Wholesale supply in a bakery involves selling large quantities of baked goods to businesses such as cafes, restaurants, or grocery stores, enabling bulk purchasing at discounted rates. Retail sales focus on direct consumer purchases, offering a variety of fresh, artisanal products in smaller quantities tailored to individual preferences. Balancing wholesale and retail channels allows bakeries to maximize revenue streams while maintaining product quality and customer satisfaction.
Table of Comparison
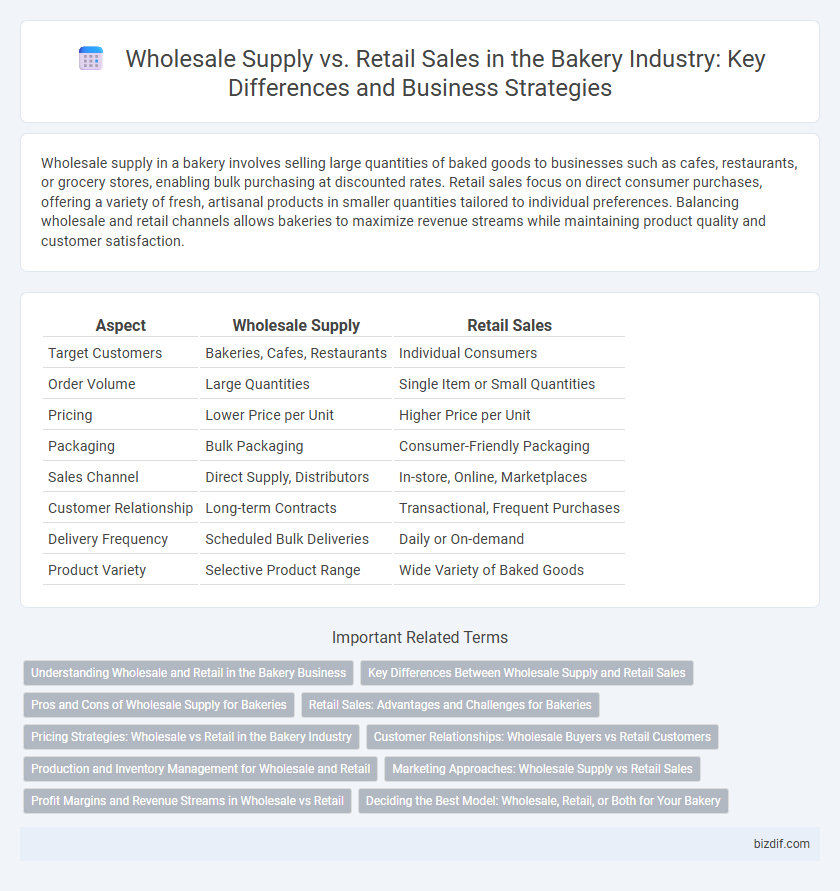
| Aspect | Wholesale Supply | Retail Sales |
|---|---|---|
| Target Customers | Bakeries, Cafes, Restaurants | Individual Consumers |
| Order Volume | Large Quantities | Single Item or Small Quantities |
| Pricing | Lower Price per Unit | Higher Price per Unit |
| Packaging | Bulk Packaging | Consumer-Friendly Packaging |
| Sales Channel | Direct Supply, Distributors | In-store, Online, Marketplaces |
| Customer Relationship | Long-term Contracts | Transactional, Frequent Purchases |
| Delivery Frequency | Scheduled Bulk Deliveries | Daily or On-demand |
| Product Variety | Selective Product Range | Wide Variety of Baked Goods |
Understanding Wholesale and Retail in the Bakery Business
Wholesale supply in the bakery business involves selling large quantities of baked goods directly to retailers, cafes, or restaurants at discounted prices, enabling bulk distribution. Retail sales focus on selling individual products to end consumers through storefronts or online platforms, often emphasizing customer experience and product variety. Understanding the distinct pricing strategies, inventory management, and customer engagement methods between wholesale and retail channels is crucial for bakery growth and profitability.
