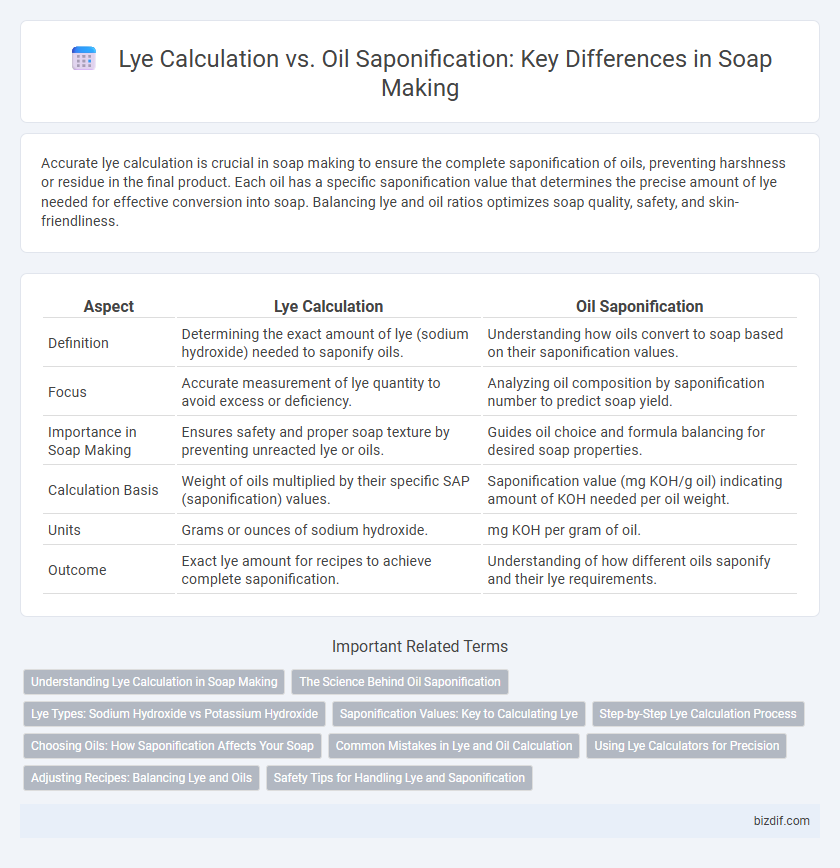
Accurate lye calculation is crucial in soap making to ensure the complete saponification of oils, preventing harshness or residue in the final product. Each oil has a specific saponification value that determines the precise amount of lye needed for effective conversion into soap. Balancing lye and oil ratios optimizes soap quality, safety, and skin-friendliness.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Lye Calculation | Oil Saponification |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Determining the exact amount of lye (sodium hydroxide) needed to saponify oils. | Understanding how oils convert to soap based on their saponification values. |
| Focus | Accurate measurement of lye quantity to avoid excess or deficiency. | Analyzing oil composition by saponification number to predict soap yield. |
| Importance in Soap Making | Ensures safety and proper soap texture by preventing unreacted lye or oils. | Guides oil choice and formula balancing for desired soap properties. |
| Calculation Basis | Weight of oils multiplied by their specific SAP (saponification) values. | Saponification value (mg KOH/g oil) indicating amount of KOH needed per oil weight. |
| Units | Grams or ounces of sodium hydroxide. | mg KOH per gram of oil. |
| Outcome | Exact lye amount for recipes to achieve complete saponification. | Understanding of how different oils saponify and their lye requirements. |
Understanding Lye Calculation in Soap Making
Accurate lye calculation is crucial in soap making to ensure complete saponification of oils without leftover caustic soda, preventing harsh or unsafe soap. Each oil has a specific saponification value that determines the precise amount of lye needed to transform the fat into soap and glycerin. Understanding the balance between lye quantity and oil types optimizes the soap's texture, hardness, and moisturizing properties for the desired end product.
The Science Behind Oil Saponification
Oil saponification involves a chemical reaction where triglycerides in oils react with lye (sodium hydroxide) to produce soap and glycerin. Each oil has a specific saponification value indicating the precise amount of lye needed to fully convert the oil into soap without excess caustic residue. Accurate lye calculation based on these saponification values ensures optimal soap quality, safety, and consistency in the soap making process.
Lye Types: Sodium Hydroxide vs Potassium Hydroxide
Lye calculation is crucial in soap making to ensure the correct neutralization of oils based on their saponification values. Sodium hydroxide (NaOH) and potassium hydroxide (KOH) are the primary lye types; NaOH produces hard, solid soaps while KOH creates softer, liquid or gel soaps. Accurate measurement of each oil's saponification value combined with the chosen lye type optimizes the soap's texture, cleansing ability, and curing time.
Saponification Values: Key to Calculating Lye
Saponification values are crucial metrics representing the amount of lye needed to fully convert oils into soap, expressed in milligrams of KOH per gram of oil. Accurate lye calculation depends on these values to ensure a proper chemical reaction, preventing harsh residual lye or excess oils. Manufacturers and hobbyists rely on saponification values to balance oil blends, optimize soap hardness, and enhance overall soap quality.
Step-by-Step Lye Calculation Process
Accurate lye calculation depends on determining the saponification values of each oil used, which indicates the exact amount of lye needed to fully react without excess. Begin by listing each oil's weight and corresponding SAP value, then multiply these to find the required lye per oil type. Sum all individual lye amounts for total lye needed, adjusting precisely to prevent harshness or incomplete saponification in the finished soap.
Choosing Oils: How Saponification Affects Your Soap
Choosing oils with appropriate saponification values is essential for precise lye calculation in soap making, ensuring complete oil-to-soap conversion without excess lye. Each oil's unique fatty acid composition determines its saponification number, directly influencing the amount of lye required to achieve a balanced, mild bar. Accurate saponification data prevents unsaponified oils or leftover alkali, optimizing soap quality and user safety.
Common Mistakes in Lye and Oil Calculation
Incorrect lye calculation often results in soap that is either too harsh or too soft due to unbalanced saponification of oils. Common mistakes include neglecting the specific saponification values of different oils and failing to adjust lye amounts for water content or impurities. Precise measurements using reliable lye calculators and accurate oil weights are essential for achieving the optimal chemical reaction and high-quality soap.
Using Lye Calculators for Precision
Lye calculation is critical in soap making to ensure the correct amount of sodium hydroxide (lye) neutralizes the saponifiable oils, preventing harsh or poorly cured soap. Using lye calculators provides precise measurements by factoring in each oil's saponification value, enabling consistent and safe batch outcomes. Accurate lye-to-oil ratios optimize hardness, cleansing, and moisturizing properties, essential for high-quality handmade soap.
Adjusting Recipes: Balancing Lye and Oils
Accurate lye calculation is essential for balancing oils during soap making to ensure complete saponification and avoid excess lye or unreacted oils. Adjusting recipes requires precise measurement of the saponification values (SAP) of each oil, which determines the exact amount of lye needed for a stable, safe soap. Properly balancing lye and oils enhances the soap's texture, hardness, and moisturizing properties while preventing skin irritation.
Safety Tips for Handling Lye and Saponification
Accurate lye calculation is critical for safe soap making, as incorrect amounts can cause incomplete saponification, resulting in harsh or unsafe soap. Always wear protective gloves, goggles, and work in a well-ventilated area to prevent chemical burns or inhalation of caustic fumes during lye handling. Measure oils and lye precisely using saponification values to ensure the complete reaction of fats, minimizing residual alkali and maximizing soap quality and safety.
Lye Calculation vs Oil Saponification Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com