Marketplaces offer sellers access to a large, ready-made customer base, reducing the need for extensive marketing efforts while providing built-in trust and streamlined transactions. Standalone stores grant businesses full control over branding, customer experience, and data, enabling personalized marketing and direct customer relationships. Choosing between marketplaces and standalone stores depends on factors like budget, scalability goals, and the desired level of control over the sales process.
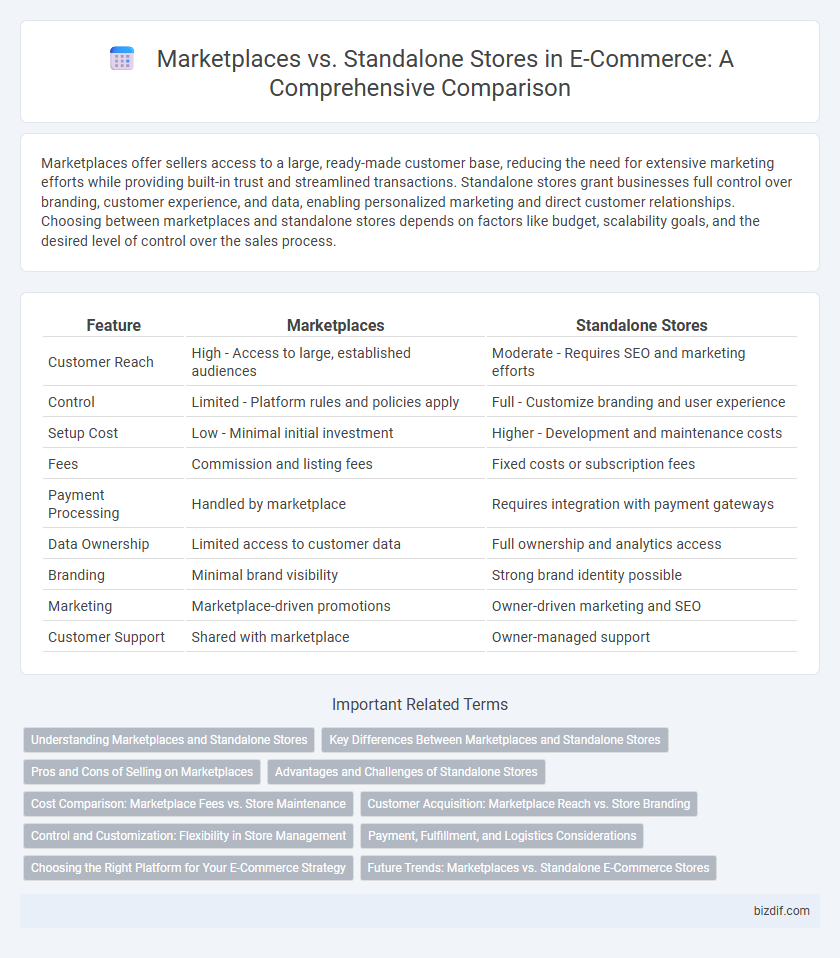
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Marketplaces | Standalone Stores |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Reach | High - Access to large, established audiences | Moderate - Requires SEO and marketing efforts |
| Control | Limited - Platform rules and policies apply | Full - Customize branding and user experience |
| Setup Cost | Low - Minimal initial investment | Higher - Development and maintenance costs |
| Fees | Commission and listing fees | Fixed costs or subscription fees |
| Payment Processing | Handled by marketplace | Requires integration with payment gateways |
| Data Ownership | Limited access to customer data | Full ownership and analytics access |
| Branding | Minimal brand visibility | Strong brand identity possible |
| Marketing | Marketplace-driven promotions | Owner-driven marketing and SEO |
| Customer Support | Shared with marketplace | Owner-managed support |
Understanding Marketplaces and Standalone Stores
Marketplaces aggregate multiple sellers, providing broad product variety and increased visibility through established customer bases, which drives higher traffic and competitive pricing. Standalone stores offer complete control over brand experience, customer data, and pricing strategies while requiring investment in marketing and infrastructure to attract and retain shoppers. Understanding the trade-offs between marketplaces' scale and standalone stores' brand autonomy is crucial for developing an effective e-commerce growth strategy.
