Cure time is essential for candles to develop optimal scent throw and burn quality, allowing the wax and fragrance oils to fully bind. Burn time refers to how long a candle can safely and effectively burn, which depends on factors like wax type, wick size, and candle shape. Properly cured candles generally offer longer, cleaner burns with enhanced fragrance release.
Table of Comparison
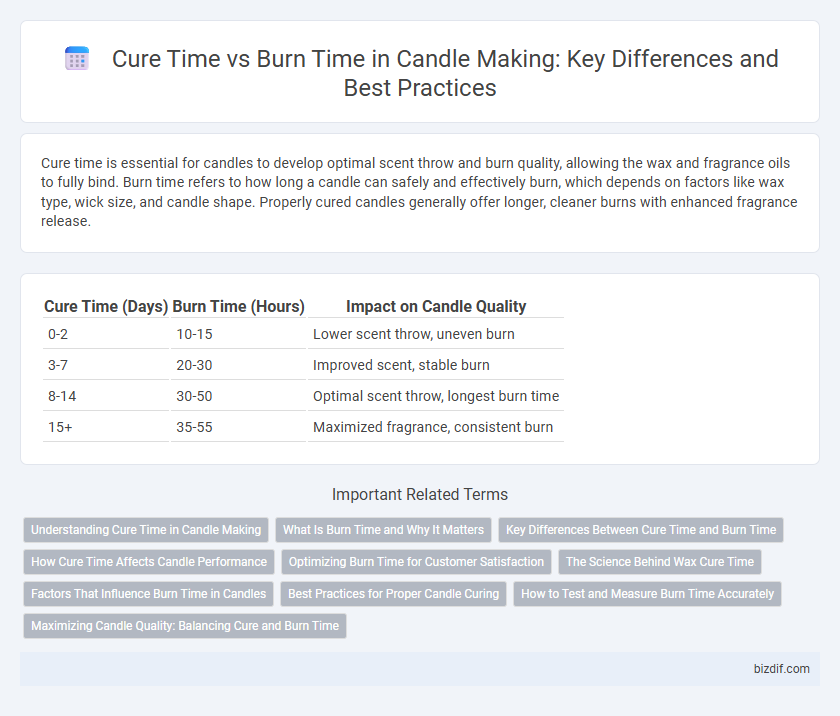
| Cure Time (Days) | Burn Time (Hours) | Impact on Candle Quality |
|---|---|---|
| 0-2 | 10-15 | Lower scent throw, uneven burn |
| 3-7 | 20-30 | Improved scent, stable burn |
| 8-14 | 30-50 | Optimal scent throw, longest burn time |
| 15+ | 35-55 | Maximized fragrance, consistent burn |
Understanding Cure Time in Candle Making
Cure time in candle making refers to the period needed for the wax and fragrance oils to fully bind and stabilize, typically ranging from 48 to 72 hours. Proper cure time enhances scent throw and burn quality, resulting in a more consistent and longer-lasting flame during burn time. Skipping or shortening cure time can lead to weak fragrance release and uneven burning, affecting the overall candle performance.
What Is Burn Time and Why It Matters
Burn time refers to the duration a candle can continuously burn before extinguishing, crucial for evaluating candle performance and user experience. It depends on factors such as wax type, wick size, and candle dimensions, directly influencing how long the candle provides light and fragrance. Understanding burn time helps consumers select candles that match their desired usage and ensures manufacturers create products with consistent quality and safety standards.
Key Differences Between Cure Time and Burn Time
Cure time in candle making refers to the period required for the wax and fragrance oils to fully set and blend, typically lasting from 24 to 48 hours or longer depending on the wax type. Burn time denotes the total duration a candle can safely and effectively burn, influenced by factors such as candle size, wax composition, and wick type. Understanding the key differences ensures optimal scent throw and candle performance, with cure time affecting fragrance diffusion and burn time determining usage longevity.
How Cure Time Affects Candle Performance
Cure time significantly impacts candle performance by allowing wax and fragrance oils to fully bind, enhancing scent throw and burn consistency. Proper cure time, typically 48-72 hours or more, ensures an even melt pool and reduces tunneling during burn time. Insufficient cure time can lead to weak fragrance diffusion and uneven burning, diminishing overall candle quality.
Optimizing Burn Time for Customer Satisfaction
Cure time significantly affects candle performance, as fully cured candles deliver a cleaner and longer burn time by allowing wax and fragrance oils to properly bind. Optimizing burn time involves balancing wax type, cure duration, and wick size to enhance scent throw and minimize tunneling, thereby elevating customer satisfaction. Properly cured candles ensure efficient fuel usage, consistent flame, and a more enjoyable aromatic experience for consumers.
The Science Behind Wax Cure Time
Wax cure time significantly influences candle burn quality by allowing solvents, additives, and moisture to evenly distribute and stabilize within the wax matrix. During this period, the crystalline structure of the wax forms optimally, enhancing fragrance throw and reducing issues like tunneling or uneven burning. Research shows that a proper cure time of 1 to 2 weeks maximizes the wax's molecular integration, resulting in a consistent, longer-lasting flame and improved scent release during the candle's burn time.
Factors That Influence Burn Time in Candles
Burn time in candles is influenced by factors such as wax type, wick size, and environmental conditions, which directly affect how long a candle will last when lit. Cure time, the period needed for the wax and fragrance to fully set, enhances scent throw and ensures even burning but does not extend the burn duration itself. Proper cure time optimizes the candle's performance, while factors like wax formulation, wick selection, and ambient airflow primarily determine the actual burn time.
Best Practices for Proper Candle Curing
Proper candle curing enhances scent throw and burn quality by allowing wax and fragrance oils to fully bind, requiring a minimum of 48 hours to several days depending on wax type. Paraffin candles typically need 24-48 hours curing, while soy and beeswax may benefit from 7-14 days for optimal scent diffusion and even burning. Storing candles in a cool, dry place during curing preserves fragrance integrity and prevents surface imperfections for a cleaner, longer-lasting burn time.
How to Test and Measure Burn Time Accurately
To accurately test and measure burn time, light the candle in a draft-free environment and record the duration until the wick extinguishes naturally, avoiding interruptions. Monitor the candle's melt pool and wick length throughout the burn to ensure consistent conditions, as irregularities can skew results. Use a stopwatch and maintain a detailed log of burn intervals during multiple tests to obtain an average burn time for reliable data.
Maximizing Candle Quality: Balancing Cure and Burn Time
Maximizing candle quality depends on balancing cure time and burn time to ensure optimal scent throw and wax performance. Allowing candles to cure for 1 to 2 weeks enhances fragrance diffusion and wax hardness, while an appropriate burn time of 2-4 hours per session prevents tunneling and maintains even melting. Properly managing these factors results in a longer-lasting, aesthetically pleasing candle with a consistent burn.
Cure time vs Burn time Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com