Cross-docking minimizes storage time by directly transferring goods from inbound to outbound transportation, reducing inventory costs and speeding up order fulfillment. Traditional warehousing involves storing products for longer periods, offering greater inventory control but requiring more space and higher handling expenses. Choosing between cross-docking and traditional warehousing depends on product type, demand variability, and supply chain efficiency priorities.
Table of Comparison
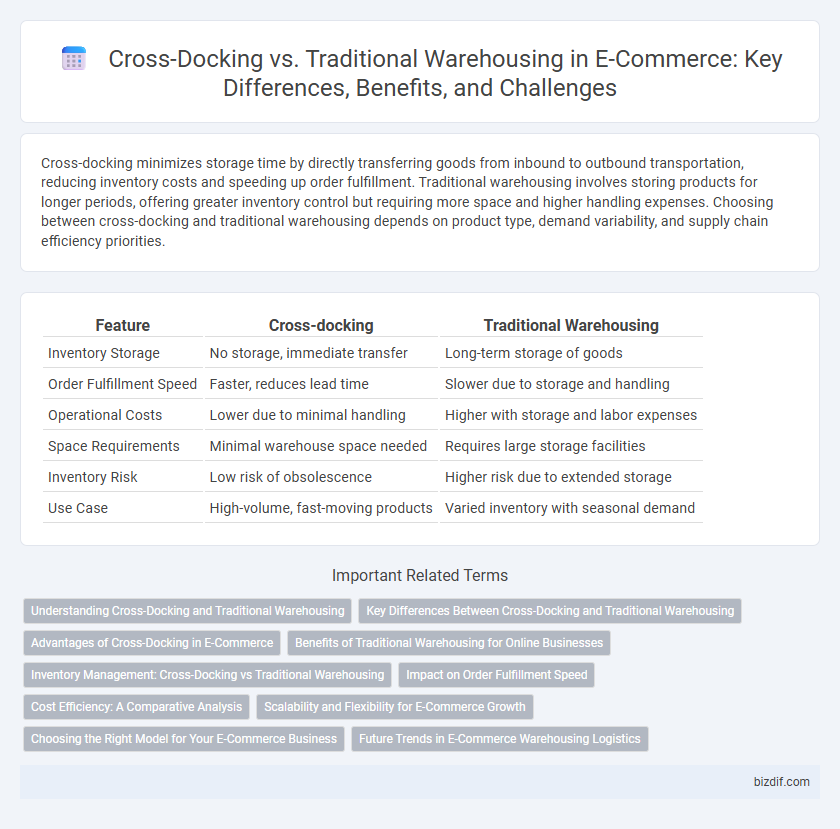
| Feature | Cross-docking | Traditional Warehousing |
|---|---|---|
| Inventory Storage | No storage, immediate transfer | Long-term storage of goods |
| Order Fulfillment Speed | Faster, reduces lead time | Slower due to storage and handling |
| Operational Costs | Lower due to minimal handling | Higher with storage and labor expenses |
| Space Requirements | Minimal warehouse space needed | Requires large storage facilities |
| Inventory Risk | Low risk of obsolescence | Higher risk due to extended storage |
| Use Case | High-volume, fast-moving products | Varied inventory with seasonal demand |
Understanding Cross-Docking and Traditional Warehousing
Cross-docking is a logistics practice where incoming goods are directly transferred from inbound to outbound transportation with minimal storage time, reducing inventory holding costs and speeding up delivery. Traditional warehousing involves storing products for extended periods, managing inventory levels, and supporting order fulfillment through picking, packing, and shipping processes. Understanding these models helps e-commerce businesses optimize supply chain efficiency, balancing speed with inventory management.
Key Differences Between Cross-Docking and Traditional Warehousing
Cross-docking minimizes inventory holding by directly transferring products from inbound to outbound transportation, accelerating order fulfillment and reducing storage costs. Traditional warehousing involves storing goods for extended periods, enabling inventory buffering but increasing storage expenses and handling times. Key differences include inventory turnover rates, space utilization, and the speed of product movement within the supply chain.
