Craft guilds historically established standardized techniques and quality controls, fostering collaboration and shared resources among members, which ensured consistent craftsmanship and market reliability. Independent artisans operate with greater creative freedom, allowing for innovative and unique designs that reflect personal artistry but often lack the collective support and networking advantages of guilds. Both models play vital roles in the handicraft industry, balancing tradition and innovation to meet diverse consumer demands.
Table of Comparison
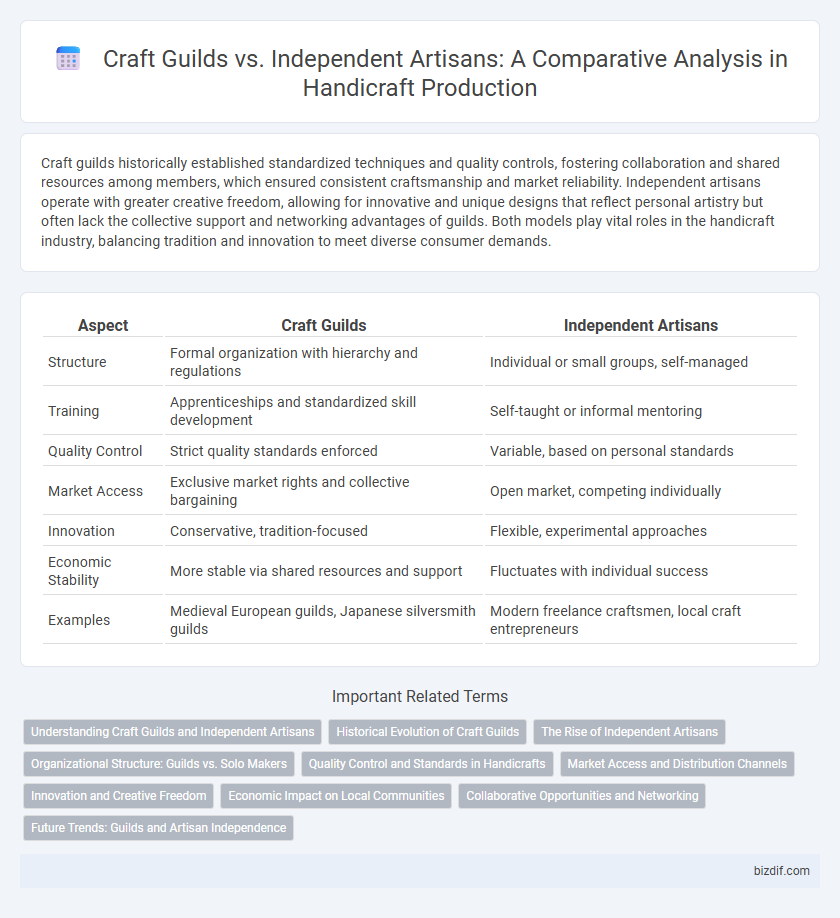
| Aspect | Craft Guilds | Independent Artisans |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Formal organization with hierarchy and regulations | Individual or small groups, self-managed |
| Training | Apprenticeships and standardized skill development | Self-taught or informal mentoring |
| Quality Control | Strict quality standards enforced | Variable, based on personal standards |
| Market Access | Exclusive market rights and collective bargaining | Open market, competing individually |
| Innovation | Conservative, tradition-focused | Flexible, experimental approaches |
| Economic Stability | More stable via shared resources and support | Fluctuates with individual success |
| Examples | Medieval European guilds, Japanese silversmith guilds | Modern freelance craftsmen, local craft entrepreneurs |
Understanding Craft Guilds and Independent Artisans
Craft guilds historically organized artisans into structured communities that regulated standards, training, and market access, fostering skill development and quality control. Independent artisans operate without guild oversight, allowing greater creative freedom and direct engagement with customers but often facing challenges in marketing and resource acquisition. Understanding the balance between guild support and independent autonomy highlights the dynamic nature of handicraft production and economic sustainability.
