Handicraft pet products prioritize ethical production by supporting skilled artisans and using sustainable materials, ensuring each item is made with care and respect for the environment. This approach contrasts sharply with fast fashion's mass production methods that often exploit labor and generate excessive waste. Choosing handicraft pet items promotes responsible consumption and helps preserve traditional craftsmanship.
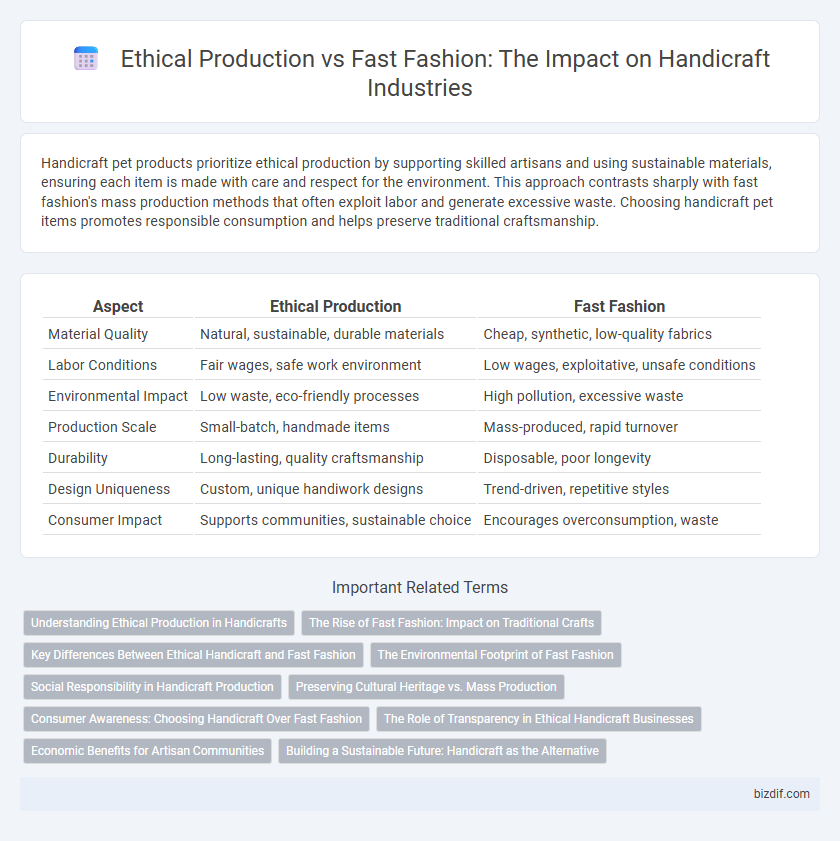
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Ethical Production | Fast Fashion |
|---|---|---|
| Material Quality | Natural, sustainable, durable materials | Cheap, synthetic, low-quality fabrics |
| Labor Conditions | Fair wages, safe work environment | Low wages, exploitative, unsafe conditions |
| Environmental Impact | Low waste, eco-friendly processes | High pollution, excessive waste |
| Production Scale | Small-batch, handmade items | Mass-produced, rapid turnover |
| Durability | Long-lasting, quality craftsmanship | Disposable, poor longevity |
| Design Uniqueness | Custom, unique handiwork designs | Trend-driven, repetitive styles |
| Consumer Impact | Supports communities, sustainable choice | Encourages overconsumption, waste |
Understanding Ethical Production in Handicrafts
Ethical production in handicrafts emphasizes sustainable sourcing, fair labor practices, and preserving traditional techniques to create high-quality, culturally significant products. This approach contrasts sharply with fast fashion, which prioritizes mass production, low costs, and rapid turnover, often at the expense of environmental and social responsibility. Consumers who support ethical handicrafts contribute to protecting artisans' livelihoods and fostering environmentally friendly, socially conscious supply chains.