Key Differences Between Marketplaces and Standalone Stores
Marketplaces aggregate multiple sellers, offering diverse product ranges and increased customer traffic, while standalone stores provide complete brand control and personalized shopping experiences. Transaction fees and competition levels differ, with marketplaces often charging commissions but enabling broader reach, whereas standalone stores bear costs of marketing and infrastructure independently. Data ownership varies significantly; marketplaces restrict access to customer insights, whereas standalone stores retain full control over consumer data for targeted marketing strategies.
Pros and Cons of Selling on Marketplaces
Selling on marketplaces offers access to a vast, established customer base and streamlined payment and logistics solutions, which can significantly enhance visibility and sales volume. However, marketplace sellers face intense competition, limited control over branding, and often incur higher fees compared to standalone stores. Dependence on marketplace policies and algorithms also poses risks to seller autonomy and long-term customer relationships.
Advantages and Challenges of Standalone Stores
Standalone stores offer full control over branding, customer experience, and data ownership, enabling businesses to build a unique identity and foster direct customer relationships. However, challenges include higher upfront costs for website development, ongoing maintenance, and the need for effective marketing strategies to drive traffic without relying on marketplace platforms. Limited exposure compared to marketplaces requires standalone stores to invest significantly in SEO, advertising, and customer retention to achieve sustainable growth.
Cost Comparison: Marketplace Fees vs. Store Maintenance
Marketplace fees typically include listing charges, transaction commissions averaging 10-15%, and advertising costs, which can significantly reduce profit margins. Standalone stores incur fixed expenses such as web hosting, platform subscriptions averaging $29-$299 per month, and payment processing fees around 2.9% plus $0.30 per transaction, offering more control over total costs. Evaluating the balance between variable marketplace fees and predictable standalone store maintenance expenses is crucial for cost-effective e-commerce strategy.
Customer Acquisition: Marketplace Reach vs. Store Branding
Marketplaces offer expansive customer acquisition through their vast, established user bases, providing immediate access to millions of potential buyers. Standalone stores rely on strong brand identity and tailored customer experiences to drive loyalty and repeat purchases, leveraging SEO and targeted marketing strategies. Effective customer acquisition balances marketplace reach with distinctive store branding to maximize visibility and long-term growth.
Control and Customization: Flexibility in Store Management
Standalone stores offer unmatched control and customization, allowing businesses to tailor the user experience, design, and product presentation without restrictions. Marketplaces limit flexibility due to standardized templates and shared platform rules, restricting brand differentiation and unique promotional strategies. Enhanced store management options in standalone stores empower sellers to implement personalized marketing tools, optimize customer journeys, and quickly adapt to market trends.
Payment, Fulfillment, and Logistics Considerations
Marketplaces offer integrated payment systems and streamlined logistics solutions that reduce operational complexity for sellers, while standalone stores require merchants to independently manage payment gateways and fulfillment processes. Payment security, transaction fees, and multi-currency support vary significantly between marketplaces and standalone platforms, impacting overall cost-effectiveness and customer experience. Efficient inventory management and last-mile delivery capabilities depend heavily on the chosen model, with marketplaces leveraging centralized fulfillment networks and standalone stores often relying on third-party logistics providers.
Choosing the Right Platform for Your E-Commerce Strategy
Choosing the right platform for your e-commerce strategy depends on your business goals, target audience, and budget. Marketplaces like Amazon and eBay offer extensive reach and built-in customer trust but come with fees and limited brand control, while standalone stores using platforms like Shopify or WooCommerce provide full customization and brand identity at the cost of driving your own traffic. Evaluating factors such as scalability, marketing capabilities, and operational flexibility will help determine whether integrating into a marketplace or developing a standalone store best aligns with your strategic objectives.
Future Trends: Marketplaces vs. Standalone E-Commerce Stores
Future trends indicate that marketplaces will continue leveraging AI-driven personalization and integrated logistics to enhance customer experience and streamline operations. Standalone e-commerce stores are increasingly adopting headless commerce architectures and augmented reality features to offer unique, brand-centric shopping experiences. Both models are expected to integrate sustainable practices and advanced data analytics to drive growth and customer loyalty in a competitive digital commerce landscape.
Marketplaces vs Standalone Stores Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com