Fact-checking ensures all information about pets is accurate and verifiable, focusing on data such as breed characteristics, health advice, and care requirements. Sensitivity reading in pet-related content identifies and corrects language or portrayals that might offend pet owners or marginalized groups, promoting inclusive and respectful communication. Both processes work together to create reliable and empathetic pet content that resonates with readers.
Table of Comparison
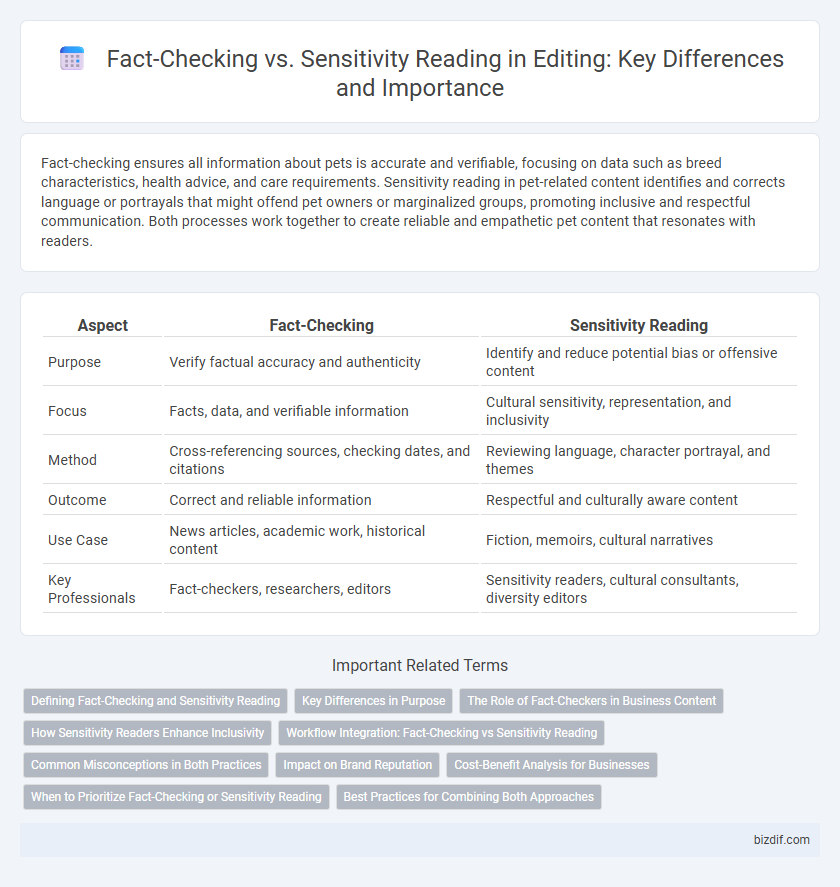
| Aspect | Fact-Checking | Sensitivity Reading |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Verify factual accuracy and authenticity | Identify and reduce potential bias or offensive content |
| Focus | Facts, data, and verifiable information | Cultural sensitivity, representation, and inclusivity |
| Method | Cross-referencing sources, checking dates, and citations | Reviewing language, character portrayal, and themes |
| Outcome | Correct and reliable information | Respectful and culturally aware content |
| Use Case | News articles, academic work, historical content | Fiction, memoirs, cultural narratives |
| Key Professionals | Fact-checkers, researchers, editors | Sensitivity readers, cultural consultants, diversity editors |
Defining Fact-Checking and Sensitivity Reading
Fact-checking involves verifying factual accuracy, dates, statistics, and claims within a text to ensure credibility and prevent misinformation. Sensitivity reading focuses on identifying and addressing potentially offensive content, stereotypes, or cultural inaccuracies to promote respectful and inclusive representation. Both processes enhance the quality and integrity of a manuscript but target different aspects of content evaluation.
Key Differences in Purpose
Fact-checking ensures the accuracy of factual information by verifying dates, statistics, and statements against reliable sources to prevent misinformation. Sensitivity reading focuses on identifying and addressing potential cultural, racial, or gender biases, stereotypes, and offensive content to promote respectful and inclusive narratives. The key difference lies in fact-checking validating truth and data, while sensitivity reading safeguards representation and ethical considerations in content.
The Role of Fact-Checkers in Business Content
Fact-checkers play a crucial role in business content by verifying data accuracy, ensuring credibility, and maintaining the integrity of published information. Their work helps prevent the spread of misinformation, protecting a company's reputation and fostering consumer trust. Unlike sensitivity reading, which focuses on cultural and social nuances, fact-checking centers on confirming factual correctness and source reliability.
How Sensitivity Readers Enhance Inclusivity
Sensitivity readers enhance inclusivity by identifying culturally specific biases and stereotypes that fact-checking might overlook, ensuring authentic and respectful representation. Their nuanced feedback addresses language, character portrayals, and cultural contexts, fostering diversity and reducing inadvertent harm in narratives. This process enriches the editorial quality by promoting empathy and accuracy in representing marginalized perspectives.
Workflow Integration: Fact-Checking vs Sensitivity Reading
Fact-checking integrates into the editing workflow by systematically verifying factual information, dates, and sources to ensure accuracy and credibility. Sensitivity reading fits as a targeted review phase where manuscripts are examined for cultural, racial, or social biases, enhancing inclusivity without altering core content. Both processes complement each other by addressing distinct aspects of content integrity and ethical responsibility within editorial operations.
Common Misconceptions in Both Practices
Fact-checking is often misunderstood as solely verifying factual accuracy, but it also involves assessing the credibility of sources and context relevance. Sensitivity reading is commonly mistaken for censorship, whereas its primary goal is to identify and address potential cultural insensitivities or harmful stereotypes. Both practices require critical attention to detail but serve distinct purposes: fact-checking ensures truthfulness, and sensitivity reading promotes respectful representation.
Impact on Brand Reputation
Fact-checking ensures the accuracy and credibility of published content, directly protecting a brand's trustworthiness and authority in its industry. Sensitivity reading identifies potential cultural, social, or ethical issues that could offend audiences or spark controversy, thereby preventing negative publicity and enhancing brand inclusivity. Together, these editing processes safeguard brand reputation by promoting both factual reliability and respectful communication.
Cost-Benefit Analysis for Businesses
Fact-checking ensures accuracy and credibility by verifying data, which reduces the risk of misinformation and potential legal issues, ultimately safeguarding a business's reputation. Sensitivity reading mitigates cultural insensitivity and potential backlash by identifying biased or offensive content, enhancing brand inclusivity and customer trust. Businesses must weigh the higher immediate costs of sensitivity reading against the long-term benefits of broader market appeal, while fact-checking presents more quantifiable risk management advantages.
When to Prioritize Fact-Checking or Sensitivity Reading
Prioritize fact-checking when verifying accuracy, data integrity, and factual claims to ensure content credibility and avoid misinformation. Opt for sensitivity reading when addressing cultural, racial, gender, or identity representations to prevent stereotypes, biases, and offensive language. Balancing fact-checking in early manuscript stages with sensitivity reading during content refinement enhances both accuracy and inclusivity.
Best Practices for Combining Both Approaches
Fact-checking ensures accuracy by verifying factual information, while sensitivity reading addresses cultural, social, and ethical nuances to prevent bias and misrepresentation. Combining both practices involves establishing clear workflows where fact-checkers validate data and sensitivity readers assess context-specific concerns, promoting integrity and inclusivity in content. Utilizing collaborative tools and diverse expert teams enhances thorough review processes, leading to reliable and respectful publications.
Fact-checking vs Sensitivity reading Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com