Mockups provide a static visual representation of a design, allowing designers to showcase the appearance and layout without interactive functionality. Prototypes, however, simulate user interactions and workflows, enabling usability testing and iterative improvements. Selecting between mockups and prototypes depends on the project phase and specific design goals.
Table of Comparison
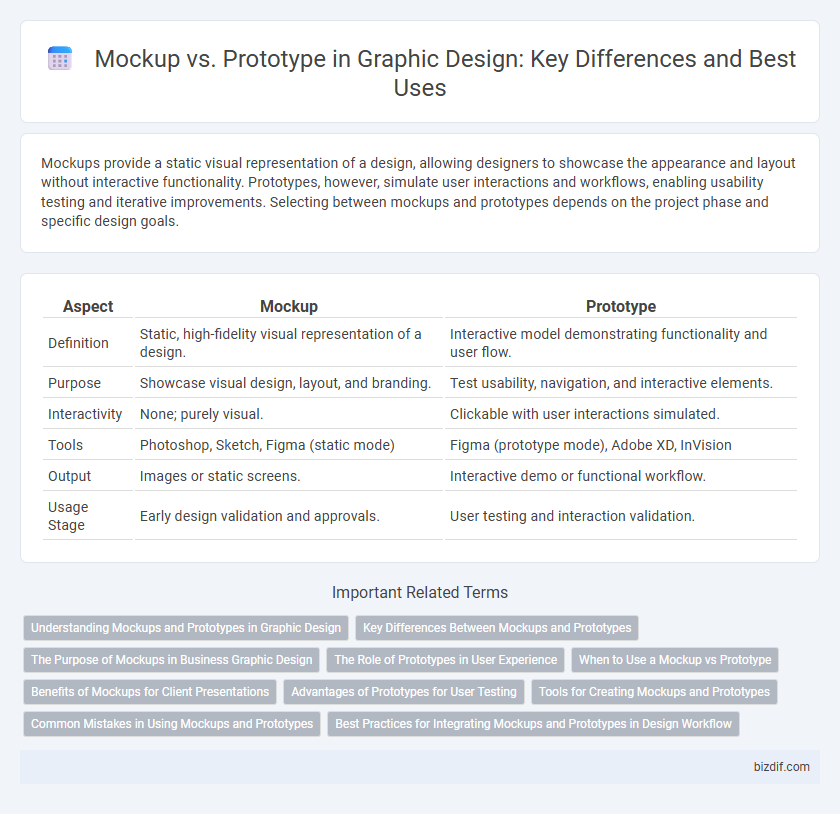
| Aspect | Mockup | Prototype |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Static, high-fidelity visual representation of a design. | Interactive model demonstrating functionality and user flow. |
| Purpose | Showcase visual design, layout, and branding. | Test usability, navigation, and interactive elements. |
| Interactivity | None; purely visual. | Clickable with user interactions simulated. |
| Tools | Photoshop, Sketch, Figma (static mode) | Figma (prototype mode), Adobe XD, InVision |
| Output | Images or static screens. | Interactive demo or functional workflow. |
| Usage Stage | Early design validation and approvals. | User testing and interaction validation. |
Understanding Mockups and Prototypes in Graphic Design
Mockups are static, high-fidelity visual representations used to showcase the design's appearance, focusing on layout, color schemes, typography, and overall aesthetics in graphic design projects. Prototypes go beyond visuals by incorporating interactive elements, simulating user experience and functionality to evaluate usability and design flow. Both tools are essential for iterating designs efficiently, with mockups emphasizing visual communication and prototypes enabling practical user testing and feedback.
Key Differences Between Mockups and Prototypes
Mockups are static, high-fidelity visual representations of a design used to demonstrate the appearance and layout, while prototypes are interactive models that simulate user experience and functionality. Mockups primarily focus on aesthetics, color schemes, typography, and overall design consistency, whereas prototypes emphasize user flow, navigation, and interface interactions. The key difference lies in mockups being visual tools for design approval, and prototypes serving as functional tools for user testing and experience validation.
The Purpose of Mockups in Business Graphic Design
Mockups in business graphic design serve to visually represent the final product's layout and aesthetics, enabling stakeholders to evaluate design elements before development. They facilitate clear communication of ideas, ensuring brand consistency and alignment with business goals. By providing a tangible preview, mockups reduce misunderstandings and costly revisions during production.
The Role of Prototypes in User Experience
Prototypes play a crucial role in user experience by allowing designers to test and refine interactive elements before final development, ensuring usability and functionality align with user needs. Unlike static mockups that only showcase visual design, prototypes simulate real user interactions, providing valuable feedback on navigation, responsiveness, and overall flow. This iterative process helps identify potential issues early, reducing development costs and improving the quality of the final product.
When to Use a Mockup vs Prototype
Mockups are ideal for presenting visual design concepts and refining aesthetic details, enabling stakeholders to evaluate color schemes, typography, and layout without interactive functionality. Prototypes are essential when testing user experience, interaction flow, and functionality, allowing designers to simulate real user behavior and gather feedback on usability. Use mockups during early design stages to gain visual consensus and switch to prototypes when validating user interaction before development.
Benefits of Mockups for Client Presentations
Mockups offer high-fidelity, visually detailed representations of a design, enabling clients to visualize the final product with realistic aesthetics and layout. They facilitate clear communication and feedback, reducing misunderstandings by showcasing exact colors, typography, and interface elements. Presenting mockups enhances client confidence and accelerates approval processes by providing tangible, polished visuals.
Advantages of Prototypes for User Testing
Prototypes offer interactive and realistic simulations of a design, enabling users to engage directly with the interface and provide valuable feedback on usability and functionality. This hands-on experience uncovers potential issues and user pain points early in the design process, improving overall user satisfaction. By testing prototypes, designers can iterate quickly, reduce development costs, and ensure the final product aligns closely with user needs and expectations.
Tools for Creating Mockups and Prototypes
Graphic designers rely on tools such as Adobe XD, Sketch, and Figma for creating interactive prototypes that simulate user experience and functionality. For mockups, tools like Photoshop and Canva are preferred for producing high-fidelity static visuals that showcase design aesthetics and layout. Selecting the right tool depends on whether the focus is on visual presentation or user interaction testing in the design process.
Common Mistakes in Using Mockups and Prototypes
Common mistakes in using mockups and prototypes include confusing the two tools' purposes, leading to ineffective design feedback and wasted resources. Designers often treat static mockups as interactive prototypes, resulting in missed usability insights and poor user experience testing. Failing to update prototypes with user feedback or relying solely on high-fidelity mockups can hinder iterative design improvements and project success.
Best Practices for Integrating Mockups and Prototypes in Design Workflow
Effective integration of mockups and prototypes in graphic design workflows enhances user experience validation and stakeholder communication. Utilize high-fidelity mockups for detailed visual presentation and interactive prototypes to test functionality and user interactions early in the design process. Consistent version control and collaborative feedback tools optimize iterations, ensuring design accuracy and alignment with project goals.
Mockup vs Prototype Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com