High ticket dropshipping in the pet niche involves selling premium products like high-end pet furniture or advanced grooming tools, resulting in higher profit margins per sale but lower purchase frequency. Low ticket dropshipping focuses on affordable pet items such as toys, collars, or treats, offering higher sales volume but smaller profits per transaction. Choosing between the two depends on your target audience, marketing strategy, and willingness to manage customer relationships and shipping complexities.
Table of Comparison
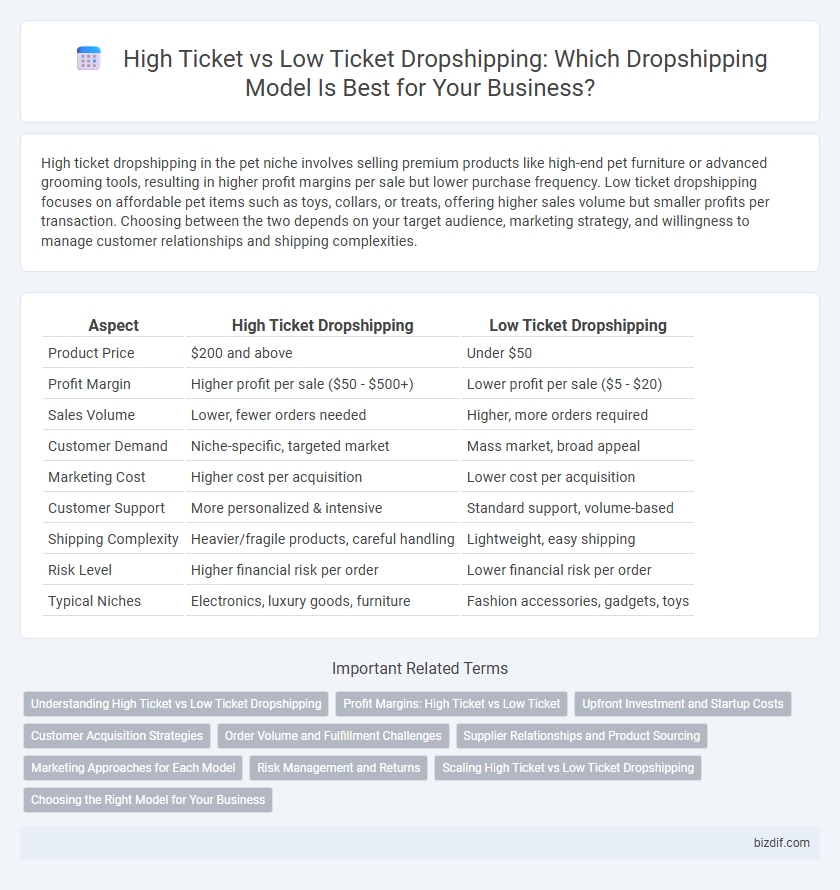
| Aspect | High Ticket Dropshipping | Low Ticket Dropshipping |
|---|---|---|
| Product Price | $200 and above | Under $50 |
| Profit Margin | Higher profit per sale ($50 - $500+) | Lower profit per sale ($5 - $20) |
| Sales Volume | Lower, fewer orders needed | Higher, more orders required |
| Customer Demand | Niche-specific, targeted market | Mass market, broad appeal |
| Marketing Cost | Higher cost per acquisition | Lower cost per acquisition |
| Customer Support | More personalized & intensive | Standard support, volume-based |
| Shipping Complexity | Heavier/fragile products, careful handling | Lightweight, easy shipping |
| Risk Level | Higher financial risk per order | Lower financial risk per order |
| Typical Niches | Electronics, luxury goods, furniture | Fashion accessories, gadgets, toys |
Understanding High Ticket vs Low Ticket Dropshipping
High ticket dropshipping involves selling expensive products with higher profit margins but typically lower sales volume, while low ticket dropshipping focuses on selling affordable items with lower profit margins and higher sales volume. Understanding the difference helps optimize inventory management, customer acquisition strategies, and marketing efforts for better revenue streams. Selecting the right model depends on market demand, supplier reliability, and capital investment capacity.
