Fair trade gemstones ensure ethical mining practices, fair wages, and sustainable environmental impact, promoting transparency in jewelry making. Conventional sourcing often involves exploitative labor, environmental damage, and lack of accountability, risking harm to both miners and ecosystems. Choosing fair trade gemstones supports responsible artisanship and aligns with conscious consumer values in the jewelry industry.
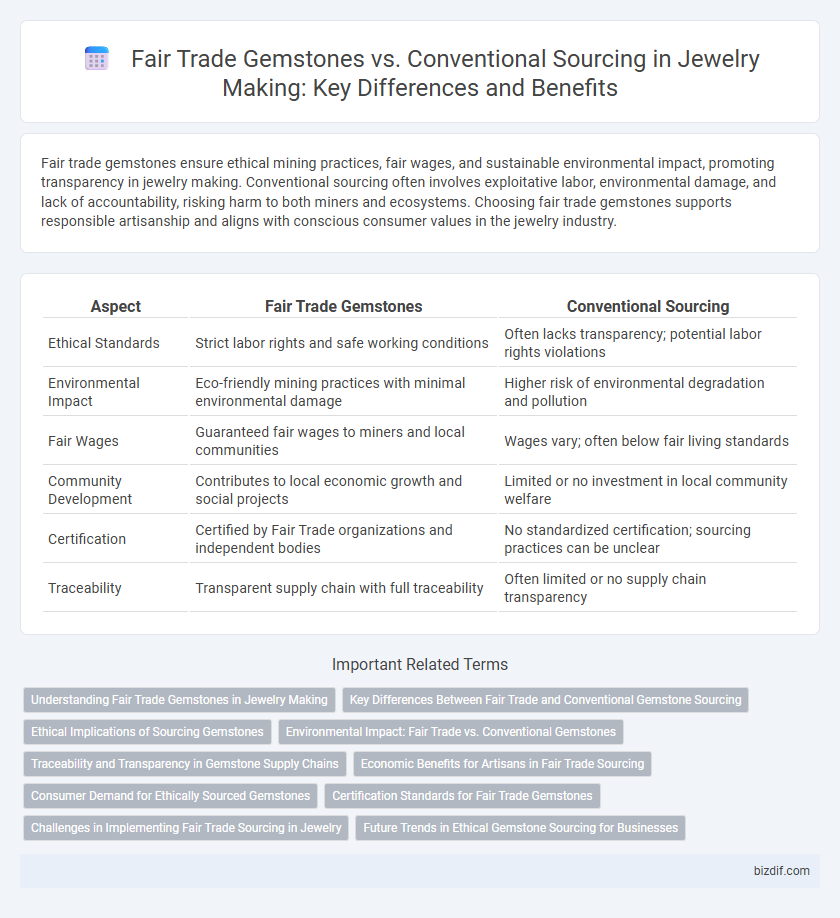
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Fair Trade Gemstones | Conventional Sourcing |
|---|---|---|
| Ethical Standards | Strict labor rights and safe working conditions | Often lacks transparency; potential labor rights violations |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly mining practices with minimal environmental damage | Higher risk of environmental degradation and pollution |
| Fair Wages | Guaranteed fair wages to miners and local communities | Wages vary; often below fair living standards |
| Community Development | Contributes to local economic growth and social projects | Limited or no investment in local community welfare |
| Certification | Certified by Fair Trade organizations and independent bodies | No standardized certification; sourcing practices can be unclear |
| Traceability | Transparent supply chain with full traceability | Often limited or no supply chain transparency |
Understanding Fair Trade Gemstones in Jewelry Making
Fair trade gemstones in jewelry making ensure ethical sourcing by guaranteeing miners fair wages, safe working conditions, and environmental sustainability. These gemstones are traceable and certified to prevent exploitation and illegal mining practices common in conventional sourcing. Incorporating fair trade gemstones promotes transparency and social responsibility in the jewelry supply chain.