Advantages of Cross-Docking in E-Commerce
Cross-docking in e-commerce significantly reduces inventory holding costs by minimizing storage time, allowing products to move swiftly from suppliers to customers. This method enhances order fulfillment speed and accuracy, which leads to improved customer satisfaction and reduced delivery times. Efficient use of cross-docking helps e-commerce businesses lower operational expenses while optimizing supply chain responsiveness and scalability.
Benefits of Traditional Warehousing for Online Businesses
Traditional warehousing offers online businesses robust inventory management, enabling precise stock control that reduces the risk of stockouts and overstock situations. It supports bulk storage, facilitating cost savings through economies of scale and allowing businesses to manage seasonal demand effectively. This method enhances order accuracy and fulfillment reliability, contributing to improved customer satisfaction in e-commerce operations.
Inventory Management: Cross-Docking vs Traditional Warehousing
Cross-docking minimizes inventory holding by directly transferring products from inbound to outbound shipments, reducing storage needs and improving inventory turnover rates. Traditional warehousing requires maintaining significant stock levels, which can increase carrying costs and risk of obsolescence. Efficient inventory management in cross-docking enhances order fulfillment speed, while traditional warehousing supports bulk storage and buffer stock for demand variability.
Impact on Order Fulfillment Speed
Cross-docking significantly accelerates order fulfillment speed by minimizing inventory holding time and enabling direct transfer of goods from inbound to outbound transportation. Traditional warehousing involves longer processing times due to storage, picking, and replenishment activities, which can delay shipments. Implementing cross-docking reduces lead times, enhances supply chain responsiveness, and improves customer satisfaction in e-commerce operations.
Cost Efficiency: A Comparative Analysis
Cross-docking significantly reduces storage costs by minimizing inventory holding time, leading to lower warehousing expenses compared to traditional warehousing that requires maintaining large stock levels. Traditional warehousing incurs costs tied to extensive space rental, labor for inventory management, and prolonged storage duration, increasing overall operational expenses. Cross-docking streamlines order fulfillment and transportation efficiency, directly enhancing cost savings in e-commerce supply chains through rapid goods turnover and optimized logistics.
Scalability and Flexibility for E-Commerce Growth
Cross-docking enhances scalability by enabling rapid sorting and direct shipment of products, minimizing storage space and reducing handling time, which is critical for e-commerce growth with fluctuating order volumes. Traditional warehousing offers flexibility through inventory storage that supports bulk purchasing and seasonal stockpiling but may struggle with rapid scaling due to longer processing times and increased storage costs. E-commerce businesses experiencing fast growth benefit from cross-docking's streamlined operations and just-in-time inventory management while maintaining traditional warehousing for products requiring longer lead times and inventory buffers.
Choosing the Right Model for Your E-Commerce Business
Cross-docking minimizes storage costs and accelerates delivery by transferring products directly from inbound to outbound transportation, ideal for businesses prioritizing speed and reduced inventory holding. Traditional warehousing offers extensive stock management and order customization, suitable for e-commerce businesses requiring buffer inventory and complex order fulfillment. Selecting the right model involves analyzing order volume, product types, delivery speed expectations, and cost management strategies specific to your e-commerce operations.
Future Trends in E-Commerce Warehousing Logistics
Cross-docking reduces storage costs by transferring products directly from inbound to outbound transportation, enhancing speed in e-commerce order fulfillment. Traditional warehousing remains vital for inventory management and value-added services but faces increasing pressure from automation and real-time inventory tracking technologies. Future trends emphasize hybrid approaches integrating AI-driven demand forecasting and robotics to optimize space, reduce handling times, and support rapid delivery expectations in e-commerce logistics.
Cross-docking vs Traditional Warehousing Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com