Cottage industry handicraft pets offer unique, artisanal qualities with intricate details reflecting skilled craftsmanship, contrasting sharply with factory-based manufacturing that prioritizes mass production and uniformity. The cottage approach supports local economies and preserves traditional techniques, while factory methods enable large-scale distribution and consistent product standards. Consumers seeking personalized and eco-friendly options often prefer cottage industry products over factory-made counterparts.
Table of Comparison
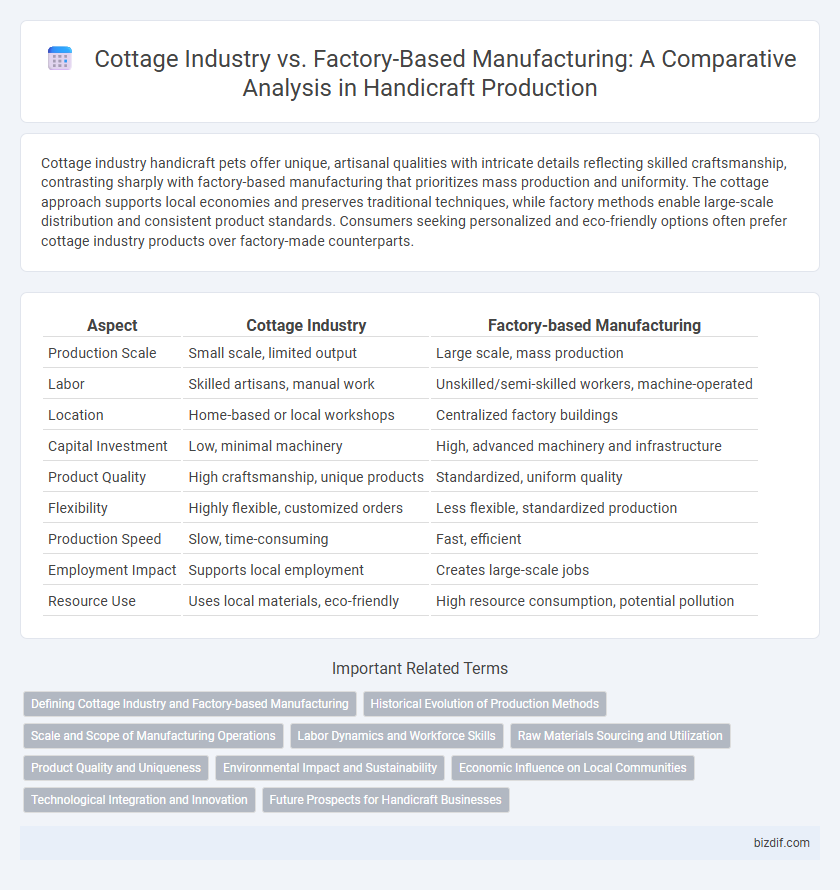
| Aspect | Cottage Industry | Factory-based Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|
| Production Scale | Small scale, limited output | Large scale, mass production |
| Labor | Skilled artisans, manual work | Unskilled/semi-skilled workers, machine-operated |
| Location | Home-based or local workshops | Centralized factory buildings |
| Capital Investment | Low, minimal machinery | High, advanced machinery and infrastructure |
| Product Quality | High craftsmanship, unique products | Standardized, uniform quality |
| Flexibility | Highly flexible, customized orders | Less flexible, standardized production |
| Production Speed | Slow, time-consuming | Fast, efficient |
| Employment Impact | Supports local employment | Creates large-scale jobs |
| Resource Use | Uses local materials, eco-friendly | High resource consumption, potential pollution |
Defining Cottage Industry and Factory-based Manufacturing
Cottage industry refers to small-scale, home-based production where artisans create handmade goods using traditional techniques and minimal machinery, emphasizing craftsmanship and local materials. Factory-based manufacturing involves large-scale production in centralized facilities, utilizing automated machinery and assembly lines to achieve high volume and standardized products. The key differences lie in scale, technology use, and the degree of manual skill versus mechanization in production processes.
