Heat treatment enhances jewelry by improving metal hardness and refining gemstone clarity through controlled temperature exposure. Irradiation alters the color of gemstones by bombarding them with high-energy particles, creating vibrant hues that cannot be achieved naturally. Both methods are widely used to increase the aesthetic appeal and value of jewelry pieces while maintaining structural integrity.
Table of Comparison
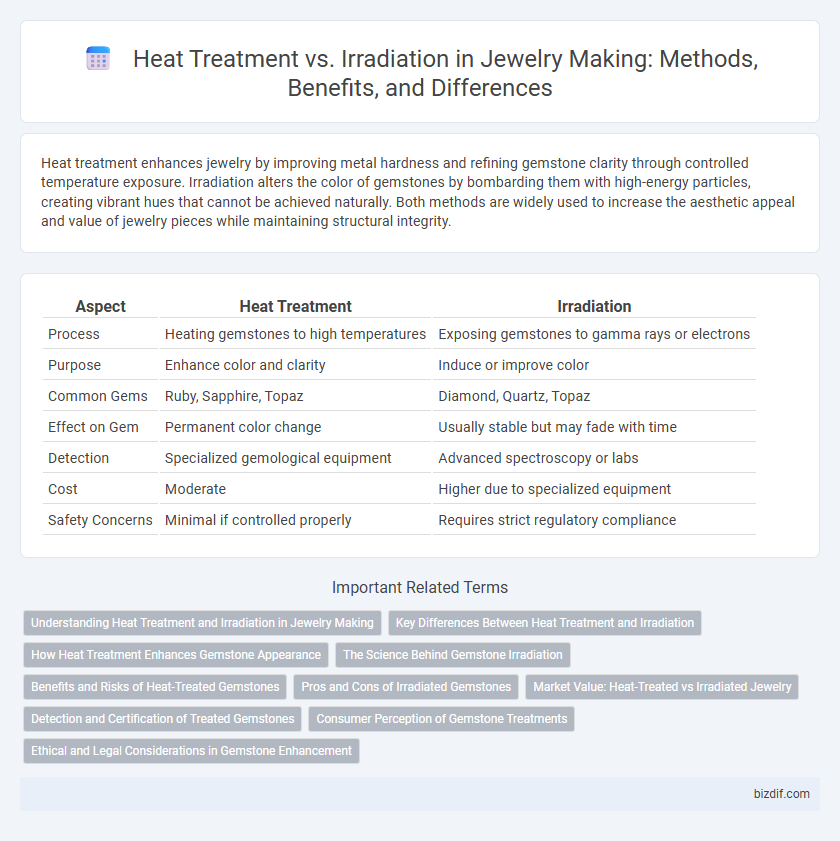
| Aspect | Heat Treatment | Irradiation |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Heating gemstones to high temperatures | Exposing gemstones to gamma rays or electrons |
| Purpose | Enhance color and clarity | Induce or improve color |
| Common Gems | Ruby, Sapphire, Topaz | Diamond, Quartz, Topaz |
| Effect on Gem | Permanent color change | Usually stable but may fade with time |
| Detection | Specialized gemological equipment | Advanced spectroscopy or labs |
| Cost | Moderate | Higher due to specialized equipment |
| Safety Concerns | Minimal if controlled properly | Requires strict regulatory compliance |
Understanding Heat Treatment and Irradiation in Jewelry Making
Heat treatment in jewelry making involves controlled heating and cooling processes to enhance the color, clarity, and durability of gemstones, particularly sapphires and rubies. Irradiation uses controlled exposure to radiation to alter gemstone colors, commonly applied to diamonds, topaz, and pearls for achieving vibrant hues. Both techniques require precise expertise to maintain gemstone integrity while optimizing aesthetic qualities and market value.