Historical Evolution of Craft Guilds
Craft guilds emerged during the medieval period as structured organizations that regulated skills, quality, and trade secrets among artisans, fostering community standards and collective bargaining power. Unlike independent artisans who earned income on individual merit and market demand, guild members benefited from shared resources, apprenticeships, and protection within urban economies. The decline of craft guilds in the early modern era coincided with the rise of industrialization and the shift towards individualized craftsmanship and mass production.
The Rise of Independent Artisans
The rise of independent artisans reflects a significant shift from traditional craft guilds, emphasizing personal creativity and direct market engagement over rigid regulations. Independent artisans utilize modern digital platforms to showcase and sell their work globally, bypassing guild-imposed restrictions and broadening their customer base. This movement fosters innovation and diversification within handicrafts, empowering creators to develop unique, culturally infused products.
Organizational Structure: Guilds vs. Solo Makers
Craft guilds operate under a hierarchical organizational structure, establishing strict regulations, apprenticeship systems, and quality standards that govern members' work and production methods. Independent artisans function as solo makers, managing all aspects of their craft autonomously without external oversight, allowing for greater flexibility and individual creativity. The guild model emphasizes collective identity and tradition preservation, while solo artisans prioritize personalized craftsmanship and direct client relationships.
Quality Control and Standards in Handicrafts
Craft guilds historically implemented strict quality control and standardized techniques to maintain the reputation of handicrafts, ensuring consistency and skilled workmanship across their members. Independent artisans often prioritize unique, personalized creations, which can lead to variable quality but foster innovation and artistic expression. The balance between guild-enforced standards and the flexibility of independent craftsmanship shapes the diversity and evolution of handicraft traditions worldwide.
Market Access and Distribution Channels
Craft guilds historically controlled market access and distribution channels by regulating production quality and limiting competition, ensuring member artisans had exclusive rights to sell within specific regions. Independent artisans often faced challenges entering broader markets due to these guild-imposed restrictions but sometimes utilized informal networks and direct-to-consumer sales to reach buyers. Digital platforms and local artisan fairs now increasingly empower independent creators by providing diversified, accessible channels beyond traditional guild monopolies.
Innovation and Creative Freedom
Craft guilds historically maintained strict regulations that limited innovation by enforcing traditional techniques and standardized designs, thereby constraining creative freedom. Independent artisans, free from guild constraints, often experiment with new materials, styles, and methods, fostering greater innovation and artistic expression. This autonomy enables independent crafters to respond rapidly to market trends and personal inspiration, driving unique and innovative handicraft creations.
Economic Impact on Local Communities
Craft guilds historically structured local economies by regulating production quality and prices, fostering collaborative markets that ensured steady income for members and stable supply chains. Independent artisans contribute to economic diversity by introducing innovative designs and flexible production methods, often attracting niche markets and boosting local tourism. Both models significantly impact local communities by generating employment opportunities and preserving cultural heritage through skilled craftsmanship.
Collaborative Opportunities and Networking
Craft guilds foster collaborative opportunities by uniting artisans under a shared identity, enabling resource pooling, skill exchange, and joint marketing efforts that amplify members' visibility. Independent artisans benefit from flexible networking that allows diverse partnerships across markets and innovative fusion of styles without guild constraints. Both frameworks offer unique pathways for growth: guilds emphasize collective strength and tradition, while independents pursue personalized connections and adaptive collaboration in evolving craft landscapes.
Future Trends: Guilds and Artisan Independence
Craft guilds are increasingly adopting digital platforms to enhance collaboration and market reach, blending traditional techniques with modern technology to maintain relevance. Independent artisans leverage social media and e-commerce to build personal brands and access global markets, promoting unique, customized products. The future of handicrafts involves a dynamic balance where guilds provide structured skill development and community support, while independent artisans drive innovation and niche specialization.
Craft guilds vs Independent artisans Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com