Candle curing involves allowing the wax and fragrance oils to fully blend and harden over several days, enhancing scent throw and burn quality. Candle testing assesses the candle's performance by checking factors such as burn time, flame stability, and fragrance release. Proper curing is essential before testing to ensure accurate evaluation and a safe, enjoyable candle experience.
Table of Comparison
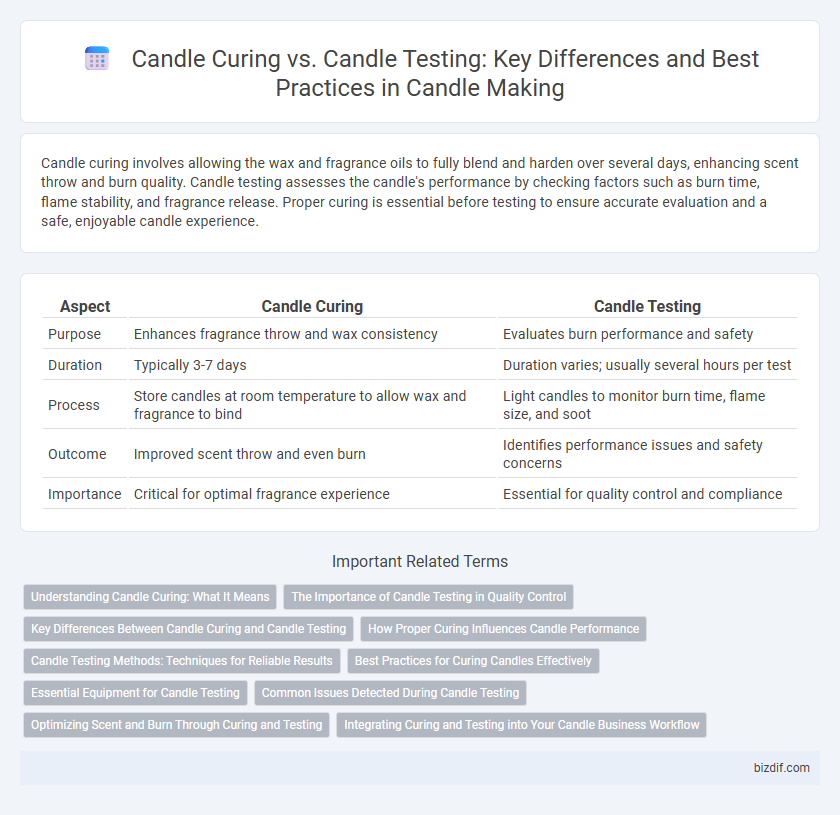
| Aspect | Candle Curing | Candle Testing |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Enhances fragrance throw and wax consistency | Evaluates burn performance and safety |
| Duration | Typically 3-7 days | Duration varies; usually several hours per test |
| Process | Store candles at room temperature to allow wax and fragrance to bind | Light candles to monitor burn time, flame size, and soot |
| Outcome | Improved scent throw and even burn | Identifies performance issues and safety concerns |
| Importance | Critical for optimal fragrance experience | Essential for quality control and compliance |
Understanding Candle Curing: What It Means
Candle curing refers to the process of allowing candles to rest after they are poured, enabling the wax and fragrance oils to fully bind and stabilize, which enhances scent throw and burn quality. This period varies depending on the wax type but typically ranges from 24 hours to several weeks, ensuring optimal fragrance diffusion and consistent performance. Understanding candle curing is essential for makers to produce high-quality candles that deliver a balanced and long-lasting aroma during use.
The Importance of Candle Testing in Quality Control
Candle testing plays a crucial role in quality control by ensuring consistent fragrance throw, burn time, and safety standards are met before products reach consumers. While candle curing allows wax and fragrance oils to fully meld over time, testing evaluates the candle's actual performance under controlled conditions. Accurate candle testing reduces defects, improves customer satisfaction, and confirms compliance with industry regulations.
Key Differences Between Candle Curing and Candle Testing
Candle curing involves allowing poured wax candles to solidify and stabilize over a set period, typically 1 to 2 weeks, ensuring optimal scent throw and burn quality. Candle testing refers to the process of burning the cured candles to evaluate performance factors such as flame stability, scent throw, and burn time. Key differences lie in curing improving candle quality through time-dependent chemical processes, while testing provides empirical data on the candle's functional characteristics.
How Proper Curing Influences Candle Performance
Proper candle curing enhances scent throw and burn quality by allowing the wax and fragrance oils to fully bind and stabilize, reducing issues like uneven burning or weak scent release. During the curing process, wax crystallization and fragrance retention improve, resulting in a consistent and stronger aroma when the candle is lit. Candle testing after curing confirms optimal performance, ensuring the candle meets safety and sensory standards before sale or use.
Candle Testing Methods: Techniques for Reliable Results
Candle testing methods such as burn time analysis, scent throw evaluation, and wick performance assessment provide reliable insights into candle quality and safety. Standardized procedures include testing in controlled environments, measuring burn duration, and observing soot production to ensure consistent results. Incorporating sensory tests and physical measurements guarantees accurate evaluation of fragrance diffusion and combustion efficiency.
Best Practices for Curing Candles Effectively
Candle curing involves allowing candles to solidify and mature over a specific period, usually ranging from 48 hours to two weeks, to enhance scent throw and burning quality. Best practices for curing include storing candles in a cool, dry environment away from direct sunlight and aggressive temperature changes, ensuring even wax crystallization and fragrance absorption. Candle testing follows curing and involves monitoring burn time, scent diffusion, and wick performance to confirm a safe and high-quality product.
Essential Equipment for Candle Testing
Candle testing requires essential equipment such as a wick trimmer, a thermometer, and a lightbox to evaluate burn performance, fragrance throw, and color consistency accurately. Precise testing tools help detect issues like tunneling, uneven burning, or scent diffusion, ensuring high-quality final products. Reliable candle testers also include a burn timer and an airflow-controlled environment to simulate optimal candle usage conditions.
Common Issues Detected During Candle Testing
Candle testing identifies common issues such as uneven burning, tunneling, excessive soot, and fragrance throw inconsistencies, which can signal problems with wax formulation or wick size. During candle curing, the wax solidifies and fragrance molecules bind properly, but testing reveals if the curing time was insufficient or environmental factors affected quality. Detecting these defects early during testing ensures the final product maintains optimal burn performance and scent diffusion for consumer satisfaction.
Optimizing Scent and Burn Through Curing and Testing
Candle curing enhances fragrance throw and burn quality by allowing wax and essential oils to meld over time, typically between 48 hours and two weeks, depending on wax type and scent load. Candle testing involves burning the candle in controlled conditions to evaluate scent diffusion, burn rate, and wick performance, ensuring optimal throw and minimizing soot or tunneling. Combining thorough curing with systematic testing maximizes scent potency and burn efficiency, resulting in a superior candle experience.
Integrating Curing and Testing into Your Candle Business Workflow
Integrating candle curing and testing into your candle business workflow enhances product quality by ensuring optimal scent throw and burn performance before market release. Proper curing time allows wax and fragrance oils to bind effectively, while systematic testing verifies consistency and safety standards, reducing customer complaints and returns. Streamlining these processes within production schedules increases efficiency and builds consumer trust through reliable, high-quality candles.
Candle curing vs Candle testing Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com