Key Differences Between Heat Treatment and Irradiation
Heat treatment in jewelry making involves controlled heating to enhance color and clarity by altering the crystal structure of gemstones, while irradiation uses high-energy particles to change the atomic arrangement, resulting in color modification. Heat treatment is typically applied to stones like sapphires and rubies for improved aesthetic appeal, whereas irradiation is preferred for diamonds and topaz to achieve vibrant hues not possible through heating. Both methods are widely accepted in the industry but differ significantly in process, effect, and gemstone compatibility.
How Heat Treatment Enhances Gemstone Appearance
Heat treatment enhances gemstone appearance by improving color saturation and clarity through controlled heating processes that alter the crystal structure. This method intensifies hues, removes undesirable tones, and reduces inclusions, making stones more visually appealing and valuable. Compared to irradiation, heat treatment is widely accepted in the industry for its ability to produce natural-looking enhancements without introducing artificial color zones.
The Science Behind Gemstone Irradiation
Gemstone irradiation involves exposing gems to controlled radiation sources to alter their color by changing the crystal lattice and electron structure, resulting in enhanced or rare hues. Unlike heat treatment, which relies on high temperatures to induce color changes through diffusion and structural shifts, irradiation uses neutrons, electrons, or gamma rays to create stable color centers within the gemstone. This scientific process ensures precise color enhancement without compromising the gem's clarity or overall physical integrity.
Benefits and Risks of Heat-Treated Gemstones
Heat-treated gemstones enhance color and clarity by altering mineral structures, significantly increasing their market value and aesthetic appeal. The process is stable and widely accepted in the jewelry industry, but risks include potential surface damage or color instability if improperly conducted. While heat treatment is generally considered safe, disclosure is essential to maintain consumer trust and transparency in gemstone sourcing.
Pros and Cons of Irradiated Gemstones
Irradiated gemstones offer enhanced color intensity and affordability, making them popular for vibrant jewelry designs. However, treatment can sometimes result in color instability when exposed to prolonged light or heat, requiring careful handling. While irradiation is a controlled and safe process, it may affect the gemstone's resale value compared to naturally colored stones.
Market Value: Heat-Treated vs Irradiated Jewelry
Heat treatment in jewelry enhances color and clarity, often resulting in higher market value due to its widespread acceptance and permanence. Irradiated gemstones may exhibit vibrant hues but typically hold less market value because of concerns about potential color fading and consumer skepticism. Collectors and buyers generally prefer heat-treated gems for their proven durability and stable enhancement outcomes.
Detection and Certification of Treated Gemstones
Detection and certification of heat-treated and irradiated gemstones rely on advanced spectroscopic analysis and luminescence testing to identify treatment-induced alterations in crystal structure and color centers. Gemological laboratories use techniques such as UV-Vis spectroscopy, Raman spectroscopy, and X-ray diffraction to distinguish natural stones from treated ones, ensuring accurate disclosure. Certification documents detail the type of treatment detected, providing transparency and maintaining trust in the gemstone market.
Consumer Perception of Gemstone Treatments
Consumer perception of gemstone treatments often varies significantly between heat treatment and irradiation, with heat treatment generally regarded as more natural and acceptable due to its longstanding use in enhancing color and clarity. Irradiation, while effective in modifying gemstone hues, sometimes faces skepticism owing to concerns about radiation exposure and long-term stability. Transparency and certification play crucial roles in shaping trust, as informed buyers show a preference for disclosed treatments backed by reputable gemological reports.
Ethical and Legal Considerations in Gemstone Enhancement
Heat treatment in gemstone enhancement is widely accepted and legally regulated, ensuring transparency in disclosure to consumers, whereas irradiation methods often face stricter scrutiny due to potential radioactive residue and health concerns. Ethical considerations emphasize full disclosure of any treatment to preserve consumer trust and market integrity in the jewelry industry. Regulatory frameworks vary globally, with some regions imposing stringent labeling laws on irradiated gemstones to protect buyers from misleading information.
Heat treatment vs irradiation Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com