Profit Margins: High Ticket vs Low Ticket
High ticket dropshipping offers significantly higher profit margins per sale, often ranging from $100 to $500 or more, compared to low ticket dropshipping where profit margins typically fall between $5 and $30. Although low ticket dropshipping requires higher sales volume to generate substantial income, high ticket dropshipping demands fewer sales to achieve similar or greater profits due to elevated product prices. Entrepreneurs should balance marketing costs and conversion rates when choosing between high ticket and low ticket dropshipping models to maximize overall profitability.
Upfront Investment and Startup Costs
High ticket dropshipping requires a higher upfront investment due to the cost of premium products and targeted marketing campaigns, often exceeding $1,000 before generating sales. Low ticket dropshipping demands significantly lower startup costs, frequently under $500, making it accessible for beginners with limited budgets. Managing cash flow is crucial in high ticket models, while low ticket dropshipping benefits from faster inventory turnover despite slimmer profit margins.
Customer Acquisition Strategies
High ticket dropshipping relies heavily on targeted advertising and personalized marketing to attract high-value customers willing to invest in premium products, emphasizing quality over quantity in acquisition strategies. Low ticket dropshipping focuses on volume-driven approaches, utilizing social media ads, influencers, and SEO to capture a larger audience seeking affordable and frequently purchased items, optimizing for customer retention and repeat sales. Both strategies require distinct budget allocations and customer journey mapping to maximize conversion rates and profitability.
Order Volume and Fulfillment Challenges
High ticket dropshipping typically involves lower order volume due to higher product prices, reducing the frequency of sales but increasing profit margins per order. Low ticket dropshipping sees higher order volumes with affordable products, leading to more frequent transactions but requiring efficient fulfillment systems to handle increased workload. Managing shipping times and customer service becomes more complex in low ticket models, while high ticket dropshipping demands stringent quality control and personalized customer support to justify the premium price.
Supplier Relationships and Product Sourcing
High ticket dropshipping often requires establishing strong, reliable relationships with suppliers who can consistently provide premium products and handle large order volumes with quality assurance. In contrast, low ticket dropshipping involves sourcing cheaper products from a wide range of suppliers, prioritizing quantity and variety over personalized supplier management. Building solid supplier partnerships is crucial in high ticket models to ensure trust, exclusivity, and better margins, whereas low ticket models focus more on rapid product turnover and minimizing sourcing costs.
Marketing Approaches for Each Model
High ticket dropshipping marketing focuses on targeted advertising, personalized customer service, and building brand authority through detailed product descriptions and quality visuals to justify higher price points. Low ticket dropshipping relies on high-volume sales strategies, leveraging social media ads, influencer marketing, and frequent promotions to drive impulse purchases and fast turnover. Each approach tailors its advertising channels and customer engagement techniques to optimize conversion rates based on product value and audience behavior.
Risk Management and Returns
High ticket dropshipping involves selling expensive products with higher profit margins but increased financial risk due to larger upfront costs and potential losses from returns. Low ticket dropshipping reduces risk by focusing on affordable items with lower profit per sale, minimizing the impact of returns and customer dissatisfaction. Effective risk management in dropshipping requires balancing product price points with return rates to maintain sustainable cash flow and customer trust.
Scaling High Ticket vs Low Ticket Dropshipping
High ticket dropshipping offers higher profit margins per sale, enabling faster scaling with fewer transactions and reduced customer service demands compared to low ticket dropshipping, which requires high volume sales to achieve comparable revenue. Scaling high ticket dropshipping often involves targeted marketing strategies, personalized customer experiences, and building strong supplier relationships to ensure product quality and reliability. Low ticket dropshipping scaling relies heavily on automated systems, extensive product listings, and optimizing conversion rates to maintain profitability across numerous small transactions.
Choosing the Right Model for Your Business
High ticket dropshipping involves selling expensive products with higher profit margins per sale, making it suitable for businesses targeting niche markets and willing to invest in personalized customer service. Low ticket dropshipping focuses on high-volume sales of affordable products, ideal for entrepreneurs aiming for quick turnover and broader market reach. Selecting the right model depends on your capital, marketing strategy, supplier relationships, and customer acquisition capabilities to maximize profitability and sustainability.
High Ticket Dropshipping vs Low Ticket Dropshipping Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com