The Rise of Fast Fashion: Impact on Traditional Crafts
The rise of fast fashion has significantly disrupted traditional handicraft industries by prioritizing mass production and speed over artisanal quality and ethical labor practices. This shift has led to diminished demand for handcrafted goods, threatening the livelihoods of skilled artisans and eroding cultural heritage embedded in traditional crafts. Ethical production emphasizes sustainable materials and fair wages, positioning handicrafts as a counterbalance to the environmental and social costs associated with fast fashion.
Key Differences Between Ethical Handicraft and Fast Fashion
Ethical handicraft emphasizes sustainable materials, fair wages, and preserving cultural heritage, while fast fashion prioritizes mass production, low costs, and trend replication. Handicraft products often feature unique, high-quality craftsmanship with lower environmental impact, contrasting with the rapid turnover and significant waste generated by fast fashion. Consumer demand for transparency and eco-consciousness drives the growth of ethical handicrafts, challenging the fast fashion industry's model.
The Environmental Footprint of Fast Fashion
Fast fashion significantly contributes to environmental degradation through excessive water consumption, chemical pollution, and textile waste. The rapid production cycles prioritize quantity over sustainability, resulting in increased carbon emissions and landfill overflow. In contrast, ethical handicraft practices emphasize sustainable materials and traditional methods that reduce the environmental footprint and promote resource conservation.
Social Responsibility in Handicraft Production
Ethical production in handicraft emphasizes fair wages, safe working conditions, and community empowerment, directly addressing social responsibility. Unlike fast fashion, which often exploits labor and overlooks environmental impact, handicraft production supports artisans' livelihoods and preserves cultural heritage. This sustainable approach fosters long-term social benefits and promotes transparent supply chains.
Preserving Cultural Heritage vs. Mass Production
Ethical production in handicrafts emphasizes preserving cultural heritage through traditional techniques and authentic materials, ensuring the continuation of artisanal skills passed down through generations. Fast fashion relies on mass production, prioritizing speed and cost-efficiency, which often leads to the dilution of cultural significance and loss of craftsmanship. Supporting ethical handicraft practices promotes sustainability and respects the cultural identity embedded in handmade products.
Consumer Awareness: Choosing Handicraft Over Fast Fashion
Consumer awareness has significantly shifted towards ethical production in handicraft, emphasizing sustainable materials and fair labor practices that fast fashion often neglects. Handicraft supports local artisans and reduces environmental impact through handmade, durable products rather than mass-produced, disposable clothing. Choosing handicraft promotes a conscious economy by valuing quality, cultural heritage, and social responsibility over rapid consumption trends.
The Role of Transparency in Ethical Handicraft Businesses
Transparency in ethical handicraft businesses fosters trust by openly sharing sourcing, labor practices, and environmental impact details with consumers. This clarity differentiates handcrafted products from fast fashion's opaque supply chains, emphasizing quality, sustainability, and fair wages. Transparent communication supports informed purchasing decisions that prioritize ethical production over mass-produced apparel.
Economic Benefits for Artisan Communities
Ethical production supports artisan communities by ensuring fair wages and promoting sustainable livelihoods, which fast fashion often neglects through mass production and low-cost labor exploitation. Investing in handicrafts preserves traditional skills, boosts local economies, and encourages cultural heritage that fast fashion's rapid turnover diminishes. Artisan-driven markets foster economic resilience and empower independent producers, creating long-term financial benefits beyond the short-term profits typical in fast fashion.
Building a Sustainable Future: Handicraft as the Alternative
Handicraft embraces ethical production by prioritizing fair wages, artisans' well-being, and environmentally friendly materials, contrasting sharply with fast fashion's exploitative labor practices and high waste output. This approach supports sustainable development through reduced carbon footprints and preservation of traditional skills, fostering economic resilience in local communities. Emphasizing slow, mindful consumption, handicraft paves the way for a sustainable future by balancing social responsibility with ecological integrity.
Ethical Production vs Fast Fashion Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com