Value-added crafts transform raw materials into unique, high-quality products that showcase skilled craftsmanship and creativity, significantly increasing their market value. Unlike raw material sales, which offer limited profit margins, value-added crafts create distinctive items that appeal to niche markets, enhancing customer satisfaction and brand loyalty. This approach supports sustainable economic growth by promoting artisanal heritage and encouraging innovation within the handicraft industry.
Table of Comparison
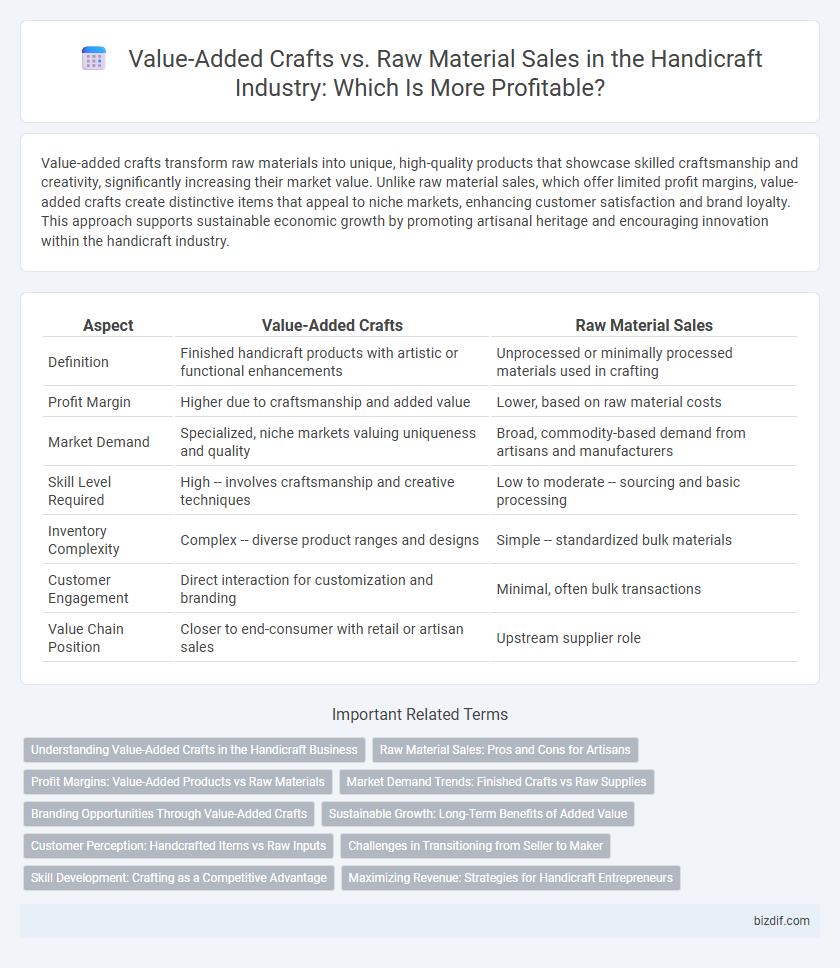
| Aspect | Value-Added Crafts | Raw Material Sales |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Finished handicraft products with artistic or functional enhancements | Unprocessed or minimally processed materials used in crafting |
| Profit Margin | Higher due to craftsmanship and added value | Lower, based on raw material costs |
| Market Demand | Specialized, niche markets valuing uniqueness and quality | Broad, commodity-based demand from artisans and manufacturers |
| Skill Level Required | High -- involves craftsmanship and creative techniques | Low to moderate -- sourcing and basic processing |
| Inventory Complexity | Complex -- diverse product ranges and designs | Simple -- standardized bulk materials |
| Customer Engagement | Direct interaction for customization and branding | Minimal, often bulk transactions |
| Value Chain Position | Closer to end-consumer with retail or artisan sales | Upstream supplier role |
Understanding Value-Added Crafts in the Handicraft Business
Value-added crafts in the handicraft business enhance raw materials through skilled artistry, increasing product uniqueness and market appeal. By transforming basic inputs into finished goods, artisans create higher profit margins compared to selling raw materials alone. This approach fosters brand differentiation and sustainable growth in competitive craft markets.
