options in both specialty and mainstream bakery markets.
Pricing and Profit Margins: Gluten-Free vs Conventional
Gluten-free bakery products often incur higher production costs due to specialized ingredients and dedicated equipment, resulting in elevated pricing compared to conventional baked goods. Despite higher retail prices, gluten-free items typically yield thinner profit margins because of increased ingredient expenses and lower economies of scale. Conventional bakery products benefit from bulk ingredient purchasing and streamlined processes, leading to lower production costs and higher overall profit margins.
Sourcing Quality Ingredients
Gluten-free baking demands sourcing high-quality alternative flours like almond, rice, or tapioca to ensure texture and flavor match conventional wheat-based products. Conventional bakery ingredients often prioritize consistency and cost-effectiveness, relying on refined wheat flour with standardized protein content for predictable results. Emphasizing locally sourced, organic grains benefits both gluten-free and conventional bakeries by enhancing flavor profiles and supporting sustainable agriculture.
Marketing Strategies for Both Bakery Options
Target marketing for gluten-free bakeries emphasizes health-conscious consumers, highlighting allergen-free ingredients and verified certifications to build trust. Conventional bakeries capitalize on traditional recipes and indulgent flavors, using nostalgic branding and seasonal promotions to attract families and comfort-seekers. Digital campaigns tailored to each segment optimize engagement by leveraging influencer partnerships for gluten-free options and loyalty programs for conventional products.
Future Outlook of Bakery Business: Gluten-Free or Conventional?
The future outlook of the bakery business reveals a growing demand for gluten-free products driven by increasing health consciousness and rising gluten intolerance awareness among consumers. Conventional bakeries continue to dominate in volume but face pressure to innovate by incorporating gluten-free and other specialty options to capture expanding market segments. Investment in gluten-free ingredient technology and certification processes is expected to accelerate, positioning gluten-free bakeries for significant growth in the coming years.
Gluten-free vs Conventional Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com