Historical Evolution of Production Methods
The historical evolution of production methods reveals a shift from cottage industries, where skilled artisans crafted goods individually at home, to factory-based manufacturing characterized by mechanization and mass production. Cottage industries thrived during pre-industrial times, emphasizing handcrafted quality and local resource use, while the Industrial Revolution introduced centralized factories that boosted output and standardized products. This transition significantly impacted labor patterns, economic structures, and the scalability of handicraft production.
Scale and Scope of Manufacturing Operations
Cottage industry manufacturing operates on a small scale with limited scope, often involving handcrafted products made by individual artisans or small groups. Factory-based manufacturing supports large-scale production with extensive scope, utilizing mechanized processes and assembly lines to produce standardized goods in high volumes. The contrast in scale and scope significantly impacts efficiency, product consistency, and market reach between the two manufacturing models.
Labor Dynamics and Workforce Skills
Cottage industry labor dynamics emphasize skilled artisanship with craftsmen often mastering multiple production stages, fostering creativity and high-quality output. Factory-based manufacturing relies on specialized labor divisions, where workers perform repetitive tasks, enhancing efficiency and production speed but limiting skill variety. This contrast influences workforce development, with cottage industries nurturing versatile talents and factories prioritizing streamlined, skill-specific training.
Raw Materials Sourcing and Utilization
Cottage industry handcrafting relies heavily on locally sourced raw materials, prioritizing sustainable and limited resource utilization to create unique, high-quality products. In contrast, factory-based manufacturing sources raw materials on a large scale, often from global suppliers, enabling mass production but sometimes sacrificing material authenticity. Efficient raw material utilization in factories focuses on minimizing waste through mechanization, whereas cottage industries emphasize manual skill, often resulting in higher material integrity and less environmental impact.
Product Quality and Uniqueness
Cottage industry handicrafts emphasize superior product quality and uniqueness through skilled artisanship and personalized attention to detail, resulting in one-of-a-kind items. Factory-based manufacturing prioritizes high-volume production with standardized processes, often compromising on intricate details and individual craftsmanship. The distinctiveness and artisanal value inherent in cottage industry products often surpass mass-produced factory goods, appealing to niche markets seeking authenticity.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Cottage industries typically generate lower carbon emissions and produce less industrial waste compared to factory-based manufacturing, making them more environmentally sustainable. The use of traditional, manual techniques in handicrafts promotes resource efficiency and reduces dependency on non-renewable energy sources. In contrast, factory-based manufacturing often involves large-scale resource consumption and pollution, posing significant sustainability challenges.
Economic Influence on Local Communities
Cottage industries preserve traditional handicraft skills and empower local artisans by generating employment within rural communities, fostering economic self-reliance and cultural heritage. Factory-based manufacturing often leads to higher production volumes but may centralize economic benefits, reducing income opportunities for individual craftsmen and impacting local economies adversely. The economic influence of handicraft cottage industries is significant in sustaining small-scale entrepreneurship and promoting equitable wealth distribution in local regions.
Technological Integration and Innovation
Cottage industry in handicrafts relies primarily on traditional skills and manual tools, fostering unique, artisanal products with limited technological integration. Factory-based manufacturing incorporates advanced machinery and automation, enabling mass production, consistent quality, and innovative design techniques through computer-aided manufacturing (CAM). The fusion of digital tools and handcrafted methods in factories accelerates product development while preserving cultural craftsmanship elements.
Future Prospects for Handicraft Businesses
Handicraft businesses rooted in cottage industry models emphasize personalized craftsmanship and sustainable practices, offering unique value in a market increasingly driven by authenticity and eco-conscious consumers. Factory-based manufacturing provides scalability and cost efficiency but often lacks the distinctiveness and cultural heritage that handcrafted products embody, attracting niche segments seeking exclusivity. Future prospects for handicraft businesses lie in integrating digital platforms for global reach, leveraging artisanal narratives, and adopting hybrid production techniques to balance tradition with innovation.
Cottage Industry vs Factory-based Manufacturing Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com