Raw Material Sales: Pros and Cons for Artisans
Raw material sales offer artisans quick liquidity and reduced labor intensity, enabling faster capital turnover without the need for intricate crafting processes. However, focusing solely on raw material sales limits profit margins and undervalues artisanal skills, often resulting in lower long-term income. Balancing raw material provision with value-added crafts can diversify income streams and enhance overall sustainability for artisans.
Profit Margins: Value-Added Products vs Raw Materials
Value-added crafts typically yield higher profit margins compared to raw material sales due to the increased labor, creativity, and unique design incorporated into the final product. Artisans who transform raw materials into handcrafted items can command premium prices, leveraging the perceived uniqueness and quality of their work. In contrast, selling raw materials generally involves lower returns, as these commodities face more competition and price sensitivity in the market.
Market Demand Trends: Finished Crafts vs Raw Supplies
Market demand trends indicate a growing preference for value-added crafts over raw material sales due to increasing consumer interest in unique, handcrafted products with distinctive designs and cultural significance. Finished crafts capture higher profit margins by meeting the desire for personalized and artisanal goods, while raw supplies face competitive pricing pressures and commodity market fluctuations. This shift drives artisans and businesses to focus on innovation and storytelling in finished products to differentiate themselves in a saturated marketplace.
Branding Opportunities Through Value-Added Crafts
Value-added crafts transform raw materials into unique, culturally-rich products that enhance brand identity and market differentiation. Artisans leveraging traditional techniques and innovative designs create compelling stories that resonate with consumers seeking authenticity and quality. This branding strategy increases perceived value, allowing for premium pricing and stronger customer loyalty compared to selling raw materials alone.
Sustainable Growth: Long-Term Benefits of Added Value
Value-added crafts significantly boost sustainable growth by transforming raw materials into unique, high-quality products that command higher market prices and foster brand loyalty. This process promotes resource efficiency and supports local economies through skilled labor, reducing dependency on volatile raw material markets. Emphasizing craftsmanship and innovation enhances product durability and cultural relevance, ensuring long-term benefits beyond short-term sales.
Customer Perception: Handcrafted Items vs Raw Inputs
Handcrafted items are perceived by customers as unique, high-quality products that embody creativity, skill, and cultural heritage, which often justify higher price points compared to raw material sales. Consumers value the authenticity and personalized touch in value-added crafts, associating them with greater emotional and aesthetic appeal. Raw materials, while essential, are seen as basic inputs lacking the distinctive character and storytelling found in finished handicraft products.
Challenges in Transitioning from Seller to Maker
Transitioning from raw material sales to value-added crafts presents significant challenges, including the need for advanced skills in design, production, and quality control, which raw material sellers often lack. Managing increased production costs, marketing finished products, and building a unique brand identity also hinder seamless progression. Limited access to market channels and insufficient knowledge of consumer preferences further complicate the shift from seller to maker in the handicraft industry.
Skill Development: Crafting as a Competitive Advantage
Value-added crafts enhance raw materials through specialized skills, increasing market value and fostering unique product identities. Mastering intricate techniques elevates artisans' expertise, enabling them to innovate and differentiate their offerings in competitive marketplaces. Skill development in crafting transforms basic resources into distinctive goods, driving economic growth and sustaining cultural heritage.
Maximizing Revenue: Strategies for Handicraft Entrepreneurs
Handicraft entrepreneurs maximize revenue by transforming raw materials into value-added crafts that command higher prices due to their uniqueness and craftsmanship. Implementing techniques such as customization, intricate detailing, and quality enhancement increases the perceived value, attracting premium customers. Prioritizing direct sales channels and storytelling marketing further boosts profit margins compared to selling raw materials alone.
Value-added crafts vs Raw material sales Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com