Key Differences Between Fair Trade and Conventional Gemstone Sourcing
Fair trade gemstones are ethically mined with fair wages, safe working conditions, and environmental sustainability as core principles, contrasting sharply with conventional sourcing, where profit often overrides ethical and ecological concerns. Fair trade certification ensures transparency and community development, whereas conventional methods may involve exploitative labor, child labor, and environmental degradation. These key differences influence consumer trust, market demand, and the overall impact on mining communities worldwide.
Ethical Implications of Sourcing Gemstones
Fair trade gemstones ensure ethical sourcing by supporting miners with fair wages, safe working conditions, and environmentally sustainable practices, contrasting sharply with conventional sourcing often linked to exploitative labor and ecological damage. The gemstone jewelry industry increasingly values transparency in supply chains to uphold human rights and reduce conflict funding. Consumers prioritizing ethical implications actively seek certifications like Fairtrade or the Responsible Jewellery Council standards to promote fair labor and environmental stewardship.
Environmental Impact: Fair Trade vs. Conventional Gemstones
Fair trade gemstones ensure environmentally sustainable mining practices, reducing habitat destruction and minimizing the use of harmful chemicals compared to conventional sourcing, which often involves extensive ecological degradation. Fair trade initiatives prioritize restoring mined areas and promoting biodiversity, while conventional gemstone extraction frequently results in soil erosion, water pollution, and ecosystem imbalance. Choosing fair trade gemstones supports eco-friendly operations that mitigate long-term environmental harm and promote sustainable resource management.
Traceability and Transparency in Gemstone Supply Chains
Fair trade gemstones guarantee traceability and transparency through certified supply chains that document every step from mine to market, ensuring ethical sourcing and fair labor practices. Conventional sourcing often lacks comprehensive tracking, increasing risks of human rights abuses and environmental harm due to opaque supply chain operations. Enhanced traceability in fair trade gemstones enables consumers to verify ethical standards and supports sustainable mining communities, contrasting with the uncertainty prevalent in conventional gemstone procurement.
Economic Benefits for Artisans in Fair Trade Sourcing
Fair trade gemstones provide artisans with higher and more stable incomes compared to conventional sourcing, as fair trade practices ensure direct purchasing and premium prices. This economic benefit empowers artisans by enabling better investment in tools, skills, and community development projects. Enhanced financial security from fair trade sourcing promotes sustainable livelihoods and reduces dependency on exploitative middlemen.
Consumer Demand for Ethically Sourced Gemstones
Consumer demand for ethically sourced gemstones in jewelry making has surged, driven by increased awareness of fair trade practices and environmental impact. Fair trade gemstones ensure miners receive fair wages and work under safe conditions, contrasting with conventional sourcing often linked to exploitation and environmental harm. Brands offering certified ethical gemstones attract socially conscious buyers seeking transparency and sustainability in their jewelry purchases.
Certification Standards for Fair Trade Gemstones
Fair trade gemstones adhere to rigorous certification standards such as Fairtrade International and Fairmined, ensuring ethical mining practices, fair wages, and environmental sustainability. These certifications require transparent supply chains and independent audits, distinguishing fair trade gemstones from conventional sources that often lack accountability. Consumers choosing certified fair trade gemstones support community development and reduce exploitation in the jewelry making industry.
Challenges in Implementing Fair Trade Sourcing in Jewelry
Implementing fair trade sourcing in jewelry faces significant challenges such as higher costs and limited availability of certified gemstones compared to conventional sources. Supply chain transparency is difficult to achieve due to complex global mining operations and lack of standardized traceability systems. Ensuring ethical labor practices and environmental standards requires rigorous audits and collaboration with multiple stakeholders across diverse geographic regions.
Future Trends in Ethical Gemstone Sourcing for Businesses
Fair trade gemstones emphasize transparency, environmental responsibility, and equitable labor practices, setting new industry standards that conventional sourcing often overlooks. Growing consumer demand for ethically sourced jewelry drives businesses to adopt blockchain technology and certifications, ensuring traceability and authenticity in gemstone supply chains. Innovative practices such as lab-grown alternatives and community empowerment initiatives are shaping the future of sustainable and ethical gemstone sourcing.
Fair trade gemstones vs Conventional sourcing Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com