Document translation involves converting written text from one language to another while preserving formatting and context, ensuring accuracy for legal, technical, or official purposes. Website translation requires adapting content dynamically for diverse audiences, including localization to maintain cultural relevance and user experience across different regions. Both types demand linguistic expertise but differ in scope, with document translation emphasizing precision and website translation focusing on interactive and multimedia content adaptation.
Table of Comparison
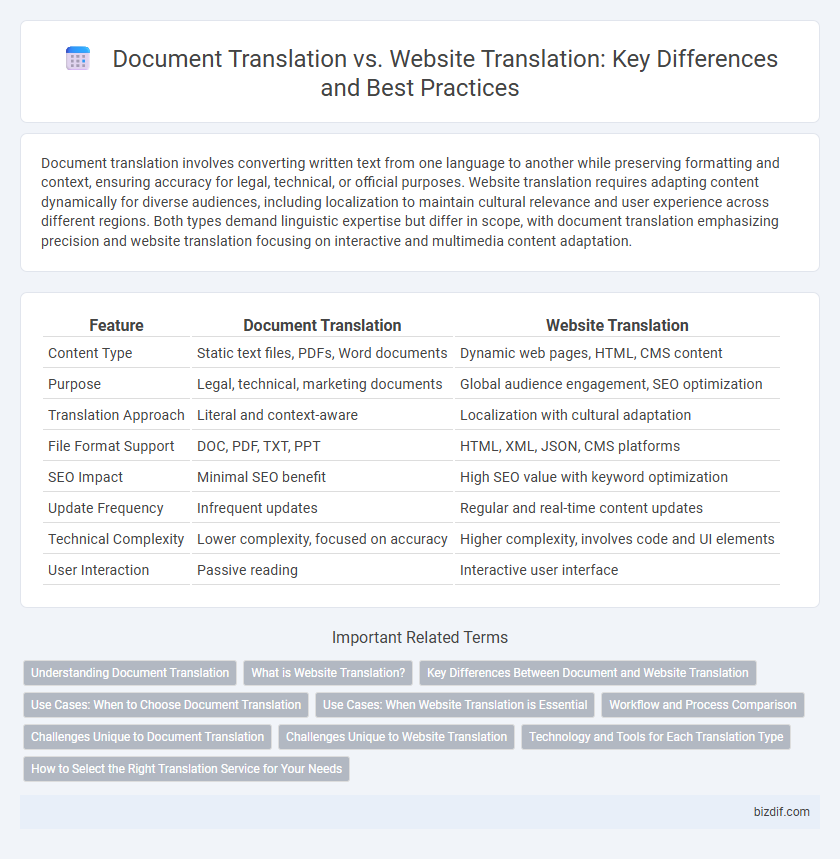
| Feature | Document Translation | Website Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Content Type | Static text files, PDFs, Word documents | Dynamic web pages, HTML, CMS content |
| Purpose | Legal, technical, marketing documents | Global audience engagement, SEO optimization |
| Translation Approach | Literal and context-aware | Localization with cultural adaptation |
| File Format Support | DOC, PDF, TXT, PPT | HTML, XML, JSON, CMS platforms |
| SEO Impact | Minimal SEO benefit | High SEO value with keyword optimization |
| Update Frequency | Infrequent updates | Regular and real-time content updates |
| Technical Complexity | Lower complexity, focused on accuracy | Higher complexity, involves code and UI elements |
| User Interaction | Passive reading | Interactive user interface |
Understanding Document Translation
Document translation involves converting written content from one language to another while preserving the original meaning, format, and style, ensuring accuracy in technical, legal, or medical texts. Unlike website translation, which requires adapting dynamic, multimedia elements and user interface components, document translation emphasizes maintaining consistency in terminology and adhering to specific formatting guidelines. Professional document translators use specialized tools and glossaries to achieve precise and culturally appropriate translations suitable for official or business purposes.
What is Website Translation?
Website translation involves converting the textual content of a website into different languages to reach a global audience while maintaining the site's original layout and functionality. This process includes multilingual SEO optimization, localization of cultural references, and adaptation of graphics and user interface elements to ensure consistent user experience across languages. Unlike document translation, website translation requires continuous updates to reflect real-time changes and integration with content management systems (CMS) for seamless content delivery.
Key Differences Between Document and Website Translation
Document translation involves converting static text files such as reports, contracts, and manuals into another language, ensuring precise terminology and formatting consistency. Website translation requires adapting dynamic content, including multimedia elements, user interface components, and cultural nuances, to enhance user experience across different languages. Unlike document translation, website localization demands ongoing updates and SEO considerations to maintain relevance and accessibility in global markets.
Use Cases: When to Choose Document Translation
Document translation is essential for legal contracts, medical records, and technical manuals requiring precise language and formatting preservation. It ensures accuracy and confidentiality in static content, suitable for regulatory submissions and official paperwork. Businesses should choose document translation when dealing with formal, non-interactive materials that need certification or notarization.
Use Cases: When Website Translation is Essential
Website translation is essential for businesses targeting global audiences, enabling seamless user experience and increased accessibility across different languages. E-commerce platforms, multinational corporations, and online service providers rely on website translation to engage diverse customer bases and improve conversion rates. Unlike document translation, which focuses on static content, website translation addresses dynamic, interactive elements critical for real-time communication and localization.
Workflow and Process Comparison
Document translation involves a structured workflow where content is extracted, translated, formatted, and proofread often using CAT tools for consistency and terminology management. Website translation requires integration with content management systems (CMS), real-time updates, and localization workflows to ensure seamless user experience across different languages and devices. Both processes demand quality assurance but differ significantly in technical complexity and continual content maintenance.
Challenges Unique to Document Translation
Document translation poses unique challenges such as maintaining formatting consistency across diverse file types, ensuring accurate conversion of specialized terms within legal or technical content, and preserving the original document's layout and style. Unlike website translation, which often leverages dynamic content management systems and real-time updates, document translation demands meticulous attention to detail to prevent errors in static text. The process requires comprehensive quality assurance to uphold linguistic precision while adapting complex structures into the target language.
Challenges Unique to Website Translation
Website translation poses unique challenges such as maintaining functionality across different languages and ensuring proper localization of user interfaces, which requires not only linguistic accuracy but also cultural adaptation. Unlike document translation, website translation must address dynamic content updates, responsive design across devices, and integration with content management systems. Technical issues like encoding, SEO optimization, and multilingual URL structures add complexity to the website translation process.
Technology and Tools for Each Translation Type
Document translation relies heavily on computer-assisted translation (CAT) tools such as SDL Trados and memoQ, enabling precise terminology management and consistent formatting across diverse file types like PDFs and Word documents. Website translation leverages content management system (CMS) plugins and localization platforms like Weglot and Lokalise, which facilitate dynamic content updates and integration with web development frameworks. Both translation types benefit from neural machine translation (NMT) engines to enhance accuracy, but website translation requires additional SEO and UX optimization tools to ensure multilingual user engagement.
How to Select the Right Translation Service for Your Needs
Choosing between document translation and website translation depends on the content type and target audience, as documents require precise, context-specific language accuracy, while websites demand seamless localization and user experience optimization. Evaluate your project scope, technical requirements, and the translator's expertise in handling file formats, SEO considerations, and cultural nuances. Prioritize services offering certified translators, technology integration, and customization options to ensure efficient, accurate communication tailored to your business objectives.
Document Translation vs Website Translation Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com