Handloom fabrics showcase intricate craftsmanship and unique textures created manually, offering superior quality and cultural value. Powerloom textiles enable mass production with consistent patterns and affordability, meeting large-scale demand efficiently. Choosing between handloom and powerloom depends on preferences for authenticity versus cost-effectiveness and production speed.
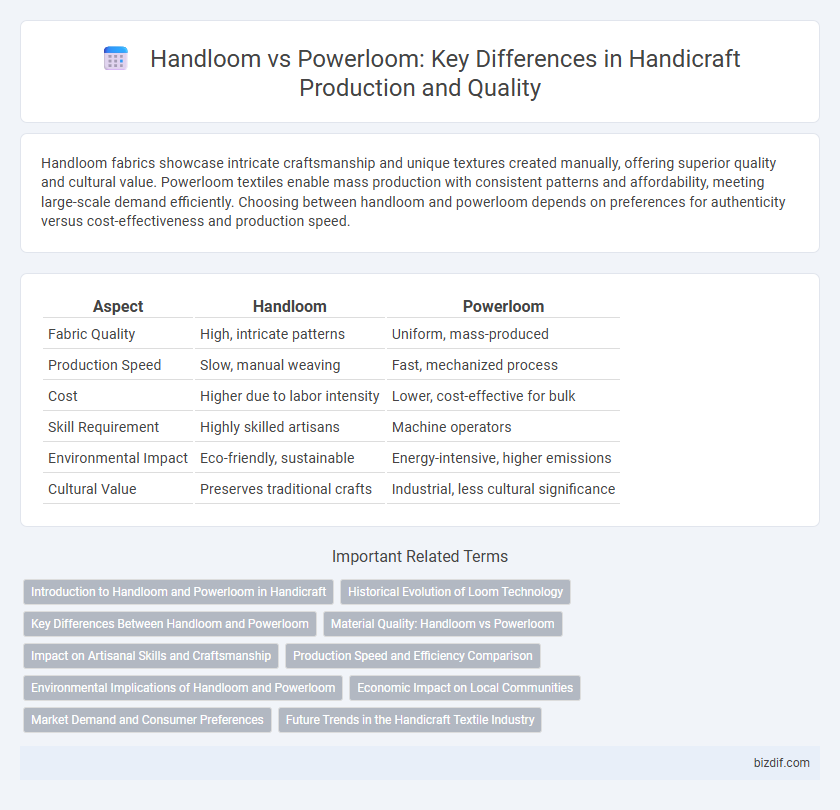
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Handloom | Powerloom |
|---|---|---|
| Fabric Quality | High, intricate patterns | Uniform, mass-produced |
| Production Speed | Slow, manual weaving | Fast, mechanized process |
| Cost | Higher due to labor intensity | Lower, cost-effective for bulk |
| Skill Requirement | Highly skilled artisans | Machine operators |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly, sustainable | Energy-intensive, higher emissions |
| Cultural Value | Preserves traditional crafts | Industrial, less cultural significance |
Introduction to Handloom and Powerloom in Handicraft
Handloom and powerloom represent two distinct methods of fabric weaving in handicraft, with handlooms relying on manual operation and intricate craftsmanship, producing unique, artisanal textiles rich in cultural heritage. Powerlooms utilize mechanized processes to enhance speed and efficiency, enabling large-scale production while often sacrificing the individual character and detailed artistry typical of handloom fabrics. The contrast between handloom and powerloom highlights the balance between tradition and industrialization in the textile handicraft sector.
Historical Evolution of Loom Technology
Handloom technology, dating back thousands of years, represents traditional, manual weaving methods that produced intricate, artisanal textiles with rich cultural significance. Powerlooms emerged during the Industrial Revolution, introducing mechanized weaving that dramatically increased production speed and volume while reducing human labor. The historical evolution from handlooms to powerlooms marks a critical shift in textile manufacturing, balancing craftsmanship with industrial efficiency.
Key Differences Between Handloom and Powerloom
Handloom fabric is created manually on traditional looms powered by human skill, resulting in unique, intricate patterns and limited production capacity. Powerloom fabric is produced using mechanized looms driven by electricity, enabling faster production and uniform texture but often less artisanal quality. Key differences include production speed, skill dependency, fabric texture, and environmental impact, with handlooms being eco-friendly and powerlooms relying on energy consumption.
Material Quality: Handloom vs Powerloom
Handloom fabrics are known for their superior material quality due to the use of natural fibers and meticulous craftsmanship, resulting in breathable, durable, and textured textiles. Powerloom fabrics, produced through mechanized weaving, often utilize synthetic blends that can compromise softness and durability but allow for mass production and uniformity. The choice between handloom and powerloom significantly impacts the fabric's tactile feel, longevity, and overall aesthetic appeal.
Impact on Artisanal Skills and Craftsmanship
Handloom weaving preserves intricate artisanal skills and traditional craftsmanship passed down through generations, fostering unique, handmade textile art with cultural significance. Powerloom production enhances efficiency and output but often sacrifices the fine detail and individuality characteristic of handloom products, leading to a decline in artisan craftsmanship. The sustainability of artisanal techniques depends heavily on supporting handloom industries that maintain the heritage and skill of handwoven textiles.
Production Speed and Efficiency Comparison
Handlooms produce textiles at a slower pace, weaving intricate patterns manually, which limits large-scale output but ensures unique craftsmanship. Powerlooms significantly enhance production speed, operating mechanized processes that yield higher fabric volumes efficiently and consistently. Efficiency in energy use and labor intensity is higher in powerlooms, making them preferred for mass production, while handlooms excel in artisanal value and detailed customization.
Environmental Implications of Handloom and Powerloom
Handlooms use manual labor and natural fibers, resulting in minimal carbon emissions and reduced energy consumption compared to powerlooms, which rely on electricity and synthetic materials, contributing to higher pollution levels. Handlooms promote sustainable practices by avoiding chemical dyes and minimizing waste, while powerlooms often involve resource-intensive production and increased environmental footprint. Emphasizing handloom production supports eco-friendly craftsmanship, conserving traditional techniques that align with low-impact ecological balance.
Economic Impact on Local Communities
Handloom weaving sustains local economies by providing employment to skilled artisans, preserving cultural heritage while generating income in rural areas. Powerloom production accelerates fabric output and lowers costs but often centralizes manufacturing, reducing job opportunities for traditional weavers. Balancing handloom and powerloom industries is crucial for economic resilience, supporting artisan livelihoods alongside industrial growth in textile regions.
Market Demand and Consumer Preferences
Handloom products attract niche markets valuing artisanal craftsmanship and sustainability, often commanding premium prices due to their uniqueness and cultural heritage. Powerloom fabrics dominate mass markets with consistent quality and affordability, meeting large-scale consumer demand for everyday wear and industrial applications. Consumer preferences increasingly favor handloom for eco-friendly fashion trends, while powerloom remains preferred for cost-effective and readily available textiles.
Future Trends in the Handicraft Textile Industry
Handloom and powerloom technologies are shaping the future trends of the handicraft textile industry through a blend of traditional craftsmanship and modern efficiency. Increasing consumer demand for sustainable and ethically produced textiles is driving innovation in eco-friendly raw materials and energy-efficient weaving processes. Digital integration and automation in powerloom manufacturing are enhancing productivity while preserving the unique aesthetic qualities that define handloom textiles.
Handloom vs Powerloom Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com