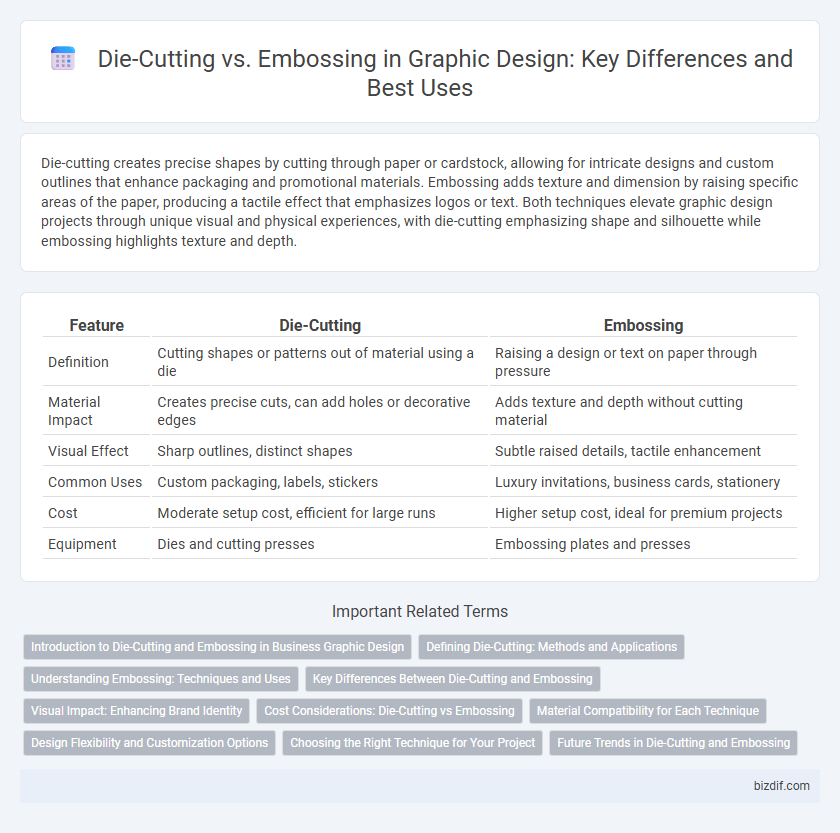
Die-cutting creates precise shapes by cutting through paper or cardstock, allowing for intricate designs and custom outlines that enhance packaging and promotional materials. Embossing adds texture and dimension by raising specific areas of the paper, producing a tactile effect that emphasizes logos or text. Both techniques elevate graphic design projects through unique visual and physical experiences, with die-cutting emphasizing shape and silhouette while embossing highlights texture and depth.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Die-Cutting | Embossing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Cutting shapes or patterns out of material using a die | Raising a design or text on paper through pressure |
| Material Impact | Creates precise cuts, can add holes or decorative edges | Adds texture and depth without cutting material |
| Visual Effect | Sharp outlines, distinct shapes | Subtle raised details, tactile enhancement |
| Common Uses | Custom packaging, labels, stickers | Luxury invitations, business cards, stationery |
| Cost | Moderate setup cost, efficient for large runs | Higher setup cost, ideal for premium projects |
| Equipment | Dies and cutting presses | Embossing plates and presses |
Introduction to Die-Cutting and Embossing in Business Graphic Design
Die-cutting and embossing are essential techniques in business graphic design that enhance the tactile and visual appeal of printed materials. Die-cutting involves precision cutting of paper or cardstock into custom shapes, creating unique designs for packaging, labels, and promotional items. Embossing adds texture by raising specific areas of the design, providing a sophisticated, dimensional effect that elevates brand identity and consumer engagement.
Defining Die-Cutting: Methods and Applications
Die-cutting in graphic design involves using steel blades or rotary tools to cut specific shapes or patterns from paper, cardstock, or other materials with precision and consistency. This method allows for creating customized designs such as intricate logos, packaging windows, and promotional materials that enhance tactile appeal and visual interest. Common applications of die-cutting span across product packaging, business cards, labels, and direct mail campaigns, offering designers versatility in shaping and detailing their printed materials.
Understanding Embossing: Techniques and Uses
Embossing is a graphic design technique that creates a raised, three-dimensional effect on paper or cardstock, enhancing tactile appeal and visual interest. Common embossing methods include blind embossing, which uses no ink or foil, and combination embossing, where embossing is paired with foil stamping for added elegance. This technique is widely used in branding, packaging, and invitations to add sophistication and a premium feel by emphasizing logos, text, or intricate patterns.
Key Differences Between Die-Cutting and Embossing
Die-cutting involves cutting precise shapes or patterns out of materials using sharp steel blades, creating custom designs with clean edges and negative space. Embossing presses a raised design into the material's surface, adding texture and depth without cutting through, often enhancing logos or decorative elements. While die-cutting alters the material's shape, embossing modifies its surface, making each technique suitable for different visual and tactile effects in graphic design.
Visual Impact: Enhancing Brand Identity
Die-cutting creates unique shapes and custom contours that instantly grab attention and differentiate a brand's packaging or marketing materials. Embossing adds tactile depth and elegance through raised textures, enhancing perceived quality and sophistication. Both techniques elevate visual impact by reinforcing brand identity through distinct physical and aesthetic experiences.
Cost Considerations: Die-Cutting vs Embossing
Die-cutting typically incurs lower setup costs compared to embossing, making it ideal for large-scale production runs with complex shapes. Embossing involves higher costs due to custom metal dies and precise pressure requirements, which can increase expenses for smaller batches. Budget constraints often guide the choice, with die-cutting favored for cost-effective, intricate designs and embossing selected for premium, tactile finishes despite its higher pricing.
Material Compatibility for Each Technique
Die-cutting excels with a wide range of materials including paper, cardstock, vinyl, and thin plastics, making it highly versatile for intricate shapes and custom designs. Embossing works best on thicker, sturdy papers and cardstock, where the raised impression can be cleanly formed without tearing or distortion. Understanding material compatibility ensures optimal results, as die-cutting requires precision cuts while embossing demands a surface capable of withstanding pressure without damage.
Design Flexibility and Customization Options
Die-cutting offers superior design flexibility by allowing intricate shapes and precise cutouts that enhance visual appeal and brand identity. Embossing provides customization through raised textures that add tactile depth and sophistication to printed materials, elevating the sensory experience. Combining both techniques can create unique, multi-dimensional designs that stand out in competitive markets.
Choosing the Right Technique for Your Project
Die-cutting creates precise shapes by cutting through materials, ideal for custom packaging and unique promotional items that require distinct outlines and intricate designs. Embossing adds texture and dimension by raising elements on the surface, perfect for luxury branding, business cards, and invitations that need a tactile, elegant finish. Selecting between die-cutting and embossing depends on whether your project emphasizes visual impact with shape or a sophisticated tactile experience.
Future Trends in Die-Cutting and Embossing
Future trends in die-cutting and embossing integrate advanced laser technology and 3D printing to enhance precision and complexity in graphic design projects. Sustainable materials combined with eco-friendly inks are increasingly prioritized, promoting greener production methods. Customization through digital die-cutting and embossing tools allows designers to create intricate, personalized packaging and marketing materials that engage consumers on a tactile level.
die-cutting vs embossing Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com