Key Differences Between Wholesale Supply and Retail Sales
Wholesale supply in the bakery industry involves selling large quantities of baked goods to businesses such as cafes, restaurants, and grocery stores, often at discounted prices. Retail sales focus on direct consumer purchases of single or small quantities of items, emphasizing convenience and variety. Key differences include order volume, pricing models, customer type, and distribution channels.
Pros and Cons of Wholesale Supply for Bakeries
Wholesale supply for bakeries enables bulk production with lower per-unit costs, increasing profit margins through economies of scale. It requires consistent demand and reliable distribution channels to avoid overproduction and inventory waste. However, wholesale contracts may limit product variety and reduce direct customer interaction, impacting brand loyalty and customization opportunities.
Retail Sales: Advantages and Challenges for Bakeries
Retail sales in bakeries provide direct access to customer feedback, enabling product customization and fostering brand loyalty. Higher profit margins per unit are achievable by bypassing intermediaries common in wholesale supply chains. Challenges include managing fluctuating customer demand, inventory control, and increased operational costs for staffing and marketing to attract foot traffic.
Pricing Strategies: Wholesale vs Retail in the Bakery Industry
Wholesale pricing in the bakery industry often involves bulk discounts and lower per-unit costs to attract large orders from retailers or food service businesses. Retail sales focus on higher profit margins per item, incorporating packaging, branding, and convenience factors to justify elevated prices. Strategic pricing balances production costs, market demand, and competition to optimize revenue across both wholesale and retail channels.
Customer Relationships: Wholesale Buyers vs Retail Customers
Wholesale supply in the bakery industry often involves building long-term partnerships with bulk buyers such as cafes and restaurants, focusing on reliability, volume discounts, and consistent product quality. Retail sales prioritize personalized customer relationships, emphasizing product variety, in-store experience, and immediate consumer feedback. Understanding these distinct customer dynamics enables bakeries to tailor marketing strategies and optimize service delivery effectively.
Production and Inventory Management for Wholesale and Retail
Wholesale supply in bakery involves large-scale production with optimized batch processing to ensure consistent quality and efficient inventory turnover, minimizing storage costs and reducing waste. Retail sales require smaller, more frequent production runs tailored to diverse consumer preferences, maintaining fresh inventory through just-in-time stock management and real-time demand forecasting. Inventory management for wholesale prioritizes bulk raw material procurement and extended shelf-life products, while retail focuses on dynamic stock levels, rapid replenishment, and managing product variety to meet fluctuating customer demand.
Marketing Approaches: Wholesale Supply vs Retail Sales
Wholesale supply in the bakery industry targets bulk buyers such as cafes, supermarkets, and restaurants, emphasizing volume discounts and long-term contracts to build steady demand. Retail sales focus on direct consumer engagement through appealing store displays, seasonal promotions, and personalized customer experiences to drive impulse purchases. Effective marketing strategies differentiate based on customer behavior, with wholesale relying on B2B networks and retail leveraging local branding and social media campaigns.
Profit Margins and Revenue Streams in Wholesale vs Retail
Wholesale supply in bakery offers lower profit margins per unit but generates higher overall revenue through bulk sales to retailers or foodservice businesses. Retail sales typically yield higher profit margins per item due to direct customer interaction, allowing bakeries to set premium prices and leverage impulse buying. Combining wholesale and retail revenue streams enables bakeries to diversify income, optimize production efficiency, and stabilize cash flow.
Deciding the Best Model: Wholesale, Retail, or Both for Your Bakery
Wholesale supply offers bakeries the advantage of consistent large-volume orders, reducing production costs and stabilizing cash flow, while retail sales provide direct customer engagement and higher profit margins per unit. Choosing the best model depends on factors like production capacity, local market demand, and brand positioning; combining both wholesale and retail can diversify revenue streams and increase market reach. Evaluating operational capabilities alongside customer preferences ensures an optimal balance between wholesale contracts and walk-in sales for sustainable bakery growth.
Wholesale supply vs Retail sales Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com